|
Cape Weyprecht
Cape WeyprechtConway, William Martin. 1897. ''The First Crossing of Spitsbergen''. London: J.M. Dent & Company, p. 288. ( no, Kapp Weyprecht) is a headland in the northeast part of Spitsbergen in Svalbard, in the area known as Olav V Land. The cape is named after Karl Weyprecht, an Austro-Hungarian officer and polar explorer. Together with Julius von Payer, he led the Austro-Hungarian North Pole Expedition that discovered Franz Josef Land in 1873. Weyprecht himself was never on Svalbard. About east of Cape Weyprecht lie Mack Island, Torkildsen Island, and Isaksen Island, all part of the Rønnbeck Islands The Rønnbeck Islands ( no, Rønnbeckøyane) are a group of islands in Hinlopen Strait, Svalbard. They are located south of the Bastian Islands, southeast of Wilhelm Island. The islands are named after Norwegian sailor and seal hunter Nils Fredrik .... References Headlands of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape (geography)
In geography, a cape is a headland or a promontory of large size extending into a body of water, usually the sea.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, p. 80. . A cape usually represents a marked change in trend of the Coast, coastline, often making them important landmarks in sea navigation. This also makes them prone to natural forms of erosion, mainly tidal actions, which results in them having a relatively short geological lifespan. Capes can be formed by glaciers, volcanoes, and changes in sea level. Erosion plays a large role in each of these methods of formation. List of some well-known capes Gallery File:Cape Cornwall.jpg, Cape Cornwall, England File:Nasa photo cape fear.jpg, Satellite image of Cape Fear, North Carolina File:Cape McLear, Malawi (2499273862).jpg, Cape MacLear, Malawi File:Cape horn.png, Map depicting Cape Horn at the southernmost portion of South America File:Spain.Santander.Cabo.Mayor.jpeg, Photograph o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
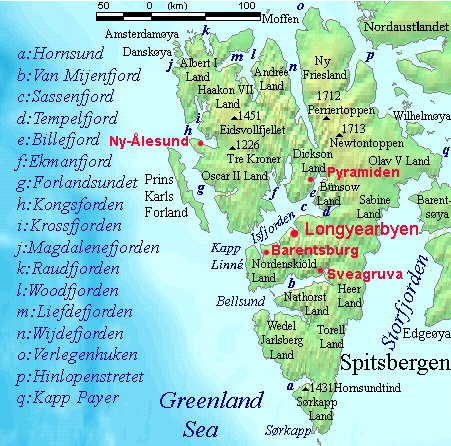
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olav V Land
Olav V Land is a peninsula in eastern Spitsbergen Island, Svalbard named after Olav V of Norway. It is covered by the Olav V Icefield, measuring about .''Glacier Atlas of Svalbard and Jan Mayen''. 1993. Oslo: Norsk polarinstitutt, p. 32. The only larger ice cap in the Svalbard Archipelago is Austfonna in Nordaustlandet Nordaustlandet (sometimes translated as North East Land) is the second-largest island in the archipelago of Svalbard, Norway, with an area of . It lies north east of Spitsbergen, separated by Hinlopen Strait. Much of Nordaustlandet lies under la ..., with an area of . References * http://www.ssb.no/aarbok/kart/i.html Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Weyprecht
Karl Weyprecht, also spelt Carl Weyprecht, (8 September 1838 – 2 March 1881) was an Austro-Hungarian explorer. He was an officer (''k.u.k. Linienschiffsleutnant'') in the Austro-Hungarian Navy. He is most famous as an Arctic explorer, and an advocate of international cooperation for scientific polar exploration. Although he did not live to see it occur, he is associated with the organisation of the first International Polar Year. In 1852, he studied at Gymnasium in Darmstadt, but later switched to Höhere Gewerbeschule Darmstadt, now the Technische Universität Darmstadt. In 1856, he joined the Austro-Hungarian Navy (''Kriegsmarine'') as a provisional sea cadet. He served in the Austro-Sardinian War. From 1860 to 1862, he served on the frigate ''Radetzky'' under the command of Admiral Tegetthoff. From 1863 to 1865, he was instructional officer on the training ship ''Hussar.'' On 23 July 1865, he became known to the German geographer August Petermann at a meeting of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after its defeat in the First World War. Austria-Hungary was ruled by the House of Habsburg and constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy. It was a multinational state and one of Europe's major powers at the time. Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe after the Russian Empire, at and the third-most populous (after Russia and the German Empire). The Empire built up the fourth-largest machine building industry in the world, after the United States, Germany and the United Kingdom. Austria-Hungary also became the world's third-largest manufacturer and exporter of electric home appliances, el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Von Payer
Julius Johannes Ludovicus Ritter von Payer (2 September 1841, – 29 August 1915), ennobled Ritter von Payer in 1876, was an officer of the Austro-Hungarian Army, mountaineer, arctic explorer, cartographer, painter, and professor at the Theresian Military Academy. He is chiefly known for the Austro-Hungarian North Pole expedition in 1872–74 and the discovery of Franz Josef Land. Early life and military career Born in Schönau, Bohemia, his father Franz Anton Rudolf Payer was a retired officer of the Austrian Uhlans who died when Julius was only fourteen. His mother was Blandine, née John. Payer attended the '' k.k.'' cadet school in Łobzów near Kraków, Galicia (present-day Poland). Between 1857 and 1859 he studied at the Theresian Military Academy in Wiener Neustadt. From 1859, Payer served as a sub-lieutenant with the Austrian 36th infantry regiment in Verona, Venetia. He participated in the disastrous Battle of Solferino on 24 June 1859 and was honoured for his se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Hungarian North Pole Expedition
The Austro-Hungarian North Pole expedition was an Arctic expedition to find the North-East Passage that ran from 1872 to 1874 under the leadership of Julius Payer and Karl Weyprecht. The expedition discovered and partially explored Franz Josef Land. Background The Austro-Hungarian North Pole expedition was largely an initiative of geographer August Petermann who was a proponent of a navigable northern Arctic Sea. Petermann had previously been involved in the German North Pole expeditions of 1868–1870 that had failed to find navigable paths on the east coast of Greenland. Petermann then advocated for probing the area between Svalbard and Novaya Zemlya which he assumed would be less obstructed by ice due to the influence of the Gulf Stream. In 1871, a trial expedition took place. Weyprecht and Payer were put in charge. They chartered the Norwegian schooner ''Isbjørn'' and hired captain Johan Kjeldsen and a Norwegian crew in Tromsø. ''Isbjørn'' sailed to the east coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Josef Land
, native_name = , image_name = Map of Franz Josef Land-en.svg , image_caption = Map of Franz Josef Land , image_size = , map_image = Franz Josef Land location-en.svg , map_caption = Location of Franz Josef Land , nickname = , location = Arctic Ocean , coordinates = , archipelago = , total_islands = 192 , major_islands = , area_km2 = 16134 , length_km = , width_km = , highest_mount = Wilczek Land , elevation_m = 670 , population = 0 , population_as_of = 2017 , density_km2 = , ethnic_groups = , country = , country_admin_divisions_title = Federal subject , country_admin_divisions = Arkhangelsk Oblast , additional_info = Franz Josef Land, Frantz Iosef Land, Franz Joseph Land or Francis Joseph's Land ( rus, Земля́ Фра́нца-Ио́сифа, r=Zemlya Frantsa-Iosifa, no, Fridtjof Nansen Land) is a Russian archipelago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mack Island (Svalbard)
Mack Island ( no, Mackøya) is a small island in Hinlopen Strait. It is part of the Rønnbeck Islands in the Svalbard archipelago. It lies east of Cape Weyprecht on Spitsbergen. The island is a low basalt cliff and its highest point is above sea level. The closest neighboring islands are Torkildsen Island about to the east and Isaksen Island about to the north. The wildlife consists largely of polar bears. The island was discovered in 1867 by the Swedish-Norwegian polar explorer Nils Fredrik Rønnbeck Nils Fredrik Røn(n)beck ( sv, Rönnbäck, March 22, 1820 – January 4, 1891) was a Swedish-Norwegian polar skipper and ice pilot. He discovered Franz Josef Land in 1865. Life Rønnbeck was born Nils Johansson Söderlund in Storön in Kalix, in .... The Rønnbeck Islands are named after Norwegian seal hunters, and this one is named after the Norwegian sealing captain Fridrich "Fritz" Christian Mack (1836–1876), who also made several important discoveries in the Arctic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torkildsen Island
Torkildsen Island ( no, Torkildsenøya) is a small island in Hinlopen Strait. It is part of the Rønnbeck Islands in the Svalbard archipelago. It lies east of Cape Weyprecht on Spitsbergen. The island is a low basalt cliff and its highest point is above sea level. It is elongated and consists of four parts. At its east and west ends there are two small peninsulas. The central part of the island itself is divided into two parts by a narrow area, probably a sandbank like that at Kiepert Island in the nearby Bastian Islands. The closest neighboring islands are Mack Island about to the west and Isaksen Island about to the northwest. The wildlife consists largely of polar bears. The island was discovered in 1867 by the Swedish-Norwegian polar explorer Nils Fredrik Rønnbeck Nils Fredrik Røn(n)beck ( sv, Rönnbäck, March 22, 1820 – January 4, 1891) was a Swedish-Norwegian polar skipper and ice pilot. He discovered Franz Josef Land in 1865. Life Rønnbeck was born Nils Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_b_593.jpg)