|
Candace Hartley
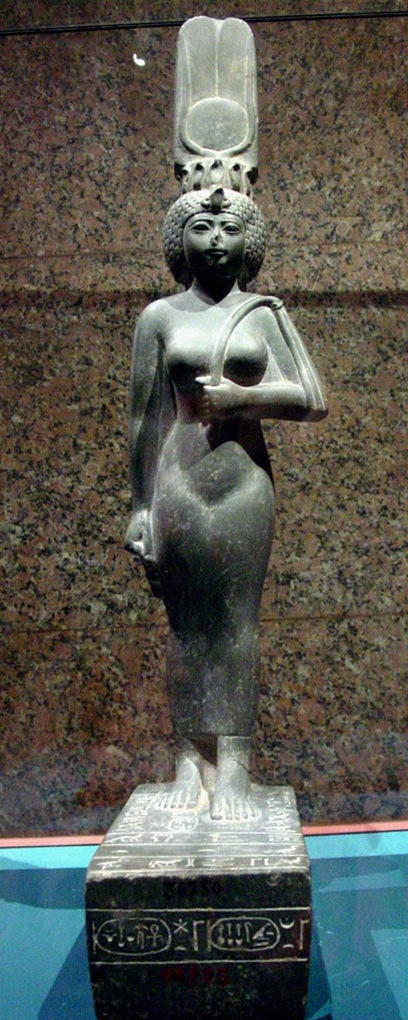
Kandake, kadake or kentake ( Meroitic: 𐦲𐦷𐦲𐦡 ''kdke''),Kirsty Rowan"Revising the Sound Value of Meroitic D: A Phonological Approach,"''Beitrage zur Sudanforschung'' 10 (2009). often Latinised as Candace ( grc, Κανδάκη, ''Kandakē''), was the Meroitic term for the sister of the king of Kush who, due to the matrilineal succession, would bear the next heir, making her a queen mother. She had her own court, probably acted as a landholder and held a prominent secular role as regent. Contemporary Greek and Roman sources treated it, incorrectly, as a name. The name Candace is derived from the way the word is used in the New Testament (). Archaeological sources The Kandakes of Meroe were first described through the Greek geographer's Strabo account of the "one-eyed Candace" in 23 BCE in his encyclopedia Geographica. '' ''There are at least ten regnant Meroitic queens during the 500 years between 260 BCE and 320 CE, and at least six during the 140 periods between 60 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qalhata
Qalhata was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton: The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson, 2004, , p.234-240 Qalhata was a daughter of King Piye and a queen consort to her brother Shabaka. She is known from the Dream Stela of King Tantamani and from her pyramid in El-Kurru (Ku. 5). Assyrian records state that King Tantamani was the son of Taharqa Taharqa, also spelled Taharka or Taharqo (Egyptian: 𓇿𓉔𓃭𓈎 ''tꜣ-h-rw-k'', Akkadian: ''Tar-qu-u2'', , Manetho's ''Tarakos'', Strabo's ''Tearco''), was a pharaoh of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt and qore (king) of the Kingdom of ...'s sister. The tomb of Qalhata at El-Kurru contains texts that say she is a King's Mother, giving some evidence of the family relationships.R. Morkot: The Black Pharaohs, Egypt's Nubian Rulers, London 2000, pg 205 References 8th-century BC Egyptian women Queens consort of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt 8th-cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ezana Of Axum
Ezana ( gez, ዔዛና ''‘Ezana'', unvocalized ዐዘነ ''‘zn''; also spelled Aezana or Aizan) was ruler of the Kingdom of Axum, an ancient kingdom located in what is now Eritrea and Ethiopia. (320s – c. 360 AD). He himself employed the style (official title) "king of Saba and Salhen, Himyar and Dhu-Raydan". Tradition states that ‘Ezana succeeded his father Ella Amida (Ousanas) as king while still a child but his mother, Sofya then served as regent until he came of age. He conquered the Kingdom of Kush around the year 350 AD. Reign Ezana was the first monarch of the Kingdom of Aksum to embrace Christianity, after he was converted by his slave-teacher, Frumentius. He was the first monarch after Za Haqala (possibly Zoskales) to be mentioned by contemporary historians, a situation that lead S. C. Munro-Hay to comment that he was "the most famous of the Aksumite kings before Kaleb." In early life he considered himself a son of Mars, but later inscriptions show a growing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Eunuch
The Ethiopian eunuch ( gez, ኢትዮጵያዊው ጃንደረባ) is a figure in the New Testament of the Bible; the story of his conversion to Christianity is recounted in Acts 8. Biblical narrative Philip the Evangelist was told by an angel to go to the road from Jerusalem to Gaza, and there he encountered the Ethiopian eunuch, the treasurer of the Candace, Queen of the Ethiopians (Ancient Greek: Κανδάκη, the "Candace" was the Meroitic language term for "queen" or possibly "royal woman"). The eunuch had been to Jerusalem to worship and was returning home. Sitting in his chariot, he was reading the Book of Isaiah, specifically . Philip asked the Ethiopian, "Do you understand what you are reading?" He said he did not ("How can I understand unless I have a teacher to teach me?"), and asked Philip to explain the text to him. Philip told him the Gospel of Jesus, and the Ethiopian asked to be baptized. They went down into a water source, traditionally thought to be the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Legendary Monarchs Of Ethiopia
This is a list of legendary monarchs of Ethiopia, based on a king list provided by Ethiopian prince regent Tafari Makonnen (later known as Emperor Haile Selassie), with reference to multiple Ethiopian traditions and legends. Other Ethiopian king lists are discussed in the Other King Lists section. Over Ethiopia's long history, multiple kingdoms and states have ruled, with one of the earliest known being Dʿmt from the 10th century BC. The last royal dynasty of Ethiopia was the Solomonic dynasty, who ruled until 1975 when the monarchy was abolished. Numerous king lists are in existence which chronicle the lineage of kings before the Solomonic dynasty, but often with noticeable disagreements between them. An official chronicle of the kings of Ethiopia from the royal family was published in Charles Fernand Rey's book ''In the Country of the Blue Nile'' in 1927, and is the longest Ethiopian king list published in the Western world. However, there is considerable debate on the historici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haile Selassie
Haile Selassie I ( gez, ቀዳማዊ ኀይለ ሥላሴ, Qädamawi Häylä Səllasé, ; born Tafari Makonnen; 23 July 189227 August 1975) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as Regent Plenipotentiary of Ethiopia (''Enderase'') for Empress Zewditu from 1916. Haile Selassie is widely considered a defining figure in modern Ethiopian history, and the key figure of Rastafari, a religious movement in Jamaica that emerged shortly after he became emperor in the 1930s. He was a member of the Solomonic dynasty, which claims to trace lineage to Emperor Menelik I, believed to be the son of King Solomon and Makeda the Queen of Sheba. Haile Selassie attempted to modernize the country through a series of political and social reforms, including the introduction of the 1931 constitution, its first written constitution, and the abolition of slavery. He led the failed efforts to defend Ethiopia during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War and spent most of the period of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelik I
Menelik I ( Ge'ez: ምኒልክ) was the claimed first Emperor of Ethiopia. According to Kebra Nagast, a 14th-century national epic, in the 10th century BC he is said to have inaugurated the Solomonic dynasty of Ethiopia, so named because Menelik I was the son of the biblical King Solomon of ancient Israel and of Makeda, the Queen of Sheba. Life According to the medieval Ethiopian book, the ''Kebra Nagast,'' translated into Geʽez in 1321 CE, his name was ''Bäynä Ləḥkəm'' (from ar, ابن الحكيم, , "So''n of the Wise."'')''.'' He was conceived when his father Solomon tricked his visiting mother, the Queen of Sheba, into sleeping with him. His mother raised him as a Jew in her homeland and he only traveled to Jerusalem to meet his father for the first time when he was in his twenties. While his father begged Menelik to stay and rule over Israel, Menelik told him that he wanted to return home. Thus, Solomon sent many Israelites with him, to aid him in ruling accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanakdakheto
Shanakhdakheto or Shanakdakhete was a Queen of the Kingdom of Kush, when the polity was centered at Meroë, an ancient city in north Sudan. She is the earliest known ruling African queen of ancient Nubia, and reigned from c. 170–150 BC, although the period 170–160 BC is also mentioned. She is said to have ruled with absolute power in the Meroë Empire. She is also said to have ruled without a king. It is also stated that as queen she played a significant role in the Meroitic religion. In the 2nd century BC, Shanakdakheto built the Temple F at Naqa, which has an unusual feature in the first half of the temple with the interior partitions where the gods face the back wall. Overview Shanakdakheto's name is inscribed as a royal queen in the Egyptian Meroitic hieroglyphs. This inscription is the one seen on the doorjambs of the altar niche of Temple F in Naqa. Shanakdakheto styled herself as: ''Son of Re, Lord of the Two Lands, Shanakdakheto'' (Sa Re nebtawy, Shanakdakheto).Lász ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God's Wife Of Amun
God's Wife of Amun (Egyptian: ''ḥm.t nṯr n ỉmn'') was the highest-ranking priestess of the Amun cult, an important religious institution in ancient Egypt. The cult was centered in Thebes in Upper Egypt during the Twenty-fifth and Twenty-sixth dynasties (circa 740–525 BC). The office had political importance as well as religious, since the two were closely related in ancient Egypt. Although the title is first attested in the Middle Kingdom, its full political potential was not realized until the advent of the Eighteenth Dynasty. History of the office nTr-N41:X1 The shorter version of the title, God's Wife, is in use by the time of the Twelfth Dynasty, when the title is attested for the non-royal women Iy-meret-nebes and Neferu.Mariam F. Ayad (2009), ''God’s Wife, God’s Servant''. As early as the First Intermediate Period, there is mention of A "Wife of the God" in reference to the god Min. The full title of God's Wife of Amun is only used during and after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. Stelae were created for many reasons. Grave stelae were used for funerary or commemorative purposes. Stelae as slabs of stone would also be used as ancient Greek and Roman government notices or as boundary markers to mark borders or property lines. Stelae were occasionally erected as memorials to battles. For example, along with other memorials, there are more than half-a-dozen steles erected on the battlefield of Waterloo at the locations of notable actions by participants in battle. A traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nastasen
Nastasen was a king of Kush (335 – 315/310 BC). According to a stela from Dongola his mother was named Queen Pelkha and his father may have been King Harsiotef. His successor was Aryamani. He is known from three types of objects. There is a stela with a long historical inscription, a silver handle of a mirror and several ''shabti''-figures. The mirror handle and the ''shabti'' were found in a pyramid at Nuri (Nu. 15), which was obviously his burial place. He was the last Kushite king to be buried in the royal cemetery at Napata. The 1.63 m high granite stela was found at New Dongola and is now in the Berlin Museum Inv. no. 2268. Originally it was most likely placed in the Amun temple of Jebel Barkal. In the upper part appear the pictures and name of his mother, Pelkha and his wife, Sekhmakh, next to the king. The tomb of Nastasen is among several in Nuri that are slated for excavation by archaeologists using underwater archaeological methods. That is necessary because of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harsiotef
Harsiotef was a Kushite King of Meroe (about 404 – 369 BC). Harsiotef took on a full set of titles based on those of the Egyptian Pharaohs: ''Horus name:'' Kanakht Khaemnepet ("Mighty Bull appears in Napata") ''Nebty Name:'' Nednetjeru ("Who seeks the council of Gods") ''Golden Horus Name:'' Uftikhesutnebut ("Subduer given all the Desert Lands") ''Prenomen:'' Sameryamun ("Beloved son of Amun") ''Nomen:'' Harsiotef ("Horus Son of his Father") Harsiotef was the son of Queen Atasamale and likely of King Amanineteyerike. He had a wife named Queen Batahaliye and may have had another wife named Queen Pelkha. If Queen Pelkha was his wife, he would also be the father of King Nastasen. It is possible that King Akhraten was also a son of Harsiotef, and Queen Sakhmakh, the wife of Nastasen, may be his daughter. He left an inscription dated to his thirty-third regnal year, listing the battles from his successful campaign east of his kingdom against a town called ''Habasa'', whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)