|
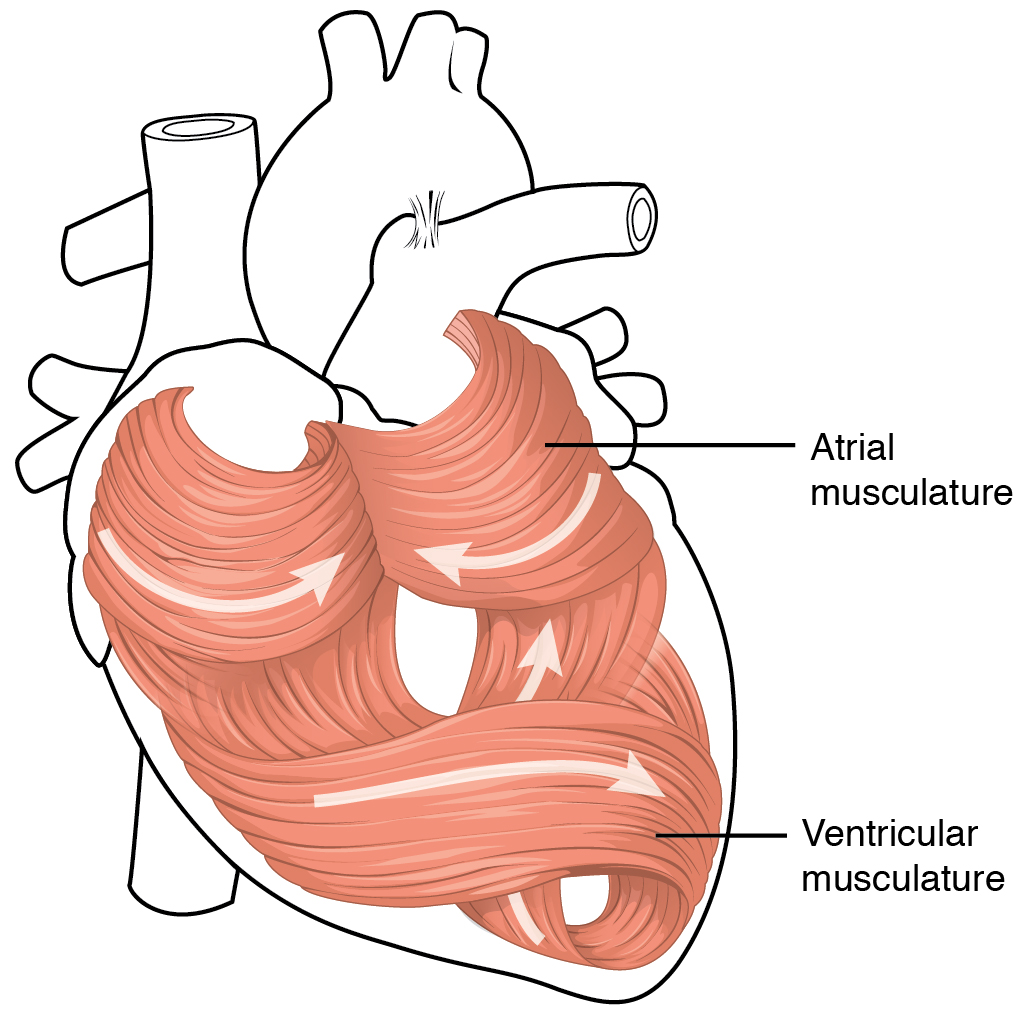
Cardiac Skeleton
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through them. The cardiac skeleton separates and partitions the atria (the smaller, upper two chambers) from the ventricles (the larger, lower two chambers). The unique matrix of connective tissue within the cardiac skeleton isolates electrical influence within these defined chambers. In normal anatomy, there is only one conduit for electrical conduction from the upper chambers to the lower chambers, known as the atrioventricular node. The physiologic cardiac skeleton forms a firewall governing autonomic/electrical influence until bordering the bundle of His which further governs autonomic flow to the bundle branches of the ventricles. Understood as such, the cardiac skeleton efficiently centers and robustly funnels electrical energy from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat adult heart disease. Surgical aspects are not included in cardiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AV Node
The atrioventricular node or AV node electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of the interatrial septum near the opening of the coronary sinus, and conducts the normal electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles. The AV node is quite compact (~1 x 3 x 5 mm).Full Size Picture triangle of-Koch.jpg Retrieved on 2008-12-22 Structure Location The AV node lies at the lower back section of the |
Sinoatrial Node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node or sinus node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approximately fifteen mm long, three mm wide, and one mm thick, located directly below and to the side of the superior vena cava. These cells can produce an electrical impulse an action potential known as a cardiac action potential that travels through the electrical conduction system of the heart, causing it to contract. In a healthy heart, the SA node continuously produces action potentials, setting the rhythm of the heart (sinus rhythm), and so is known as the heart's natural pacemaker. The rate of action potentials produced (and therefore the heart rate) is influenced by the nerves that supply it. Structure The sinoatrial node is a oval-shaped structure that is approximately fifteen mm long, three mm wide, and one mm thick, located directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray's Anatomy
''Gray's Anatomy'' is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter, and first published in London in 1858. It has gone through multiple revised editions and the current edition, the 42nd (October 2020), remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible". Earlier editions were called ''Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical'', ''Anatomy of the Human Body'' and ''Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied'', but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, ''Gray's Anatomy''. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject. Publication history Origins The English anatomist Henry Gray was born in 1827. He studied the development of the endocrine glands and spleen and in 1853 was appointed Lecturer on Anatomy at St George's Hospital Medical School in London. In 1855, he approached his colleague Henry Vandyke Carter with his idea to produce an inexpensive and ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of the most accomplished of all medical researchers of antiquity, Galen influenced the development of various scientific disciplines, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and neurology, as well as philosophy and logic. The son of Aelius Nicon, a wealthy Greek architect with scholarly interests, Galen received a comprehensive education that prepared him for a successful career as a physician and philosopher. Born in the ancient city of Pergamon (present-day Bergama, Turkey), Galen traveled extensively, exposing himself to a wide variety of medical theories and discoveries before settling in Rome, where he served prominent members of Roman society and eventually was given the position of personal physician to several emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocardium
The endocardium is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. The endocardium also provides protection to the valves and heart chambers. The endocardium underlies the much more voluminous myocardium, the muscular tissue responsible for the contraction of the heart. The outer layer of the heart is termed epicardium and the heart is surrounded by a small amount of fluid enclosed by a fibrous sac called the pericardium. Function The endocardium, which is primarily made up of endothelial cells, controls myocardial function. This modulating role is separate from the homeometric and heterometric regulatory mechanisms that control myocardial contractility. Moreover, the endothelium of the myocardial (heart muscle) capillaries, which is also closely appositioned to the cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells), is involved in this modulatory role. Thus, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semilunar Valves
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart valve opens or closes according to differential blood pressure on each side. The four valves in the mammalian heart are two atrioventricular valves separating the upper atria from the lower ventricles – the mitral valve in the left heart, and the tricuspid valve in the right heart. The other two valves are at the entrance to the arteries leaving the heart these are the semilunar valves – the aortic valve at the aorta, and the pulmonary valve at the pulmonary artery. The heart also has a coronary sinus valve, and an inferior vena cava valve, not discussed here. Structure The heart valves and the chambers are lined with endocardium. Heart valves separate the atria from the ventricles, or the ventricles from a blood vessel. Heart va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conus Arteriosus
The infundibulum (also known as ''conus arteriosus'') is a conical pouch formed from the upper and left angle of the right ventricle in the chordate heart, from which the pulmonary trunk arises. It develops from the bulbus cordis. Typically, the infundibulum refers to the corresponding internal structure, whereas the conus arteriosus refers to the external structure. Defects in infundibulum development can result in a heart condition known as tetralogy of Fallot. A tendinous band extends upward from the right atrioventricular fibrous ring and connects the posterior surface of the infundibulum to the aorta. The infundibulum is the entrance from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery and pulmonary trunk. The wall of the infundibulum is smooth. Additional images File:Gray490.png, Front view of human Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricuspid Valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle during diastole, and to close to prevent backflow ( regurgitation) from the right ventricle into the right atrium during right ventricular contraction ( systole). Structure The tricuspid valve usually has three cusps or leaflets, named the anterior, posterior, and septal cusps. Each leaflet is connected via chordae tendineae to the anterior, posterior, and septal papillary muscles of the right ventricle, respectively. Tricuspid valves may also occur with two or four leaflets; the number may change over a lifetime. Function The tricuspid valve functions as a one-way valve that closes during ventricular systole to prevent regurgitation of blood from the right ventricle back into the right atrium. It opens during ventricular diastol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicuspid Valve
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-way valves allowing blood flow in just one direction. The mitral valve and the tricuspid valve are known as the atrioventricular valves because they lie between the atria and the ventricles. In normal conditions, blood flows through an open mitral valve during diastole with contraction of the left atrium, and the mitral valve closes during systole with contraction of the left ventricle. The valve opens and closes because of pressure differences, opening when there is greater pressure in the left atrium than ventricle and closing when there is greater pressure in the left ventricle than atrium. In abnormal conditions, blood may flow backward through the valve (mitral regurgitation) or the mitral valve may be narrowed (mitral stenosis). Rheu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomyocyte
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's my ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_Veloso_Salgado.png)