|
Castle Hill, Thetford
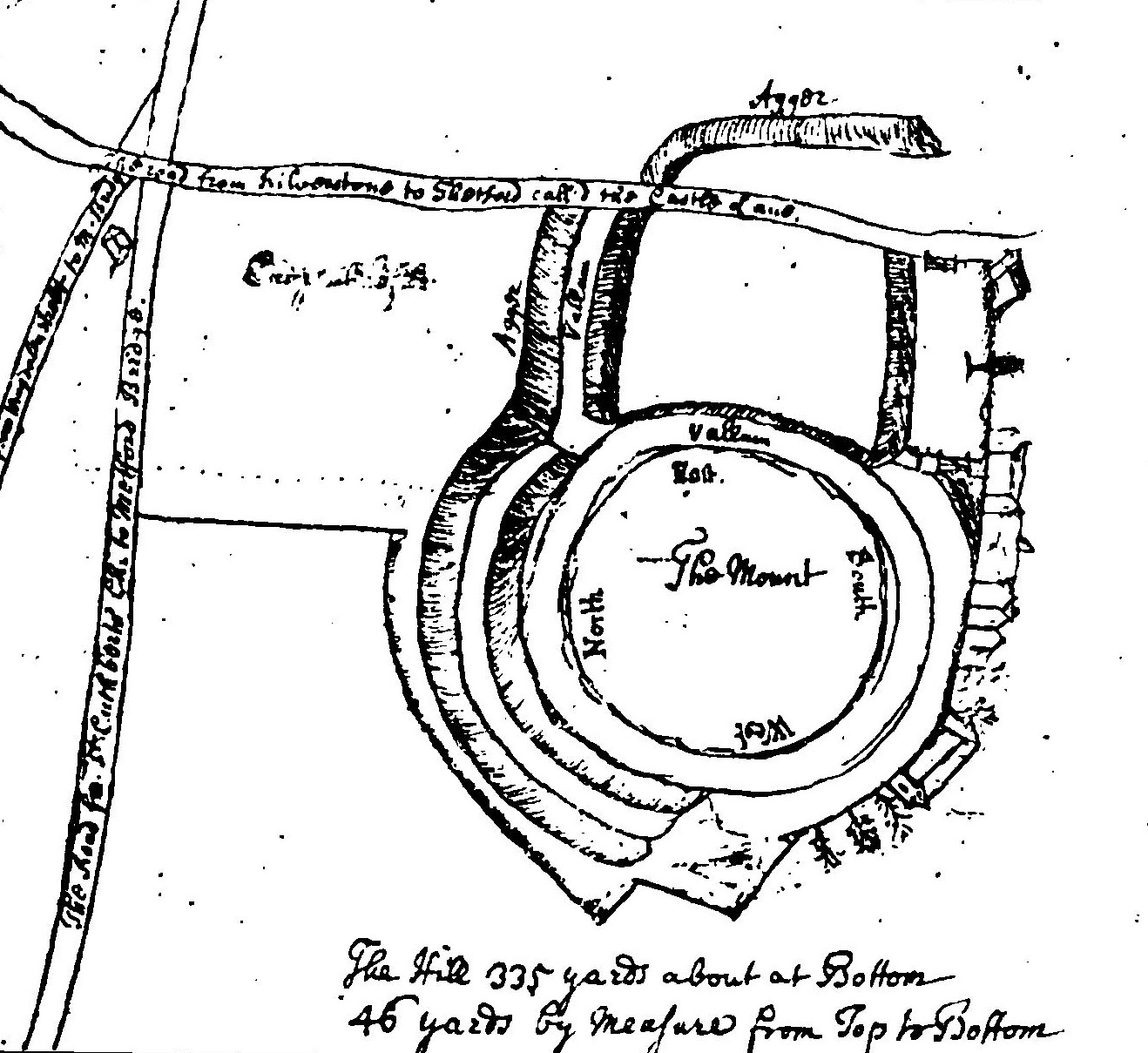
Thetford Castle is a medieval motte and bailey castle in the market town of Thetford in the Breckland area of Norfolk, England. The first castle in Thetford, a probable 11th-century Norman ringwork called Red Castle, was replaced in the 12th century by a much larger motte and bailey castle on the other side of the town. This new castle was largely destroyed in 1173 by Henry II, although the huge motte, the second largest man-made mound in England, remained intact. The motte, recognised as a scheduled monument, now forms part of a local park, and the remains are known variously as Castle Hill, Castle Mound and Military Parade. History 11th century In the 11th century the largest towns in England were concentrated in the east and south-east of the country, especially in East Anglia. Thetford was an important settlement during the period and the second largest town in East Anglia. Thetford comes from "Thaetford", or "the ford", and was a key point on the ancient Icknield Way. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea, with The Wash to the north-west. The county town is the city of Norwich. With an area of and a population of 859,400, Norfolk is a largely rural county with a population density of 401 per square mile (155 per km2). Of the county's population, 40% live in four major built up areas: Norwich (213,000), Great Yarmouth (63,000), King's Lynn (46,000) and Thetford (25,000). The Broads is a network of rivers and lakes in the east of the county, extending south into Suffolk. The area is protected by the Broads Authority and has similar status to a national park. History The area that was to become Norfolk was settled in pre-Roman times, (there were Palaeolithic settlers as early as 950,000 years ago) with camps along the highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William De Warenne, 1st Earl Of Surrey
William de Warenne, 1st Earl of Surrey, Lord of Lewes, Seigneur de Varennes (died 1088), was a Norman nobleman created Earl of Surrey under William II Rufus. He is among the few known from documents to have fought under William the Conqueror at the Battle of Hastings in 1066. At the time of the Domesday Survey in 1086, he held extensive lands in 13 counties, including the Rape of Lewes, a tract now divided between the ceremonial counties of East Sussex and West Sussex. Early career William was a son of Rodulf or Ralph de Warenne and Emma, and reported to have descended from a sibling of Duchess Gunnor, wife of Duke Richard I. Chronicler Robert of Torigny reported, in his additions to the ''Gesta Normannorum Ducum'' of William of Jumièges, that William de Warenne and Anglo-Norman baron Roger de Mortimer were both sons of an unnamed niece of Gunnor. Unfortunately, Robert's genealogies are somewhat confused – elsewhere he gives Roger as the son of William, and yet again makes bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shovel
A shovel is a tool used for digging, lifting, and moving bulk materials, such as soil, coal, gravel, snow, sand, or ore. Most shovels are hand tools consisting of a broad blade fixed to a medium-length handle. Shovel blades are usually made of sheet steel or hard plastics and are very strong. Shovel handles are usually made of wood (especially specific varieties such as ash or maple) or glass-reinforced plastic (fiberglass). Hand shovel blades made of sheet steel usually have a folded seam or hem at the back to make a socket for the handle. This fold also commonly provides extra rigidity to the blade. The handles are usually riveted in place. A T-piece is commonly fitted to the end of the handle to aid grip and control where the shovel is designed for moving soil and heavy materials. These designs can all be easily mass-produced. The term ''shovel'' also applies to larger excavating machines called power shovels, which serve the same purpose—digging, lifting, and moving mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk is common throughout Western Europe, where deposits underlie parts of France, and steep cliffs are often seen where they meet the sea in places such as the Dover cliffs on the Kent coast of the English Channel. Chalk is mined for use in industry, such as for quicklime, bricks and builder's putty, and in agriculture, for raising pH in soils with high acidity. It is also used for " blackboard chalk" for writing and drawing on various types of surfaces, although these can also be manufactured from other carbonate-based minerals, or gypsum. Description Chalk is a fine-textured, earthy type of limestone distinguished by its light color, softness, and high porosity. It is composed mostly of tiny fragments of the calcite shells or skeletons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in castles that were fortified residences, used as a refuge of last resort should the rest of the castle fall to an adversary. The first keeps were made of timber and formed a key part of the motte-and-bailey castles that emerged in Normandy and Anjou during the 10th century; the design spread to England, south Italy and Sicily. As a result of the Norman invasion of 1066, use spread into Wales during the second half of the 11th century and into Ireland in the 1170s. The Anglo-Normans and French rulers began to build stone keeps during the 10th and 11th centuries; these included Norman keeps, with a square or rectangular design, and circular shell keeps. Stone keeps carried considerable political as well as military importance and could take up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silbury Hill
Silbury Hill is a prehistoric artificial chalk mound near Avebury in the English county of Wiltshire. It is part of the Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites UNESCO World Heritage Site. At high, it is the tallest prehistoric man-made mound in Europe and one of the largest in the world; similar in volume to contemporary Egyptian pyramids. Silbury Hill is part of the complex of Neolithic monuments around Avebury, which includes the Avebury Ring and West Kennet Long Barrow. Its original purpose is still debated. Several other important Neolithic monuments in Wiltshire in the care of English Heritage, including the large henges at Marden and Stonehenge, may be culturally or functionally related to Avebury and Silbury. Structure Composed mainly of chalk and clay excavated from the surrounding area, the mound stands high and covers about . The hill was constructed in several stages between 24002300 BC and displays immense technical skill and prolonged control over labour a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defensive Wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates for access to the city. From ancient to modern times, they were used to enclose settlements. Generally, these are referred to as city walls or town walls, although there were also walls, such as the Great Wall of China, Walls of Benin, Hadrian's Wall, Anastasian Wall, and the Atlantic Wall, which extended far beyond the borders of a city and were used to enclose regions or mark territorial boundaries. In mountainous terrain, defensive walls such as ''letzis'' were used in combination with castles to seal valleys from potential attack. Beyond their defensive utility, many walls also had important symbolic functions representing the status and independence of the communities they embraced. Existing ancient walls are almost always masonry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William I Of England
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 1087. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle to establish his throne, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading an army of Normans to victory over the Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose. William was the son of the unmarried Duke Robert I of Normandy and his mistress Herleva. His illegitimate status and his youth caused s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Little Ouse
The River Little Ouse is a river in the east of England, a tributary of the River Great Ouse. For much of its length it defines the boundary between Norfolk and Suffolk. It rises east of Thelnetham, close to the source of the River Waveney, which flows eastwards while the Little Ouse flows west. The village of Blo' Norton owes its name to the river: it was earlier known as ''Norton Bell-'eau'', from being situated near this "fair stream". In this area the river creates a number of important wetland areas such as at Blo' Norton and Thelnetham Fens, and areas managed by the Little Ouse Headwaters Project. The course continues through Rushford, Thetford, Brandon, and Hockwold before the river joins the Great Ouse north of Littleport in Cambridgeshire. The total length is about . The river is navigable from the Great Ouse to a point above Brandon. Origins A distinctive feature of the headwaters of the Little Ouse and the Waveney is the valley in which they flow; the Little O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Thet
The River Thet is a river in Norfolk, England and is a tributary of the River Little Ouse.It rises in Breckland with sources in Deopham Green and Rockland All Saints and joins the Little Ouse in Thetford after flowing approximately southwest. The primary sources for its various small tributaries include the calcareous valley fen SSSIs Swangey Fen, Old Buckenham Fen, Middle Harling Fen and Kenninghall and Banham Fens with Quidenham Mere. Carr woodland is also a prevalent habitat throughout the floodplain where open wetlands have been invaded by scrub. The underlying geology is clay/loam over chalk for the easternmost parts of the river's course and sand/gravel over chalk for the majority of the river. Etymology, course and notable settlements nearby The name actually comes from Thetford rather than the other way around as Thetford was such an important settlement during the Anglo Saxon period from which the name is derived. The other most notable settlement along the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Norfolk
Earl of Norfolk is a title which has been created several times in the Peerage of England. Created in 1070, the first major dynasty to hold the title was the 12th and 13th century Bigod family, and it then was later held by the Mowbrays, who were also made Dukes of Norfolk. Due to the Bigods' descent in the female line from William Marshal, they inherited the hereditary office of Earl Marshal, still held by the Dukes of Norfolk today. The present title was created in 1644 for Thomas Howard, 18th Earl of Arundel, the heir of the Howard Dukedom of Norfolk which had been forfeit in 1572. Arundel's grandson, the 20th Earl of Arundel and 3rd Earl of Norfolk, was restored to the Dukedom as 5th Duke upon the Restoration in 1660, and the title continues to be borne by the Dukes of Norfolk. Earls of Norfolk (and Suffolk), first creation (1066/67) *Ralph the Staller, 1st Earl of Norfolk and Suffolk (c. 1011–1068) *Ralph de Guader, 2nd Earl of Norfolk and Suffolk (c. 1040c. 1096) (fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Bigod, 1st Earl Of Norfolk
Roger Bigod (died 1107) was a Norman knight who travelled to England in the Norman Conquest. He held great power in East Anglia, and five of his descendants were earls of Norfolk. He was also known as Roger Bigot, appearing as such as a witness to the Charter of Liberties of Henry I of England. Biography Roger came from a fairly obscure family of poor knights in Normandy. Robert le Bigot, certainly a relation of Roger's, possibly his father, acquired an important position in the household of William, Duke of Normandy (later William I of England), due, the story goes, to his disclosure to the duke of a plot by the duke's cousin William Werlenc. Both Roger and Robert were rewarded with a substantial estate in East Anglia following the Norman Conquest of England. The Domesday Book lists Roger as holding six lordships in Essex, 117 in Suffolk and 187 in Norfolk. Bigod's (Bigot) base was in Thetford, Norfolk, then the see of the bishop, where he founded a priory later donated to the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_Western_Negev%2C_Israel.jpg)



.jpg)