|
Carbon Literacy
Carbon Literacy is the awareness of Global warming, climate change and the climate Human impact on the environment, impacts of mankind's everyday actions. The term has been used in a range of contexts in scientific literature and in casual usage (see Carbon literacy#Research, Research), but is most associated with The Carbon Literacy Project (CLP). Definition Carbon Literacy is the knowledge and capacity required to create a positive shift in how mankind lives, works and behaves in response to Global warming, climate change. The Carbon Literacy Project defines Carbon Literacy as "an awareness of the carbon costs and impacts of everyday activities and the ability and motivation to reduce emissions, on an individual, community and organisational basis." To distinguish between the use of the phrase in its abstract sense ('carbon literacy') (e.g.), and its use under the established definition (Carbon Literacy), the phrase is capitalised (e.g.). See Carbon literacy#Research, Researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effects Of Global Warming On Oceans
Among the effects of climate change on oceans are: an increase in sea surface temperature as well as ocean temperatures at greater depths, more frequent marine heatwaves, a reduction in pH value, a rise in sea level from ocean warming and ice sheet melting, sea ice decline in the Arctic, increased upper ocean stratification, reductions in oxygen levels, increased contrasts in salinity (salty areas becoming saltier and fresher areas becoming less salty), changes to ocean currents including a weakening of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation, and stronger tropical cyclones and monsoons. All these changes have knock-on effects which disturb marine ecosystems. The root cause of these observed changes is the Earth warming due to anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases, such as for example carbon dioxide and methane. This leads inevitably to ocean warming, because the ocean is taking up most of the additional heat in the climate system. Some of the additional carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, humans in literate societies have sets of practices for producing and consuming writing, and they also have beliefs about these practices. Reading, in this view, is always reading something for some purpose; writing is always writing something for someone for some particular ends. Beliefs about reading and writing and its value for society and for the individual always influence the ways literacy is taught, learned, and practiced over the lifespan. Some researchers suggest that the history of interest in the concept of "literacy" can be divided into two periods. Firstly is the period before 1950, when literacy was understood solely as alphabetical literacy (word and letter recognition). Secondly is the period after 1950, when literacy slowly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Opinion On Climate Change
There is a strong scientific consensus that the Earth is warming and that this warming is mainly caused by human activities. This consensus is supported by various studies of scientists' opinions and by position statements of scientific organizations, many of which explicitly agree with the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) synthesis reports. Nearly all actively publishing climate scientists say humans are causing climate change. Surveys of the scientific literature are another way to measure scientific consensus. A 2019 review of scientific papers found the consensus on the cause of climate change to be at 100%, and a 2021 study concluded that over 99% of scientific papers agree on the human cause of climate change. The small percentage of papers that disagreed with the consensus either cannot be replicated or contain errors. Consensus points The current scientific consensus is that: * Earth's climate has warmed significantly since the late 1800s. * Human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Climate Change Articles
This is a list of climate change topics. 0-9 100% renewable energy - 100,000-year problem - 1500-Year climate cycle - 4 Degrees and Beyond International Climate Conference A Abrupt climate change - '' The Age of Stupid'' - Albedo - ''An Inconvenient Truth'' - '' An Inconvenient Book'' - Antarctica cooling controversy - Antarctic Bottom Water - Antarctic Cold Reversal - Antarctic oscillation - Anthropocene extinction - Arctic amplification - Arctic Climate Impact Assessment - Arctic geoengineering - Arctic shrinkage - Arctic oscillation - Atlantic oscillation - Arctic Climate Impact Assessment - Arctic methane release - Arctic sea ice decline - Arctic shrinkage - Argo (oceanography) - ARkStorm - Athabasca oil sands - Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation - Atmospheric circulation - Atmospheric sciences - Atmospheric window - Attribution of recent climate change - Aviation and climate change - Aviation and the environment - Avoiding dangerous climate change B B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Climate Change Science
The history of the scientific discovery of climate change began in the early 19th century when ice ages and other natural changes in paleoclimate were first suspected and the natural greenhouse effect was first identified. In the late 19th century, scientists first argued that human emissions of greenhouse gases could change Earth's energy balance and climate. Many other theories of climate change were advanced, involving forces from volcanism to solar variation. In the 1960s, the evidence for the warming effect of carbon dioxide gas became increasingly convincing. Some scientists also pointed out that human activities that generated atmospheric aerosols (e.g., "pollution") could have cooling effects as well. During the 1970s, scientific opinion increasingly favored the warming viewpoint. By the 1990s, as the result of improving the fidelity of computer models and observational work confirming the Milankovitch theory of the ice ages, a consensus position formed: greenhouse gase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Climate Change
This glossary of climate change is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to climate change, global warming, and related topics. 0–9 A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P R S T U V W See also * Index of climate change articles * Climate change acronyms * Glossary of environmental science * Glossary of meteorology * Scientific opinion on climate change * Timeline of environmental history References External links "The Words You Need To Know To Talk About Climate Change Today" dictionary.comarchiveIPCC– glossary * Environmental Terminology Discovery Service — EEA(mult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
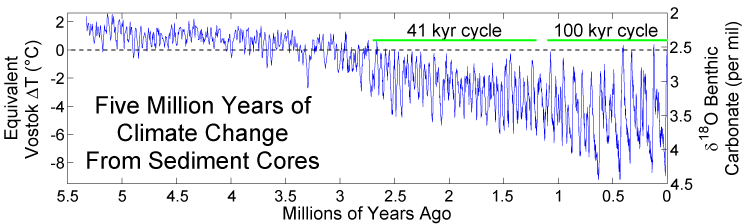
Geologic Temperature Record
The geologic temperature record are changes in Earth's environment as determined from geologic evidence on multi-million to billion (109) year time scales. The study of past temperatures provides an important paleoenvironmental insight because it is a component of the climate and oceanography of the time. Methodology Evidence for past temperatures comes mainly from isotopic considerations (especially ); the Mg/Ca ratio of foram tests, and alkenones, are also useful. Often, many are used in conjunction to get a multi-proxy estimate for the temperature. This has proven crucial in studies on glacial/interglacial temperature. Description of the temperature record Pleistocene The last 3 million years have been characterized by cycles of glacials and interglacials within a gradually deepening ice age. Currently, the Earth is in an interglacial period, beginning about 20,000 years ago (20 kya). The cycles of glaciation involve the growth and retreat of continental ice sheets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
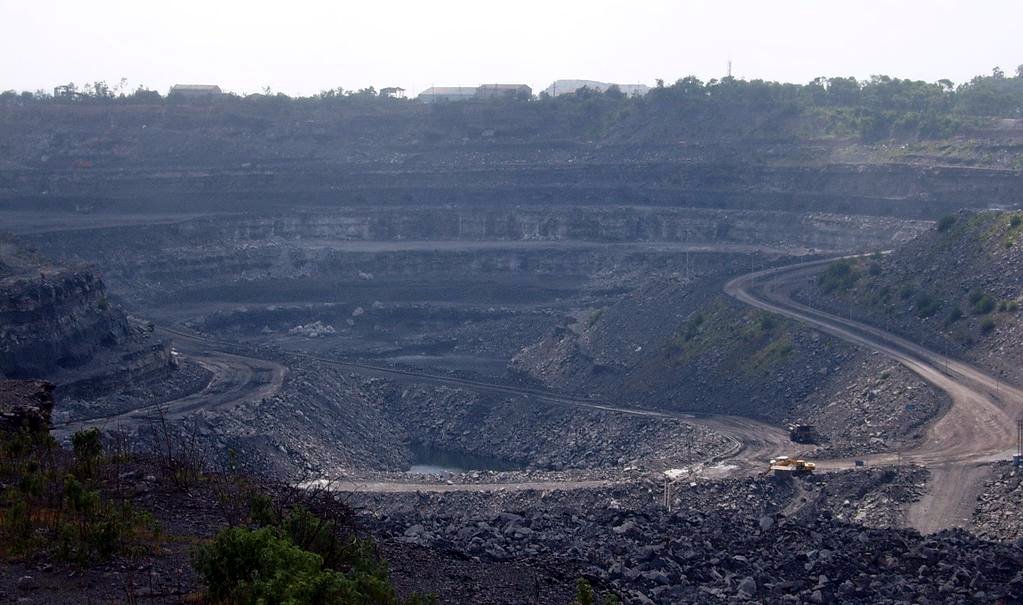
Environmental Impact Of The Coal Industry
The health and environmental impact of the coal industry includes issues such as land use, waste management, water and air pollution, caused by the coal mining, processing and the use of its products. In addition to atmospheric pollution, coal burning produces hundreds of millions of tons of solid waste products annually, including fly ash, bottom ash, and flue-gas desulfurization sludge, that contain mercury, uranium, thorium, arsenic, and other heavy metals. Coal is the largest contributor to the human-made increase of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere. There are severe health effects caused by burning coal. According to a report by the World Health Organization in 2008, coal particulates pollution are estimated to shorten approximately 10,000 lives annually worldwide. A 2004 study commissioned by environmental groups, but contested by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, concluded that coal burning costs 24,000 lives a year in the United States. More re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when energy from a planet's host star goes through the planet's atmosphere and heats the planet's surface, but greenhouse gases in the atmosphere prevent some of the heat from returning directly to space, resulting in a warmer planet. Earth's natural greenhouse effect makes life as we know it possible and carbon dioxide plays a significant role in providing for the relatively high temperature on Earth. The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary atmosphere warms the planet's surface beyond the temperature it would have in the absence of its atmosphere.A concise description of the greenhouse effect is given in the ''Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report,'' "What is the Greenhouse Effect?FAQ 1.3 – AR4 WGI Chapter 1: Historical Overview of Climate Change Science, IPCC Fourth Assessment Report, Chapter 1, p. 115: "To balance the absorbed incoming olarenergy, the Earth m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Impact On The Environment
Human impact on the environment (or anthropogenic impact) refers to changes to biophysical environments and to ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources caused directly or indirectly by humans. Modifying the environment to fit the needs of society is causing severe effects including global warming, environmental degradation (such as ocean acidification), mass extinction and biodiversity loss, ecological crisis, and ecological collapse. Some human activities that cause damage (either directly or indirectly) to the environment on a global scale include population growth, overconsumption, overexploitation, pollution, and deforestation. Some of the problems, including global warming and biodiversity loss, have been proposed as representing catastrophic risks to the survival of the human species. The term ''anthropogenic'' designates an effect or object resulting from human activity. The term was first used in the technical sense by Russian geologist Alexey Pavlov, and it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs and Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane (), nitrous oxide (), and ozone (). Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface would be about , rather than the present average of . The atmospheres of atmosphere of Venus, Venus, atmosphere of Mars, Mars and atmosphere of Titan, Titan also contain greenhouse gases. Human activities since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (around 1750) have increased the Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide by over 50%, from 280 parts per million, ppm in 1750 to 421 ppm in 2022. The last time the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide was this high was over 3&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |