|
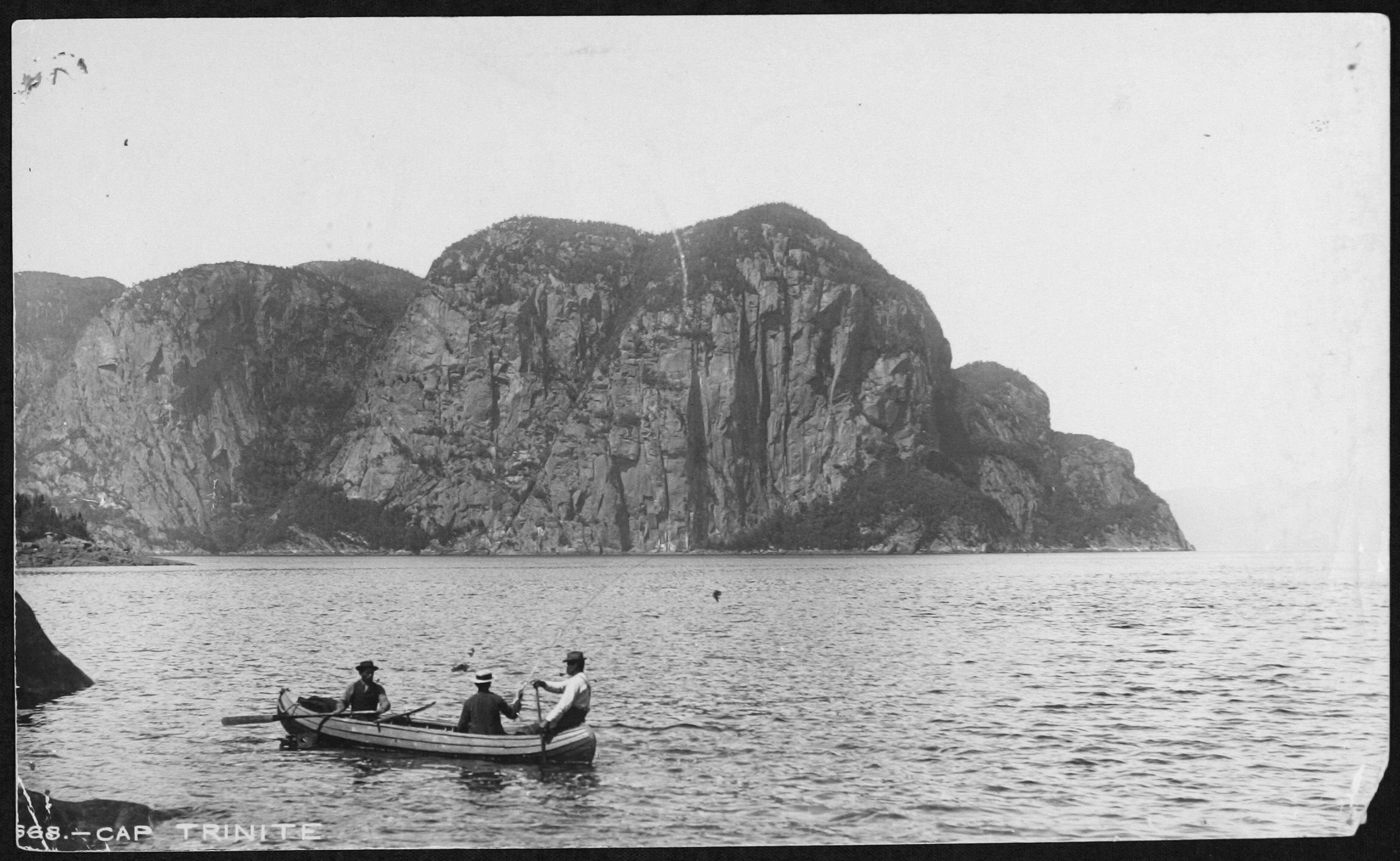
Cap Trinité
The cap Trinité is a rock wall in three plateaus of the Baie Éternité overhanging the Saguenay River, the Le Fjord-du-Saguenay Regional County Municipality, in Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean, in Quebec, Canada. This natural elevation is located in Saguenay Fjord National Park. There is the Statue of Notre-Dame-du-Saguenay. Toponymy The Commission de toponymie du Québec writes about it: "The origin of the name would be linked to its particular form as described thus :" Cape Trinité was given its name because it is actually formed by three equal caps of size and elevation, the first of which also includes three caps arranged in echelon and forming like three superimposed stages". Geography History Tourism Cape Trinité is the main attraction of Saguenay Fjord National Park. In culture Legend According to a legend montagnais, the cape Trinité would be the result of the combat between Mayo, the first Montagnais, and of a bad manitou. While he was paddling on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurentian Mountains
The Laurentian Mountains, also known as the Laurentians or Laurentides, are a mountain range in Canada. The range is long and ranges in height from with peaks over . The Laurentian Mountains extend across Labrador and Quebec within the Laurentian Upland, which contains foothills in northeastern Ontario. The range is located near the rivers of Ottawa River, Ottawa, St. Lawrence River, St. Lawrence, and Saguenay River, Saguenay. The Laurentian Mountains primarily stretch across multiple regions in Quebec, with geologic formations such as the Jacques-Cartier Massif located within the range. The Laurentians Mountains are one of the oldest mountain ranges on earth. The range formed around one billion years ago during the Grenville orogeny, in which the Grenville Province formed, a subdivision of the Canadian Shield. During that time, Laurentia, the geologic core of the Canadian Shield, collided with other continents and formed Precambrian rocks which extend across the range. The mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commission De Toponymie Du Québec
The Commission de toponymie du Québec (, ''Toponymy Commission of Québec'') is the Government of Québec's public body responsible for cataloging, preserving, making official and publicizing Québec's place names and their origins according to the province's toponymy rules. It also provides recommendations to the government with regard to toponymic changes. Its mandate covers the namings of: * natural geographical features (lakes, rivers, mountains, etc.) * constructed features (dams, embankments, bridges, etc.) * administrative units (wildlife sanctuaries, administrative regions, parks, etc.) * inhabited areas (villages, towns, Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indian reserves, etc.) * roadways (streets, roads, boulevards, etc.) A child agency of the Office québécois de la langue française, it was created in 1977 through jurisdiction defined in the Charter of the French Language to replace the Commission of Geography, created in 1912. See also * Toponymy * Toponym'elles * Offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statue Of Notre-Dame-du-Saguenay
The statue of Notre-Dame-du-Saguenay is a statue located on Cap Trinité, at the mouth of Baie Trinité, near the village of Rivière-Éternité, Quebec, Rivière-Éternité, and the river Saguenay River, in Le Fjord-du-Saguenay Regional County Municipality, in the province of Quebec, in Canada. History This statue was sculpted by in 1881. It is made entirely of pinus strobus, white pine and is covered with thin sheets of lead to protect it from the elements. It measures 9 meters high and weighs over 3 tonnes. Legend The statue of Notre-Dame-du-Saguenay was sculpted in honor of after the misadventures of "Charles-Napoléon Robitaille", a traveling salesman who, to go to Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean, Saguenay, absolutely had to take the rivers. One winter day when he was heading towards Lac Saint-Jean, the ice broke under his feet and he fell into the water; he struggled but in vain. As a last resort, he asked the Blessed Virgin to come and save him. He was miraculously strande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap Éternité
Cap Éternité is a mountain in the municipality of Rivière-Éternité, the Le Fjord-du-Saguenay Regional County Municipality, in the administrative region of Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean, in Quebec, Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun .... It overlooks, to the southwest, Éternité Bay while to the west is Cap Trinité. Reaching an altitude of , it is part of Saguenay Fjord National Park. The name of the cape was made official on December 5, 1968. To the west of the bay, the Éternité River gave its name to the municipality of Rivière-Éternité. Its impressive rock mass and steep cliffs make it a major tourist attraction site in the Saguenay Fjord National Park. Cape Eternity inspired painters, poets and writers, including Charles Gill (1871–1918) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Gill (artist)
Charles Ignace Adélard Gill (21 October 1871 – 16 October 1918) was a Canadian artist, specializing in poetry and painting. He also worked under the alternate names of Clairon and Léon Duval. Career He was born at Sorel, Quebec to Charles-Ignace Gill and Marie-Rosalie Delphire Sénécal. He studied at Collège Sainte-Marie de Montréal, Collège de Nicolet and Collège Saint-Laurent, then George de Forest Brush, who was vacationing in Pierreville, undertook to develop Gill's talent for painting. As a result, he went to the Art Association of Montreal that 1888 to study with William Brymner. Encouraged by Brymner, he went to Paris and worked with Jean-Léon Gérôme at the École des Beaux-Arts. After returning to Montreal, he established his own studio in 1894. He also published poetry in the anthology ''Les soirées du Château de Ramesay'' (1900). After his death a volume of his poetry was published under the title ''Le Cap Eternité, poème suivi des étoiles filantes' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Honoré Fréchette
Louis-Honoré Fréchette (; November 16, 1839 – May 31, 1908) was a Canadian poet, politician, playwright and short story writer. For his prose, he would be the first Quebecois to receive the Prix Montyon from the Académie française, and the first Canadian to receive any honor from a European nation. Early life and education Fréchette was born on November 16, 1839, in Lévis, Lower Canada. From 1854 to 1860, Fréchette did his classical studies at the Séminaire de Québec, the Collège de Sainte-Anne-de-la-Pocatière and at the Séminaire de Nicolet. Fréchette first showed his rebelliousness when he studied at college. He later studied law at Université Laval. Career In 1864, he opened a lawyer's office in Lévis and founded two newspapers: ''Le drapeau de Lévis'' and ''La Tribune de Levis''. He exiled himself to Chicago, where he wrote ''La voix d'un exilé''. A number of plays which he wrote during that period were lost in the Great Chicago Fire. Fréchette retur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manitou
Manitou () is the fundamental life force in the theologies of Algonquian peoples. It is said to be omnipresent and manifests everywhere: organisms, the environment, events, etc. ''Aashaa monetoo'' means "good spirit", while ''otshee monetoo'' means "bad spirit". When Turtle Island was created, the Great Spirit, ''Aasha Monetoo'', gave the land to the indigenous peoples. Overview Manitou was widely used during early European contact. In 1585, when Thomas Harriot recorded the first glossary of an Algonquian language, Roanoke (Pamlico), he included the word ''mantóac'', meaning "gods and goddesses". Similar terms are found in nearly all Algonquian languages. In some Algonquian traditions, '' Gitche Manitou'' refers to a supreme being. The term has analogues dating to before European contact, and the word uses of ''gitche'' and ''manitou'' existed before contact. After contact, however, Gitche Manitou was adopted by some Anishinaabe, such as the Ojibwe, to refer to the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
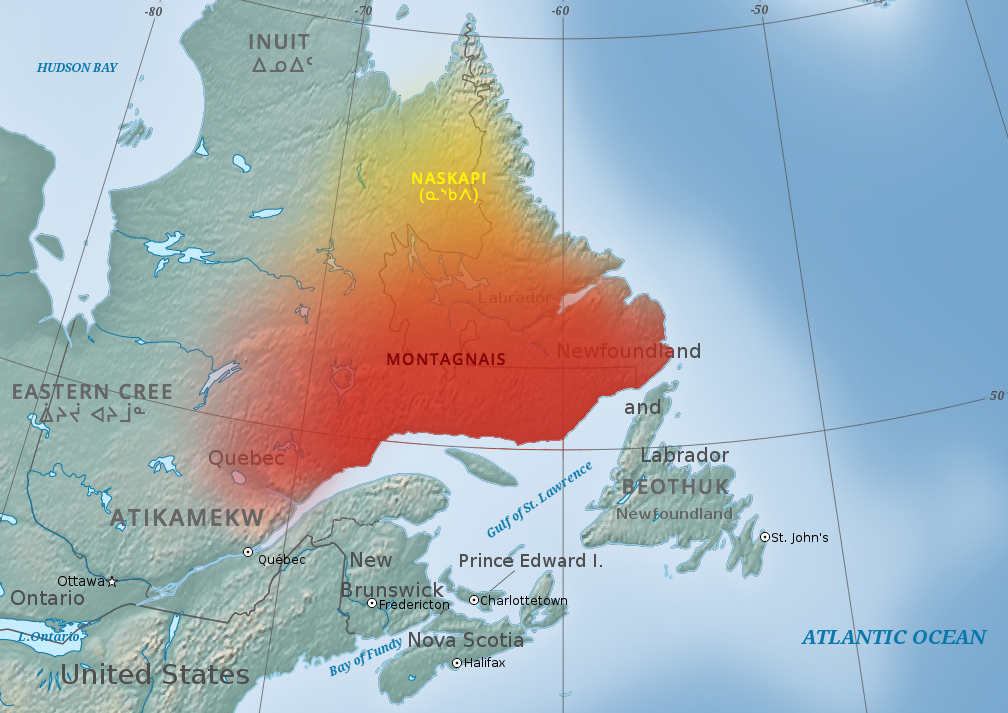
Innu
The Innu/Ilnu ('man, person'), formerly called Montagnais (French for ' mountain people'; ), are the Indigenous Canadians who inhabit northeastern Labrador in present-day Newfoundland and Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to their traditional homeland as ''Nitassinan'' ('Our Land', ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) or ''Innu-assi'' ('Innu Land'). The ancestors of the modern First Nations were known to have lived on these lands as hunter-gatherers for many thousands of years. To support their seasonal hunting migrations, they created portable tents made of animal skins. Their subsistence activities were historically centred on hunting and trapping caribou, moose, deer, and small game. Their language, which changed over time from Old Montagnais to Innu-aimun (popularly known since the French colonial era as Montagnais), is spoken throughout Nitassinan, with certain dialect differences. It is part of the Cree–Montagnais– Naskapi dialect continuum, and is unrelated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap Trinite BAnQ P560S1P668
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. The origin of the word "cap" comes from the Old French word "chapeau" which means "head covering". Over time, the word has evolved and changed its meaning, but it still retains its association with headwear. Caps typically have a visor, or no brim at all. They are popular in casual and informal settings, and are seen in sports and fashion. They are typically designed for warmth, and often incorporate a visor to block sunlight from the eyes. They come in many shapes, sizes, and are of different brands. Baseball caps are one of the most common types of cap. Types * Ascot cap * Ayam * Baggy green * Balmoral * Beanie (North America) * Bearskin * Beret * Biretta * Busby * Canterbury cap * Cap and bells * Cap of maintenance * Casquette * Caubeen * Caul * Coif * Combination cap (also known as a service cap) * Coppola * Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statue Of Notre-Dame-du-Saguenay
The statue of Notre-Dame-du-Saguenay is a statue located on Cap Trinité, at the mouth of Baie Trinité, near the village of Rivière-Éternité, Quebec, Rivière-Éternité, and the river Saguenay River, in Le Fjord-du-Saguenay Regional County Municipality, in the province of Quebec, in Canada. History This statue was sculpted by in 1881. It is made entirely of pinus strobus, white pine and is covered with thin sheets of lead to protect it from the elements. It measures 9 meters high and weighs over 3 tonnes. Legend The statue of Notre-Dame-du-Saguenay was sculpted in honor of after the misadventures of "Charles-Napoléon Robitaille", a traveling salesman who, to go to Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean, Saguenay, absolutely had to take the rivers. One winter day when he was heading towards Lac Saint-Jean, the ice broke under his feet and he fell into the water; he struggled but in vain. As a last resort, he asked the Blessed Virgin to come and save him. He was miraculously strande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast and a coastal border with the territory of Nunavut. In the south, it shares a border with the United States. Between 1534 and 1763, what is now Quebec was the List of French possessions and colonies, French colony of ''Canada (New France), Canada'' and was the most developed colony in New France. Following the Seven Years' War, ''Canada'' became a Territorial evolution of the British Empire#List of territories that were once a part of the British Empire, British colony, first as the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), Province of Quebec (1763–1791), then Lower Canada (1791–1841), and lastly part of the Province of Canada (1841–1867) as a result of the Lower Canada Rebellion. It was Canadian Confederation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saguenay Fjord National Park
Saguenay Fjord National Park () is a provincial park located in Quebec, Canada. In the regions of Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean, Charlevoix, Côte-Nord, and Bas-Saint-Laurent, the park is situated along the eastern end of the Saguenay River and adjoins the Saguenay–St. Lawrence Marine Park for over 100 km (60 mi.). The park, originally named Saguenay National Park, was renamed on April 20, 2011.Le parc national du Saguenay devient le parc national du Fjord-du-Saguenay Ministère du Développement durable, de l’Environnement et des Parcs. Retrieved 11 May 2012. History Aboriginals, including[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |