|
Carotid Ultrasonography
Carotid ultrasonography is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique to evaluate structural details of the carotid arteries. Carotid ultrasound is used to diagnose carotid artery stenosis (CAS) and can assess atherosclerotic plaque morphology and characteristics. Carotid duplex and contrast-enhanced ultrasound are two of the most common imaging techniques used to evaluate carotid artery disease. Medical Uses Carotid ultrasound is a low-cost, noninvasive, and accurate diagnostic imaging modality used to evaluate diseases of the carotid arteries. It is most often used to diagnose carotid artery stenosis, a form of atherosclerosis, and has the capability to assess plaque morphology and characteristics. Carotid artery stenosis is a major risk factor for stroke, and risk assessment of atherosclerotic carotid plaques is a critical component of stroke prevention. Advances in imaging have allowed for risk stratification including degree of stenosis and how vulnerable the athero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Arteries
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) ( in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '.) are that supply the head and neck with ; they divide in the neck to form the and |
Cavernous Sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica. Structure The cavernous sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses of the head. It is a network of veins that sit in a cavity. It sits on both sides of the sphenoidal bone and pituitary gland, approximately 1 × 2 cm in size in an adult. The carotid siphon of the internal carotid artery, and cranial nerves III, IV, V (branches V1 and V2) and VI all pass through this blood filled space. Both sides of cavernous sinus is connected to each other via intercavernous sinuses. The cavernous sinus lies in between the inner and outer layers of dura mater. Nearby structures * Above: optic tract, optic chiasma, internal carotid artery. * Inferiorly: foramen lacerum, and the junction of the body and greater wing of sphenoid bone. * Medially: pituitary gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath or chest pain. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contractions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the surfaces of intracardiac devices. Endocarditis is characterized by lesions, known as '' vegetations'', which is a mass of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies of microorganisms, and scant inflammatory cells. In the subacute form of infective endocarditis, the vegetation may also include a center of granulomatous tissue, which may fibrose or calcify. There are several ways to classify endocarditis. The simplest classification is based on cause: either ''infective'' or ''non-infective'', depending on whether a microorganism is the source of the inflammation or not. Regardless, the diagnosis of endocarditis is based on clinical features, investigations such as an echocardiogram, and blood cultures demonstrating the presence of endocarditis-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a syndrome (a set of signs and symptoms) due to decreased blood flow in the coronary arteries such that part of the heart muscle is unable to function properly or dies. The most common symptom is centrally located pressure-like chest pain, often radiating to the left shoulder or angle of the jaw, and associated with nausea and sweating. Many people with acute coronary syndromes present with symptoms other than chest pain, particularly women, older people, and people with diabetes mellitus. Acute coronary syndrome is subdivided in three scenarios depending on the duration of symptoms, the presence of ECG changes and blood test results: ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI, 30%), non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI, 25%), or unstable angina (38%). Generally, when symptoms occur for less than 30 minutes, it is unstable angina. When symptoms are prolonged for more than 30 minutes, the diagnosis is acute myocardial infarction. ACS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allergy
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, coughing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note: food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions. Common allergens include pollen and certain foods. Metals and other substances may also cause such problems. Food, insect stings, and medications are common causes of severe reactions. Their development is due to both genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves immunoglobulin E antibodies (IgE), part of the body's immune system, binding to an allergen and then to a receptor on mast cells or basophils where it triggers the release of inflammatory chemicals such as histamine. Diagnosis is ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) is the application of ultrasound contrast medium to traditional medical sonography. Ultrasound contrast agents rely on the different ways in which sound waves are reflected from interfaces between substances. This may be the surface of a small air bubble or a more complex structure. Commercially available contrast media are gas-filled microbubbles that are administered intravenously to the systemic circulation. Microbubbles have a high degree of echogenicity (the ability of an object to reflect ultrasound waves). There is a great difference in echogenicity between the gas in the microbubbles and the soft tissue surroundings of the body. Thus, ultrasonic imaging using microbubble contrast agents enhances the ultrasound backscatter, (reflection) of the ultrasound waves, to produce a sonogram with increased contrast due to the high echogenicity difference. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound can be used to image blood perfusion in organs, measure blood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Artery
The vertebral arteries are major arteries An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ... of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the ''vertebrobasilar vascular system'', the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and Cerebral circulation#Posterior cerebral circulation, posterior part of brain. Structure The vertebral arteries usually arise from the posterosuperior aspect of the central subclavian arteries on each side of the body, then enter deep to the transverse process at the level of the 6th cervical vertebrae (C6), or occasio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Temporal Artery
In human anatomy, the superficial temporal artery is a major artery of the head. It arises from the external carotid artery when it splits into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery. Its pulse can be felt above the zygomatic arch, above and in front of the tragus of the ear. Structure The superficial temporal artery is the smaller of two end branches that split superiorly from the external carotid. Based on its direction, the superficial temporal artery appears to be a continuation of the external carotid. It begins within the parotid gland, behind the neck of the mandible, and passes superficially over the posterior root of the zygomatic process of the temporal bone; about 5 cm above this process it divides into two branches: ''a. frontal'', and ''a. parietal''. Branches The parietal branch of the superficial temporal artery (posterior temporal) is a small artery in the head. It is larger than the frontal branch and curves upward and backward on the side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
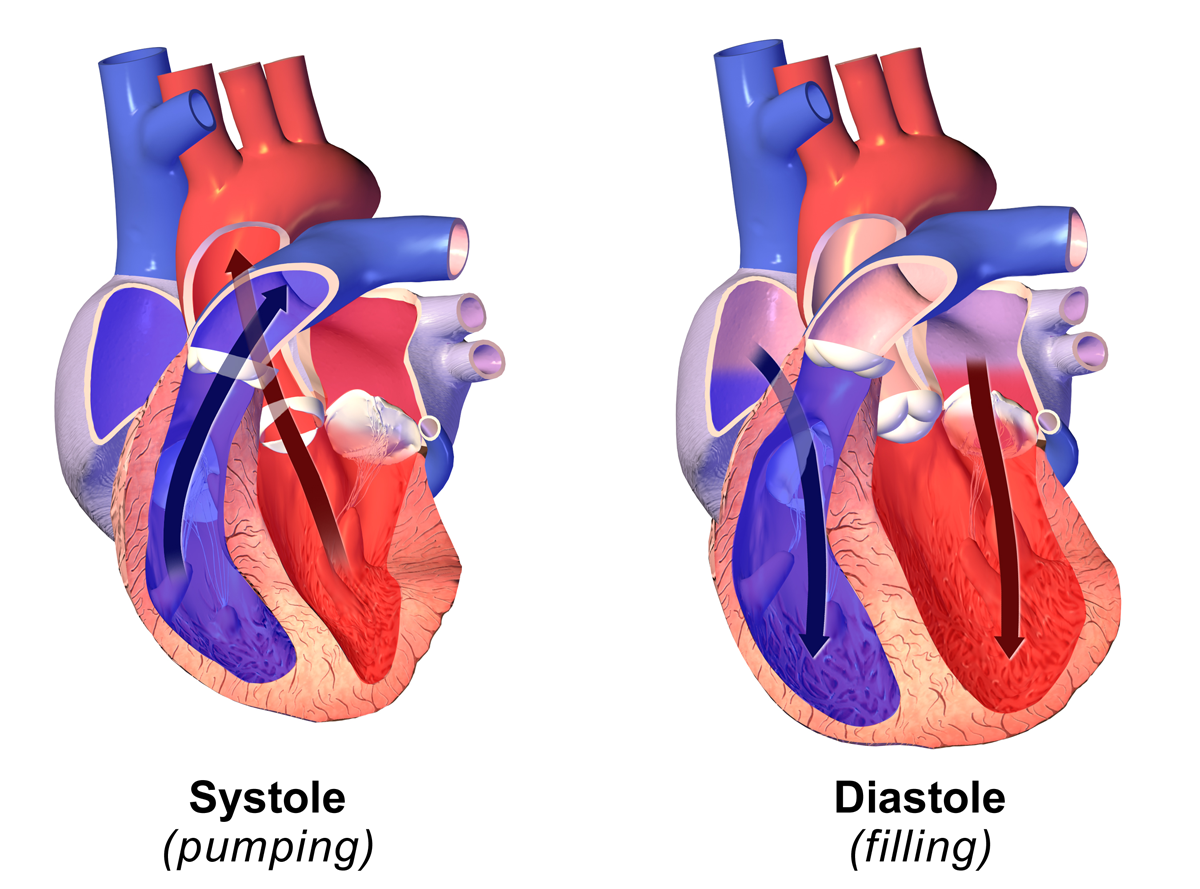
Diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles. The term originates from the Greek word (''diastolē''), meaning "dilation", from (''diá'', "apart") + (''stéllein'', "to send"). Role in cardiac cycle A typical heart rate is 75 beats per minute (bpm), which means that the cardiac cycle that produces one heartbeat, lasts for less than one second. The cycle requires 0.3 sec in ventricular systole (contraction)—pumping blood to all body systems from the two ventricles; and 0.5 sec in diastole (dilation), re-filling the four chambers of the heart, for a total of 0.8 sec to complete the cycle. Early ventricular diastole During early ventricular diastole, pressure in the two ventricles begins to drop from the peak reached during systo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and send blood to the larger, lower ventricle chambers. This flow fills the ventricles with blood, and the resulting pressure closes the valves to the atria. The ventricles now perform i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)