|
Cante Flamenco
The cante flamenco (), meaning "flamenco singing", is one of the three main components of flamenco, along with ''toque'' (playing the guitar) and ''baile'' (dance). Because the dancer is front and center in a flamenco performance, foreigners often assume the dance is the most important aspect of the art form — in fact, it is the ''cante'' which is the heart and soul of the genre. A ''cante'' singer is a ''cantaor'' or ''cantaora''. The cante flamenco is part of musical tradition in the Andalusian region of Spain. Its origins are uncertain but scholars see many influences in the cante flamenco including: The traditional song of the gitanos (Spanish Gypsies), the Perso-Arab Zyriab song form, the classical Andalusian orchestras of the Islamic Empire, the Jewish synagogue chants, Mozarabic forms such as zarchyas and zambra, Arabic zayal (the foundation for the Fandango), and Andalusian regional folk forms, as well as West African and South American influences as seen in the '' cant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flamenco
Flamenco (), in its strictest sense, is an art form based on the various folkloric music traditions of southern Spain, developed within the gitano subculture of the region of Andalusia, and also having historical presence in Extremadura and Murcia. In a wider sense, it is a portmanteau term used to refer to a variety of both contemporary and traditional musical styles typical of southern Spain. Flamenco is closely associated to the gitanos of the Romani ethnicity who have contributed significantly to its origination and professionalization. However, its style is uniquely Andalusian and flamenco artists have historically included Spaniards of both gitano and non-gitano heritage. The oldest record of flamenco music dates to 1774 in the book ''Las Cartas Marruecas'' by José Cadalso. The development of flamenco over the past two centuries is well documented: "the theatre movement of sainetes (one-act plays) and tonadillas, popular song books and song sheets, customs, studies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Tenazas
EL, El or el may refer to: Religion * El (deity), a Semitic word for "God" People * EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer * El DeBarge, music artist * El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American politician * Ephrat Livni (born 1972), American street artist Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * El, short for Eleven, a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in ''Superman'' *E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film ''Road Trip'' Literature * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 2000 Japanese adult visual novel Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él'' (Lucero album), a 1982 album by Lucero * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from ''Caminando'' (album) * "Él" (Luc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alegrías
''Alegrías'' () is a flamenco palo or musical form, which has a rhythm consisting of 12 beats. It is similar to Soleares. Its beat emphasis is as follows: 1 2 '' 4 5 '' 7 '' 9 0'' 11 2''. Alegrías originated in Cádiz. Alegrías belongs to the group of ''palos'' called Cantiñas and it is usually played in a lively rhythm (120-170 beats per minute). The livelier speeds are chosen for dancing, while quieter rhythms are preferred for the song alone. One of the structurally strictest forms of flamenco, a traditional dance in alegrías must contain each of the following sections: a salida (entrance), paseo (walkaround), silencio (similar to an adagio in ballet), castellana (upbeat section) zapateado (literally "a tap of the foot") and bulerías. This structure though, is not followed when alegrías are sung as a standalone song (with no dancing). In that case, the stanzas are combined freely, sometimes together with other types of cantiñas. Recommended listenings for this '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caló Language
Caló (; ; ; ) is a language spoken by the Spanish and Portuguese Romani. It is a mixed language (referred to as a Para-Romani language in Romani linguistics) based on Romance grammar, with an adstratum of Romani lexical items through language shift by the Romani community. It is often used as an argot, a secret language for discreet communication amongst Iberian Romani. Catalan, Galician, Portuguese, and Spanish are closely related varieties that share a common root.Adiego, I. ''Un vocabulario español-gitano del Marqués de Sentmenat (1697–1762)'' Ediciones Universitat de Barcelona (2002) Spanish caló, or Spanish Romani, was originally known as . Portuguese , or Portuguese Romani, also goes by the term ; it used to be referred to as , but this word has since acquired the general sense of jargon or slang, often with a negative undertone (cf. , 'obscene language', lit. low-level ). The language is mainly spoken in Brazil, Spain, France, Portugal and Colombia. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duende (art)
''Duende'' or ''tener duende'' ("to have duende") is a Spanish term for a heightened state of emotion, expression and authenticity, often connected with flamenco.Maurer (1998) pp. viii Originating from folkloric Andalusian vocal music (''canto jondo)'' and first theorized and enhanced by Andalusian poet Federico García Lorca, the term derives from "dueño de casa" (master of the house), which similarly inspired the ''duende'' of folklore. Origins of the term ''El duende'' has been defined as the spirit of evocation, "a state of tragedy-inspired ecstasy," "a poetic emotion which is uncontrolled." It comes from inside as a physical/emotional response to art. It is what gives you chills, makes you smile or cry as a bodily reaction to an artistic performance that is particularly expressive. Folk music in general, especially flamenco, tends to embody an authenticity that comes from a people whose culture is enriched by diaspora and hardship; vox populi, the human condition of joys and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copla (meter)
The ''copla'' is a poetic form of four verses found in many Spain, Spanish popular songs as well as in Spanish language literature. There is a copla (music), related musical genre of the same name. The form is also found widely in Latin America. The name derives from the Latin language, Latin ''copula'', ("link" or "union"). ''Coplas'' normally consist of four verses ''de arte menor'' (that is, of no more than eight syllables to a line) of four lines each, either of Spain's most characteristic popular meter, the romance (meter), romance (8- 8a 8- 8a), or of seguidilla (7- 5a 7- 5a) or redondilla (8a 8b 8b 8a). Although most commonly considered a popular form, it has not been scorned by cultivated writers. Among those who have written ''coplas'' are Íñigo López de Mendoza, Marquis of Santillana, Rafael Alberti, Luis de Góngora, Antonio Machado, Jorge Manrique and Federico García Lorca. Manuel Machado (poet and playwright), Manuel Machado wrote of ''coplas'', using the form him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soleá
''Soleares'' (plural of ''soleá'', ) is one of the most basic forms or '' palos'' of Flamenco music, probably originating among the Calé Romani people of Cádiz or Seville in Andalusia, the most southern region of Spain. It is usually accompanied by one guitar only, in phrygian mode "''por arriba''" (fundamental on the 6th string); "'' Bulerías por soleá''" is usually played "''por medio''" (fundamental on the 5th string). Soleares is sometimes called "mother of palos" although it is not the oldest one (e.g. siguiriyas is older than soleares) and not even related to every other palo (e.g. fandangos family is from a different origin) Lyrics When singers sing soleá, as with most palos, they normally choose different "''coplas''" (stanzas), with different melody, and combine them according to the inspiration of the moment or to a previous plan. Even if the singer has a previous plan, it is often altered on the spur of the moment. These stanzas are independent in subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seguiriya
''Siguiriyas'' (; also ''seguiriyas'', ''siguerillas'', ''siguirillas'', ''seguidilla gitana'', etc.) are a form of flamenco music in the cante jondo category. This deep, expressive style is among the most important in flamenco. Unlike other palos of flamenco, siguiriyas stands out for being purely Romani (Calé) in origin. Siguiriyas are normally played in the key of A Phrygian with each measure (the compás) consisting of 12 counts with emphasis on the 1st, 3rd, 5th, 8th and 11th beats as shown here: : : '' 2 '' 4 '' 6 7 '' 9 10 1'' 12 This rhythm can be contrasted with the rhythmic pattern of the soleares, which also has 12 beats, but the accents fall differently. Taking the unusual accenting into account, it can technically be seen as a measure of 3/4 (counted in eighth notes) starting on "2", then a measure of 6/8 followed by the "1 and" of the 3/4. Every note is evenly spaced apart. For example: : : '' and '' and '' 2 3 '' 5 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinetes
''Martinetes'' (, sing. ''martinete'') are a flamenco ''palo'' belonging to the group of the ''tonás'' or ''cantes a palo seco''. As the rest of the songs in this group, it is sung with no accompaniment. In some dance shows for the stage, though, it is accompanied by percussion played with the compás of siguiriya. The percussion instruments chosen for this are frequently a hammer and anvil, to evocate the origins of this ''palo'', attributed to Gypsy smiths. It is not probable, though, that they were real work songs: they demand too much effort and faculties to be sung while carrying out a heavy task like that of a smith. They were more probably sung in family gatherings. Although martinetes are often classified under the toná group on the grounds that they share its a cappella nature, the melody types differ strongly from the rest of tonás, so it is now generally considered to be a different ''palo''. A characteristic that differentiates them from the tonás, normally in majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
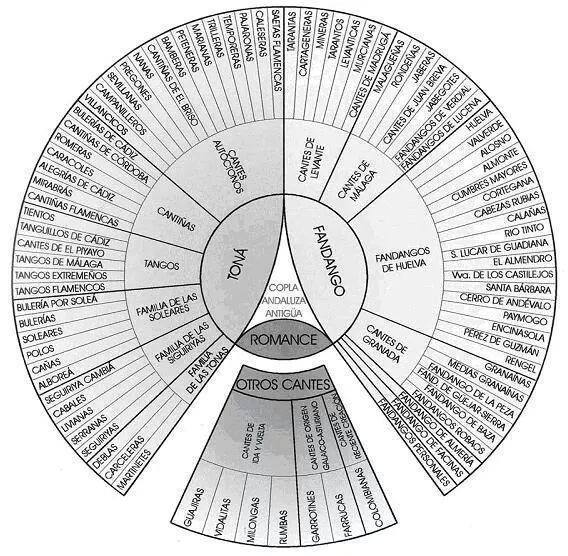
Tonás
Tonás () is a palo or type of flamenco songs. It belongs to the wider category of Cantes a palo seco, ''palos'' that are sung a cappella. Owing to this feature, they are considered by traditional flamencology to be the oldest surviving musical form of flamenco. This musical form originated in the Calé Romani subculture of Southern Spain. The first known flamenco singer, Tío Luis el de la Juliana, who lived in Jerez de la Frontera in the last third of the 18th century, was said to have excelled in this ''palo''. Other ''cantes a palo seco'', such as martinetes and debla, are sometimes classified under ''tonás'', while at other times they are referred to as ''palos'' on their own. The ''tonás'' were almost in disuse by the end of the 19th century. The reason seems to be that they were considered a difficult style by the general public, and resulted in Tonás on the near verge of disappearing. During the 1950s the tonás came back into use, with singers like Antonio Mairena, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cante Flamenco
The cante flamenco (), meaning "flamenco singing", is one of the three main components of flamenco, along with ''toque'' (playing the guitar) and ''baile'' (dance). Because the dancer is front and center in a flamenco performance, foreigners often assume the dance is the most important aspect of the art form — in fact, it is the ''cante'' which is the heart and soul of the genre. A ''cante'' singer is a ''cantaor'' or ''cantaora''. The cante flamenco is part of musical tradition in the Andalusian region of Spain. Its origins are uncertain but scholars see many influences in the cante flamenco including: The traditional song of the gitanos (Spanish Gypsies), the Perso-Arab Zyriab song form, the classical Andalusian orchestras of the Islamic Empire, the Jewish synagogue chants, Mozarabic forms such as zarchyas and zambra, Arabic zayal (the foundation for the Fandango), and Andalusian regional folk forms, as well as West African and South American influences as seen in the '' cant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cante Jondo
''Cante jondo'' (Andalusian ) is a vocal style in flamenco, an unspoiled form of Andalusian folk music. The name means "deep song" in Spanish, with ''hondo'' ("deep") spelled with J () as a form of eye dialect, because traditional Andalusian pronunciation has retained an aspirated H lost in other forms of Spanish. It is generally considered that the common traditional classification of flamenco music is divided into three groups of which the deepest, most serious forms are known as ''cante jondo''. Cultural references to ''cante jondo'' In 1922 the Spanish composer Manuel de Falla led in the organization of the Concurso de Cante Jondo for Granada. Many classical musicians, cultural and literary figures, including the young poet Federico García Lorca, participated in the program. The result was the memorable series of flamenco performances held at the Alhambra during June. Lorca had evidently used the title ' for a 1921 collection of poems, although he did not publish it fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

