|
Calyx (zoology)
Calyx is a term used in animal anatomy for some cuplike areas or structures. Etymology Latin, from ''calyx'' (from Ancient Greek ''κάλυξ, ''case of a bud, husk"). Cnidarians The spicules containing the basal portion of the upper tentacular part of the polyp of some soft corals (also called ''calice''). Entoprocta A body part of the Entoprocta from which tentacles arise and the mouth and anus are located. Echinoderms The body disk that is covered with a leathery tegumen containing calcareous plates (in crinoids and ophiuroids the main part of the body where the viscera are located). Humans Either a minor calyx in the kidney, a conglomeration of two or three minor calyces to form a major calyx, or the Calyx of Held, a particularly large synapse in the mammalian auditory central nervous system, named by H. Held in his 1893 article ''Die centrale Gehörleitung'', due to its flower-petal-like shape. Satzler, K., L. F. Sohl, et al. (2002). "Three-dimensional reconstruction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from one neuron to another. Neurons are specialized to pass signals to individual target cells, and synapses are the means by which they do so. At a synapse, the plasma membrane of the signal-passing neuron (the ''presynaptic'' neuron) comes into close apposition with the membrane of the target (''postsynaptic'') cell. Both the presynaptic and postsynaptic sites contain extensive arrays of molecular machinery that link the two membranes together and carry out the signaling process. In many synapses, the presynaptic part is located on an axon and the postsynaptic part is located on a dendrite or soma. Astrocytes also exchange information with the synaptic neurons, responding to synaptic activity and, in turn, regulating neurotransmission. Syna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidarian Anatomy
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter. Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that they use mainly for capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming medusae and sessile polyps, both of which are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. Both forms have a single orifice and body cavity that are used for digestion and respiration. Many cnidarian species produce colonies that are single organisms composed of medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both (hence they are trimorphic). Cnidarians' activities are coordinated by a decentralized nerve net and simple receptors. Several free-swimming species of Cubozoa and Scyphozoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovariole
An ovariole is a tubular component of the insect ovary, and the basic unit of egg production. Each ovariole is composed of a germarium (the germline stem cell niche) at the anterior tip, a set of developing oocytes contained within follicles, and a posterior connection to a common oviduct. While most insects have two ovaries, the number of ovarioles within each ovary varies across insect species. This number may also be variable across individuals within a species, or between the left and right ovaries within an individual. Types Ovarioles are often classified into one of several types by the presence and position of nurse cells. These specialized cells provide nutrition and molecules important for embryonic patterning to the developing oocyte. Ovarioles that lack nurse cells are referred to as ''panoistic'' and ovarioles with nurse cells are referred to as ''meroistic''. Meroistic ovarioles are further classified according to where nurse cells are located. In ''polytrophic m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviduct
The oviduct in mammals, is the passageway from an ovary. In human females this is more usually known as the Fallopian tube or uterine tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will degenerate in the body. Normally, these are paired structures, but in birds and some cartilaginous fishes, one or the other side fails to develop (together with the corresponding ovary), and only one functional oviduct can be found. Except in teleosts, the oviduct is not directly in contact with the ovary. Instead, the most anterior portion ends in a funnel-shaped structure called the infundibulum, which collects eggs as they are released by the ovary into the body cavity. The only female vertebrates to lack oviducts are the jawless fishes. In these species, the single fused ovary releases eggs directly into the body cavity. The fish eventually extrudes the eggs through a small genital pore towards the rear of the body. Fish and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Pedunculatum
Corpus is Latin for "body". It may refer to: Linguistics * Text corpus, in linguistics, a large and structured set of texts * Speech corpus, in linguistics, a large set of speech audio files * Corpus linguistics, a branch of linguistics Music * ''Corpus'' (album), by Sebastian Santa Maria * Corpus Delicti (band), also known simply as Corpus Medicine * Corpus callosum, a structure in the brain * Corpus cavernosum (other), a pair of structures in human genitals * Corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine structure in mammals * Corpus gastricum, the Latin term referring to the body of the stomach * Corpus alienum, a foreign object originating outside the body * Corpus albicans * Corpora amylacea * Corpora arenacea Other uses * ''Corpus'' (Bernini), a 1650 sculpture of Christ by Gian Lorenzo Bernini * Corpus (museum), a human body themed museum in the Netherlands * Corpus Clock, a large sculptural clock * Corpus (dance troupe), a Canadian dance troupe * Corpus (typography), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Brain
The supraesophageal ganglion (also "supraoesophageal ganglion", "arthropod brain" or "microbrain") is the first part of the arthropod, especially insect, central nervous system. It receives and processes information from the first, second, and third Metamerism (biology), metameres. The supraesophageal ganglion lies Dorsum (anatomy), dorsal to the esophagus and consists of three parts, each a pair of ganglia that may be more or less pronounced, reduced, or fused depending on the genus (biology), genus: * The ''protocerebrum'', associated with the arthropod eye, eyes (Eye#Compound eyes, compound eyes and ocelli). Directly associated with the eyes is the optic lobe (arthropod), optic lobe, as the visual center of the brain. * The ''deutocerebrum'' processes sensory information from the Antenna (biology), antennae. It consists of two parts, the antennal lobe and the dorsal lobe. The dorsal lobe also contains motor neurons which control the antennal muscles. * The ''tritocerebrum'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropil
Neuropil (or "neuropile") is any area in the nervous system composed of mostly unmyelinated axons, dendrites and glial cell processes that forms a synaptically dense region containing a relatively low number of cell bodies. The most prevalent anatomical region of neuropil is the brain which, although not completely composed of neuropil, does have the largest and highest synaptically concentrated areas of neuropil in the body. For example, the neocortex and olfactory bulb both contain neuropil. White matter, which is mostly composed of myelinated axons (hence its white color) and glial cells, is generally not considered to be a part of the neuropil. Neuropil (pl. neuropils) comes from the Greek: ''neuro'', meaning "tendon, sinew; nerve" and ''pilos'', meaning "felt". The term's origin can be traced back to the late 19th century. Location Neuropil has been found in the following regions: outer neocortex layer, barrel cortex, inner plexiform layer and outer plexiform layer, poster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
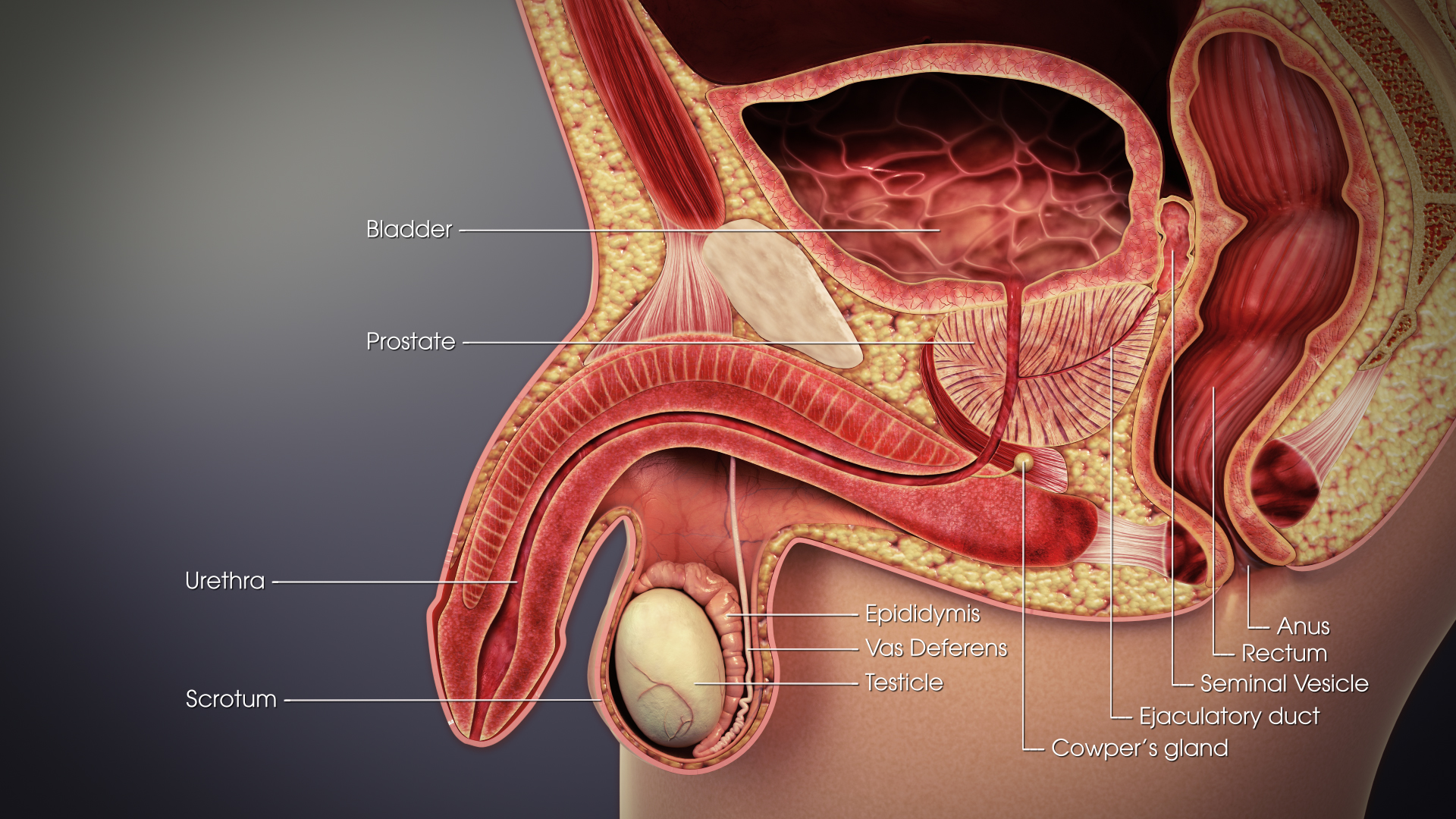
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens or ductus deferens is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel"; the plural version is ''vasa deferentia''. ''Ductus deferens'' is also Latin, meaning "carrying-away duct"; the plural version is ''ducti deferentes''. Structure There are two vasa deferentia, connecting the left and right epididymis with the seminal vesicles to form the ejaculatory duct in order to move sperm. The (human) vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. The vas deferens is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis. The vas deferens exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, it forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate outcrossing (fusion of sperm and eggs from different individuals in a population) resulting from cross-pollination or allow selfing (fusion of sperm and egg from the same flower) when self-pollination occurs. There are two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower, or another flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination is when pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. Self-pollination happens in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time, and are positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory System
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system. System overview The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasing the sound pressure in the middle frequency range. The middle-ear ossicles further amplify the vibration pressure roughly 20 times. The base of the stapes couples vibrations into the cochlea via the oval window, which vibrates the perilymph liquid (present throughout the inner ear) and causes the round window to bulb out as the oval window bulges in. Vestibular and tympanic ducts are filled with perilymph, and the smaller cochlear duct between them is filled with endolymph, a fluid with a very different ion concentration and voltage. Vestibular duct perilymph vibrations bend organ of Corti outer cells (4 lines) causing prestin to be released in cell tips. This causes the cells to be chemically elongated and shrunk ( somatic motor), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |