|
Carbon–hydrogen Bond
In chemistry, the carbon–hydrogen bond ( bond) is a chemical bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms that can be found in many organic compounds. This bond is a covalent bond, covalent, single bond, meaning that carbon shares its outer valence electrons with up to four hydrogens. This Octet rule, completes both of their Electron shell, outer shells, making them stable. Carbon–hydrogen bonds have a bond length of about 1.09 Ångström, Å (1.09 × 10−10 m) and a bond energy of about 413 Joule, kJ/Mole (unit), mol (see table below). Using Electronegativities of the elements (data page), Pauling's scale—C (2.55) and H (2.2)—the electronegativity difference between these two atoms is 0.35. Because of this small difference in electronegativities, the bond is generally regarded as being non-polar. In structural formulas of molecules, the hydrogen atoms are often omitted. Compound classes consisting solely of bonds and carbon–carbon bond, bonds are alkanes, alkenes, alkyne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
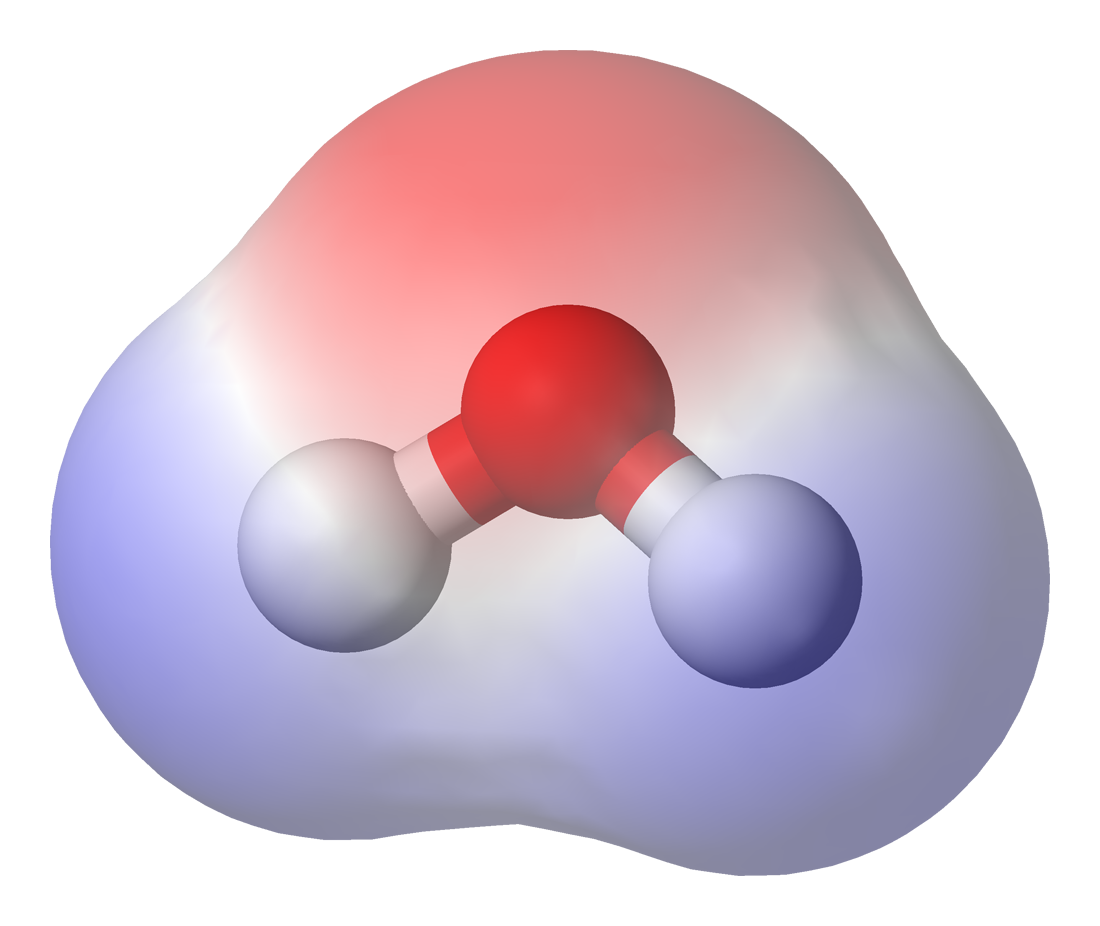
Non-polar
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole-dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young Star
A pre-main-sequence star (also known as a PMS star and PMS object) is a star in the stage when it has not yet reached the main sequence. Earlier in its life, the object is a protostar that grows by acquiring mass from its surrounding envelope of interstellar dust and gas. After the protostar blows away this envelope, it is optically visible, and appears on the stellar birthline in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. At this point, the star has acquired nearly all of its mass but has not yet started hydrogen burning (i.e. nuclear fusion of hydrogen). The star continues to contract, its internal temperature rising until it begins hydrogen burning on the zero age main sequence. This period of contraction is the pre-main sequence stage. An observed PMS object can either be a T Tauri star, if it has fewer than 2 solar masses (), or else a Herbig Ae/Be star, if it has 2 to 8 . Yet more massive stars have no pre-main-sequence stage because they contract too quickly as protostars. By t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernovae
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. The last supernova directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appearing not long after Tycho's Supernova in 1572, both of which were visible to the naked eye. The remnants of more recent supernovae have been found, and observations of supernovae in other galaxies suggest they occur in the Milky Way on average about three times every century. A supernova in the Milky Way would almost certainly be observable through modern astronomical telescopes. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and traces of heavier elements. Its stellar mass, total mass mainly determines it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet Light
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. These int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylidyne Radical
Methylidyne, or (unsubstituted) carbyne, is an organic compound whose molecule consists of a single hydrogen atom bonded to a carbon atom. It is the parent compound of the carbynes, which can be seen as obtained from it by substitution of other functional groups for the hydrogen. The carbon atom is left with either one or three unpaired electrons (unsatisfied valence bonds), depending on the molecule's excitation state; making it a radical. Accordingly, the chemical formula can be CH• or CH3• (also written as ⫶CH); each dot representing an unpaired electron. The corresponding systematic names are methylidyne or hydridocarbon(•), and methanetriyl or hydridocarbon(3•). However, the formula is often written simply as CH. Methylidyne is a highly reactive gas that is quickly destroyed in ordinary conditions but is abundant in the interstellar medium (and was one of the first molecules to be detected there). Nomenclature The trivial name ''carbyne'' is the prefer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, metabolism, Cell growth, growth, adaptation, response to stimulus (physiology), stimuli, and reproduction. All life over time eventually reaches a state of death, and none is Immortality, immortal. Many philosophical definitions of living systems have been proposed, such as self-organizing systems. Viruses in particular make definition difficult as they replicate only in Host (biology), host cells. Life exists all over the Earth in air, water, and soil, with many ecosystems forming the biosphere. Some of these are harsh environments occupied only by extremophiles. Life has been studied since ancient times, with theories such as Empedocles's materialism asserting that it was composed of Classical element, four eternal elements, and Aristotle's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbons
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may be similar to that of gasoline or lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, or their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gases are either carbon dioxide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Hydrocarbon
Aromatic compounds or arenes are organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties: * Typically unreactive * Often non polar and hydrophobic * High carbon-hydrogen ratio * Burn with a strong sooty yellow flame, due to high C:H ratio * Undergo electrophilic substitution reactions and nucleophilic aromatic substitutions Arenes are typically split into two categories - benzoids, that contain a benzene derivative and follow the benzene ring model, and non-benzoids that contain other aromatic cyclic derivatives. Aromatic compounds are commonly used in organic synthesis and are involved in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 118 picometers (for C2H2) is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (132 pm, for C2H4) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Preferred IUPAC name, recommends using the name "alkene" only for Open-chain compound, acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for Cyclic compound, cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ''n'' being a >1 natural number (which is two hydrogens less than the corresponding alkane). When ''n'' is four or more, isomers are possible, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |