|
Carboxysome And Bacterial Microcompartments
Carboxysomes are bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) consisting of polyhedral protein shells filled with the enzymes ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO)—the predominant enzyme in carbon fixation and the Rate-determining step, rate limiting enzyme in the Calvin cycle—and carbonic anhydrase. Carboxysomes are thought to have evolved as a consequence of the increase in oxygen concentration in the ancient atmosphere; this is because oxygen is a competing substrate to carbon dioxide in the RuBisCO reaction. To overcome the inefficiency of RuBisCO, carboxysomes concentrate carbon dioxide inside the shell by means of co-localized carbonic anhydrase activity, which produces carbon dioxide from the bicarbonate that diffuses into the carboxysome. The resulting concentration of carbon dioxide near RuBisCO decreases the proportion of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate oxygenation and thereby avoids costly Photorespiration, photorespiratory reactions. The surrounding she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxysomes EM
Carboxysomes are bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) consisting of polyhedral protein shells filled with the enzymes ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO)—the predominant enzyme in carbon fixation and the rate limiting enzyme in the Calvin cycle—and carbonic anhydrase. Carboxysomes are thought to have evolved as a consequence of the increase in oxygen concentration in the ancient atmosphere; this is because oxygen is a competing substrate to carbon dioxide in the RuBisCO reaction. To overcome the inefficiency of RuBisCO, carboxysomes concentrate carbon dioxide inside the shell by means of co-localized carbonic anhydrase activity, which produces carbon dioxide from the bicarbonate that diffuses into the carboxysome. The resulting concentration of carbon dioxide near RuBisCO decreases the proportion of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate oxygenation and thereby avoids costly photorespiratory reactions. The surrounding shell provides a barrier to carbon dioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The phylum Proteobacteria includes a wide variety of pathogenic genera, such as ''Escherichia'', '' Salmonella'', ''Vibrio'', ''Yersinia'', ''Legionella'', and many others.Slonczewski JL, Foster JW, Foster E. Microbiology: An Evolving Science 5th Ed. WW Norton & Company; 2020. Others are free-living (nonparasitic) and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation. Carl Woese established this grouping in 1987, calling it informally the "purple bacteria and their relatives". Because of the great diversity of forms found in this group, it was later informally named Proteobacteria, after Proteus, a Greek god of the sea capable of assuming many different shapes (not after the Proteobacteria genus ''Proteus''). In 2021 the Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
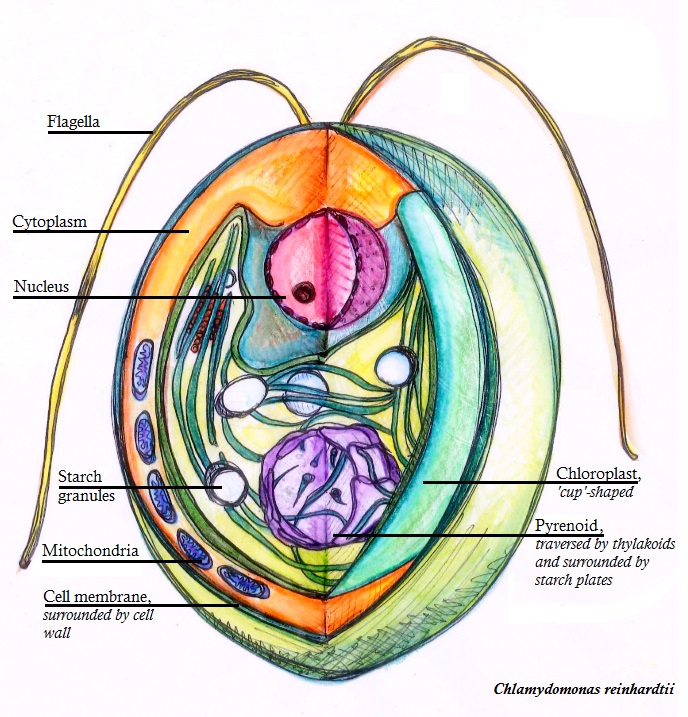
Pyrenoid
Pyrenoids are sub-cellular micro-compartments found in chloroplasts of many algae,Giordano, M., Beardall, J., & Raven, J. A. (2005). CO2 concentrating mechanisms in algae: mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 56, 99-131. and in a single group of land plants, the hornworts.Villarreal, J. C., & Renner, S. S. (2012) Hornwort pyrenoids, carbon-concentrating structures, evolved and were lost at least five times during the last 100 million years. ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences'',109(46), 1873-1887. Pyrenoids are associated with the operation of a carbon-concentrating mechanism (CCM). Their main function is to act as centres of carbon dioxide (CO2) fixation, by generating and maintaining a CO2 rich environment around the photosynthetic enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO). Pyrenoids therefore seem to have a role analogous to that of carboxysomes in cyanobacteria. Algae are restricted to aqueous env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMC Domain
In molecular biology the Bacterial Microcompartment (BMC) domain is a protein domain found in a variety of shell proteins, including CsoS1A, CsoS1B and CsoS1C of ''Thiobacillus neapolitanus'' (''Halothiobacillus neapolitanus'') and their orthologs from other bacteria. These shell proteins form the polyhedral structure of the carboxysome and related structures that plays a metabolic role in bacteria. The BMC domain consists of about 90 amino acid Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ... residues, characterized by β-α-β motif connected by a β-hairpin. The majority of the shell proteins consist of a single BMC domain in each subunit, forming a hexameric structure that assembles to form the flat facets of the polyhedral shell. To date, two shell proteins were found to cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a multidisciplinary area of research that seeks to create new biological parts, devices, and systems, or to redesign systems that are already found in nature. It is a branch of science that encompasses a broad range of methodologies from various disciplines, such as biotechnology, biomaterials, material science/engineering, genetic engineering, molecular biology, molecular engineering, systems biology, membrane science, biophysics, chemical and biological engineering, electrical and computer engineering, control engineering and evolutionary biology. Due to more powerful genetic engineering capabilities and decreased DNA synthesis and sequencing costs, the field of synthetic biology is rapidly growing. In 2016, more than 350 companies across 40 countries were actively engaged in synthetic biology applications; all these companies had an estimated net worth of $3.9 billion in the global market. Definition Synthetic biology currently has no gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue-green algae, although they are not usually scientifically classified as algae. They appear to have originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Sericytochromatia, the proposed name of the paraphyletic and most basal group, is the ancestor of both the non-photosynthetic group Melainabacteria and the photosynthetic cyanobacteria, also called Oxyphotobacteria. Cyanobacteria use photosynthetic pigments, such as carotenoids, phycobilins, and various forms of chlorophyll, which absorb energy from light. Unlike heterotrophic prokaryotes, cyanobacteria have internal membranes. These are flattened sacs called thylakoids where photosynthesis is performed. Phototrophic eukaryotes such as green plants perform photosynthesis in plast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectric Point
The isoelectric point (pI, pH(I), IEP), is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electrical charge or is electrically neutral in the statistical mean. The standard nomenclature to represent the isoelectric point is pH(I). However, pI is also used. For brevity, this article uses pI. The net charge on the molecule is affected by pH of its surrounding environment and can become more positively or negatively charged due to the gain or loss, respectively, of protons (H+). Surfaces naturally charge to form a double layer. In the common case when the surface charge-determining ions are H+/HO−, the net surface charge is affected by the pH of the liquid in which the solid is submerged. The pI value can affect the solubility of a molecule at a given pH. Such molecules have minimum solubility in water or salt solutions at the pH that corresponds to their pI and often precipitate out of solution. Biological amphoteric molecules such as proteins contain both acidic and basic function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purple Bacteria
Purple bacteria or purple photosynthetic bacteria are Gram-negative proteobacteria that are phototrophic, capable of producing their own food via photosynthesis. They are pigmented with bacteriochlorophyll ''a'' or ''b'', together with various carotenoids, which give them colours ranging between purple, red, brown, and orange. They may be divided into two groups – purple sulfur bacteria ( Chromatiales, in part) and purple non-sulfur bacteria ( Rhodospirillaceae). Purple bacteria are anoxygenic phototrophs widely spread in nature, but especially in aquatic environments, where there are anoxic conditions that favor the synthesis of their pigments. Taxonomy Purple bacteria belong to phylum of ''Pseudomonadota''. This phylum was established by Carl Woese in 1987 calling it "purple bacteria and their relatives" even if this is not appropriate because most of them are not purple or photosynthetic. Purple bacteria are distributed between 3 classes:''Alphaproteobacteria'', ''Betap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha And Beta Carboxysomes
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , which is the West Semitic word for " ox". Letters that arose from alpha include the Latin letter A and the Cyrillic letter А. Uses Greek In Ancient Greek, alpha was pronounced and could be either phonemically long ( ː or short ( . Where there is ambiguity, long and short alpha are sometimes written with a macron and breve today: Ᾱᾱ, Ᾰᾰ. * ὥρα = ὥρᾱ ''hōrā'' "a time" * γλῶσσα = γλῶσσᾰ ''glôssa'' "tongue" In Modern Greek, vowel length has been lost, and all instances of alpha simply represent the open front unrounded vowel . In the polytonic orthography of Greek, alpha, like other vowel letters, can occur with several diacritic marks: any of three accent symbols (), and either of two breathing marks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Microcompartment
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are organelle-like structures found in bacteria. They consist of a protein shell that encloses enzymes and other proteins. BMCs are typically about 40–200 nanometers in diameter and are made entirely of proteins. The shell functions like a membrane, as it is selectively permeable. Other protein-based compartments found in bacteria and archaea include encapsulin nanocompartments and gas vesicles. Discovery The first BMCs were observed in the 1950s in electron micrographs of cyanobacteria, and were later named carboxysomes after their role in carbon fixation was established. Until the 1990s, carboxysomes were thought to be an oddity confined to certain autotrophic bacteria. But then genes coding for proteins homologous to those of the carboxysome shell were identified in the ''pdu'' (propanediol utilization) and ''eut'' (ethanolamine utilization) operons. Subsequently, transmission electron micrographs of ''Salmonella'' cells grown on propaned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information. Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic, and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among various mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |