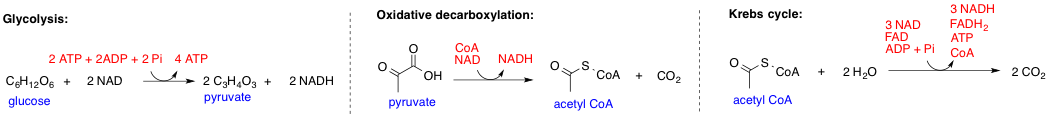|
Cancer Genetics
Oncogenomics is a sub-field of genomics that characterizes cancer-associated genes. It focuses on genomic, epigenomic and transcript alterations in cancer. Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of DNA mutations and epigenetic alterations leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment. Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiate or drive cancer progression, oncogenomics targets personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to DNA mutations and epigenetic alterations that accumulate randomly. Identifying and targeting the mutations in an individual patient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dimensional structural configuration. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of ''individual'' genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of ''all'' of an organism's genes, their interrelations and influence on the organism. Genes may direct the production of proteins with the assistance of enzymes and messenger molecules. In turn, proteins make up body structures such as organs and tissues as well as control chemical reactions and carry signals between cells. Genomics also involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes through uses of high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. Advances in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Genome Sequencing
Cancer genome sequencing is the whole genome sequencing of a single, homogeneous or heterogeneous group of cancer cells. It is a biochemical laboratory method for the characterization and identification of the DNA or RNA sequences of cancer cell(s). Unlike whole genome (WG) sequencing which is typically from blood cells, such as J. Craig Venter's and James D. Watson’s WG sequencing projects, saliva, epithelial cells or bone - cancer genome sequencing involves direct sequencing of primary tumor tissue, adjacent or distal normal tissue, the tumor micro environment such as fibroblast/stromal cells, or metastatic tumor sites. Similar to whole genome sequencing, the information generated from this technique include: identification of nucleotide bases (DNA or RNA), copy number and sequence variants, mutation status, and structural changes such as chromosomal translocations and fusion genes. Cancer genome sequencing is not limited to WG sequencing and can also include exome, transcript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Everolimus
Everolimus, sold under the brand name Afinitor among others, is a medication used as an immunosuppressant to prevent rejection of organ transplants and as a targeted therapy in the treatment of renal cell cancer and other tumours. It is the 40-''O''-(2-hydroxyethyl) derivative of sirolimus and works similarly to sirolimus as an inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). It is marketed by Novartis under the trade names Zortress (US) and Certican (European Union and other countries) in transplantation medicine, and as Afinitor (general tumours) and Votubia (tumours as a result of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)) in oncology. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. Medical uses Everolimus is approved for various conditions: * Advanced kidney cancer (US FDA approved in March 2009) * Prevention of organ rejection after renal transplant(US FDA April 2010) * Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPR124
Probable G-protein coupled receptor 124 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPR124'' gene. It is a member of the adhesion-GPCR family of receptors. Family members are characterized by an extended extracellular region with a variable number of protein domains coupled to a TM7 domain via a domain known as the GPCR-Autoproteolysis INducing (GAIN) domain. Interactions GPR124 has been shown to interact with DLG1 Discs large homolog 1 (DLG1), also known as synapse-associated protein 97 or SAP97, is a scaffold protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SAP97'' gene. SAP97 is a mammalian MAGUK-family member protein that is similar to the Drosophila protein ... and is involved in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway along with RECK. Zebrafish embryos with Gpr124 loss of function demonstrate severe angiogenic deficiencies in the central nervous system. References Further reading * * * * * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. In most cases of a metabolic pathway, the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the next. However, side products are considered waste and removed from the cell. These enzymes often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors to function. Different metabolic pathways function based on the position within a eukaryotic cell and the significance of the pathway in the given compartment of the cell. For instance, the, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation all take place in the mitochondrial membrane. In contrast, glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, and fatty acid biosynthesis all occur in the cytosol of a cell. There are two types of metabolic pathways that are character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC5A1
Sodium/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) also known as solute carrier family 5 member 1 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the gene which encodes the production of the SGLT1 protein to line the Intestinal absorptive cells, absorptive cells in the small intestine and the epithelial cells of the kidney tubules of the nephron for the purpose of glucose uptake into cells. Through the use of the sodium glucose cotransporter 1 protein, cells are able to obtain glucose which is further utilized to make and store energy for the cell. Structure The sodium glucose cotransporter 1 is classified as an integral membrane protein that is made up of 14 alpha-helices constructed from the folding of 482-718 amino acid residues with both the N-terminal, N and C-terminal residing upon the extracellular side of the plasma membrane. It is hypothesized that the protein contains protein kinase A and protein kinase C phosphorylation sites, which serve to regulate the proteins conformational shape t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCLKC
Protocadherin-24 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PCDH24'' gene. Interactions PCLKC has been shown to interact with MAST2 Microtubule-associated serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAST2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene controls TRAF6 and NF-kappaB activity. Interactions MAST2 has been shown to interact with .... References Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-5-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTPRT
Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase T is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTPRT'' gene. PTPRT is also known as PTPrho, PTPρ and human accelerated region 9. The human accelerated regions are 49 regions of the human genome that are conserved among vertebrates, but in humans show significant distinction from other vertebrates. This region may, therefore, have played a key role in differentiating humans from apes. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. PTPrho has been proposed to function during development of the nervous system and as a tumor suppressor in cancer. Structure This PTP possesses an extracellular region, a single transmembrane region, and two tandem intracellular catalytic domains, and thus represents a recept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPM1
Nucleophosmin (NPM), also known as nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 or numatrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NPM1'' gene. Function NPM1 is associated with nucleolar ribonucleoprotein structures and binds single-stranded and double-stranded nucleic acids, but it binds preferentially G-quadruplex forming nucleic acids. It is involved in the biogenesis of ribosomes and may assist small basic proteins in their transport to the nucleolus. Its regulation through SUMOylation (by SENP3 and SENP5) is another facet of the protein's regulation and cellular functions. It is located in the nucleolus, but it can be translocated to the nucleoplasm in case of serum starvation or treatment with anticancer drugs. The protein is phosphorylated. Nucleophosmin has multiple functions: # Histone chaperones # Ribosome biogenesis and transport # Genomic stability and DNA repair # Endoribonuclease activity # Centrosome duplication during cell cycle # Regulation of ARF-p53 tumor supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
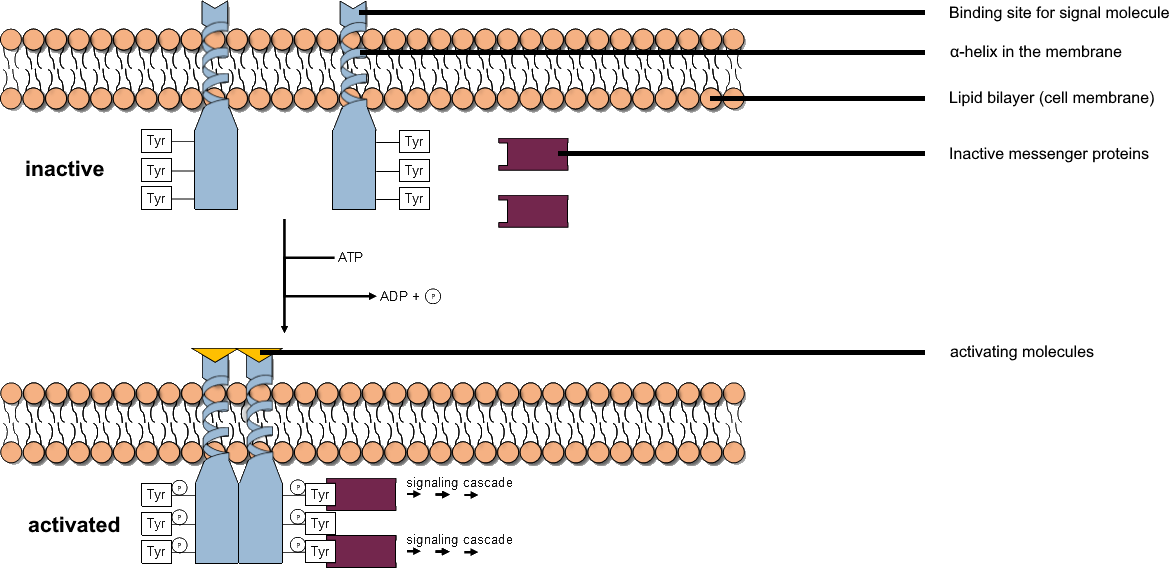
Tyrosine Kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger class of enzymes known as protein kinases which also attach phosphates to other amino acids such as serine and threonine. Phosphorylation of proteins by kinases is an important mechanism for communicating signals within a cell (signal transduction) and regulating cellular activity, such as cell division. Protein kinases can become mutated, stuck in the "on" position, and cause unregulated growth of the cell, which is a necessary step for the development of cancer. Therefore, kinase inhibitors, such as imatinib and osimertinib, are often effective cancer treatments. Most tyrosine kinases have an associated protein tyrosine phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group. Reaction Protein kinases are a group of enzymes that possess a catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLT3
Cluster of differentiation antigen 135 (CD135) also known as fms like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT-3), receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3, or fetal liver kinase-2 (Flk2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FLT3'' gene. FLT3 is a cytokine receptor which belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinase class III. CD135 is the receptor for the cytokine Flt3 ligand (FLT3L). It is expressed on the surface of many hematopoietic progenitor cells. Signalling of FLT3 is important for the normal development of haematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells. The FLT3 gene is one of the most frequently mutated genes in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). High levels of wild-type FLT3 have been reported for blast cells of some AML patients without FLT3 mutations. These high levels may be associated with worse prognosis. Structure FLT3 is composed of five extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains, an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, a juxtamembrane domain and a tyrosine-kinase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a drop in red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific blood tests. AML has several subtypes for which treatments and outcomes may vary. The fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |