|
Castra Of Sărățeni
It was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia, at modern Sărățeni, Mureș County, Romania. See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra refl ... External linksRoman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Notes Roman auxiliary forts in Romania Ancient history of Transylvania Historic monuments in Mureș County {{Dacia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohors I Alpinorum Equitata
Cohors prima Alpinorum equitata ("1st part-mounted Cohort of Alpini") was a Roman auxiliary mixed infantry and cavalry regiment. History ''Alpini'' was a generic name denoting several Celtic-speaking mountain tribes inhabiting the Alps between Italy and Gaul, which were organised as the Tres Alpes provinces. The regiment was probably raised as one of 4–6 Alpini units recruited after the final annexation of the western Alpine regions by emperor Augustus in 15 BC. It was originally stationed in Illyricum, where it is recorded in 60 AD. Not later than 80, it was based in Pannonia, later Pannonia Inferior after Pannonia was divided in two c. 107. It was still in that province c. 215, according to its last datable inscription. There were three brief interruptions to the regiment's sojourn in Pannonia. It is recorded first in Aquitania in 60–70 ( Excisum, Villeneuve-sur-Lot) from recent finds of military equipments (confirming tombstones inscriptions; secondly, in Britannia in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohors I Ubiorum
Cohors I Ubiorum was a Roman auxiliary cohort. The cohort was at one point or another stationed at Calidava/Calidaua (modern day Capidava in Romania). The Cohors I Ubiorum was likely created during the reign of Augustus, and it is known to have been in existence during the reign of Domitian in the late 1st century AD. The unit likely played a role in maintaining Roman control over the area and in defending the Roman frontier against incursions by Germanic tribes. The cohort likely played a role in maintaining Roman control over the region.Anthony R. Birley, ''The Ubii and the Auxilia," in The Roman Army in the North-West'', Symposium Held at Chester College in June 1985, ed. R. H. Jones See also * Roman auxiliaries * List of Roman auxiliary regiments This article lists , non-legionary auxiliary regiments of the imperial Roman army, attested in the epigraphic record, by Roman province of deployment during the reign of emperor Hadrian ( AD 117–138). The index of regiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to present-day Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Poland and Ukraine. A Dacian kingdom that united the Dacians and the Getae was formed under the rule of Burebista in 82 BC and lasted until the Roman conquest in AD 106. As a result of the Trajan's Dacian Wars, wars with the Roman Empire, after the conquest of Dacia, the population was dispersed, and the capital city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans. However, the Romans built a settlement bearing the same name, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetuza, 40 km away, to serve as the capital of the newly established Roman Dacia, Roman province of Dacia. A group of "Free Dacians" may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia Superior
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as ; or Dacia Felix, ) was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last region which is split among Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119 under Hadrian, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and around 158, Dacia Superi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
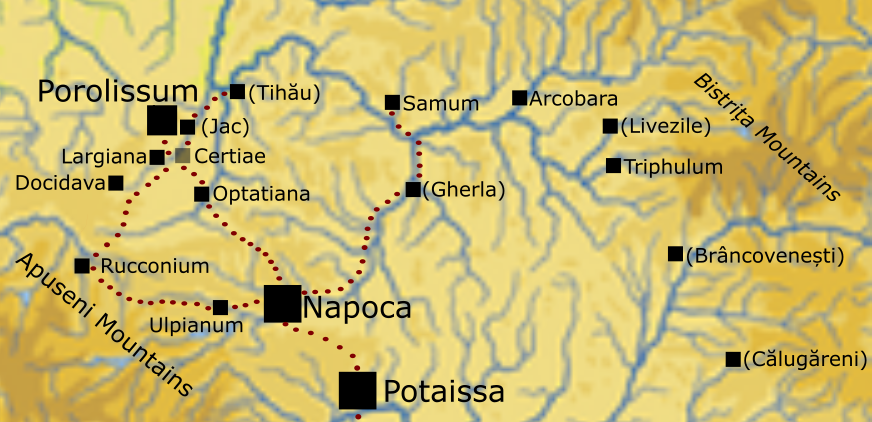
Limes Porolissensis
Located in present-day Romania, ''Limes Porolissensis'' was the frontier of the Roman Empire in Dacia Porolissensis, the northernmost of the three Roman Dacia, Dacian provinces. It was a defensive line dating from the 2nd century AD after the Conquest of Dacia up to the retreat of the Roman army from the region. The Limes (Roman Empire), Limes was a complex network of over 200 vigilarium, observation towers, Burgus, fortlets, Clausurae, palisades and Vallum, ditches, and Castra, forts disposed in an arched line following the highland chain of the Meseș Mountains over 200 km from the Apuseni Mountains to Bistrița Mountains, and required as many as 16,000 soldiers to man and defend. The Limes is named after its key defensive point: Porolissum. It also integrated the following castra, forts: Resculum (castra), Rucconium, Docidava (castra), Docidava, Largiana (castra), Largiana, Certiae (castra), Certiae, Castra of Jac, Castra of Tihău, Samum (castra), Castra of Samum, Arcobara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |