|
Caledonian Orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly 490–390 million years ago ( Ma). It was caused by the closure of the Iapetus Ocean when the continents and terranes of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia collided. The orogeny is named for Caledonia, the Latin name for Scotland. The term was first used in 1885 by Austrian geologist Eduard Suess for an episode of mountain building in northern Europe that predated the Devonian period. Geologists like Émile Haug and Hans Stille saw the Caledonian event as one of several episodic phases of mountain building that had occurred during Earth's history. Current understanding has it that the Caledonian orogeny encompasses a number of tectonic phases that can laterally be diachronous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium. Originally a margraviate of Bavaria, it developed into a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as the empire's administrative capital and Austria thus became the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. After the dissolution of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, Scramble for Africa, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
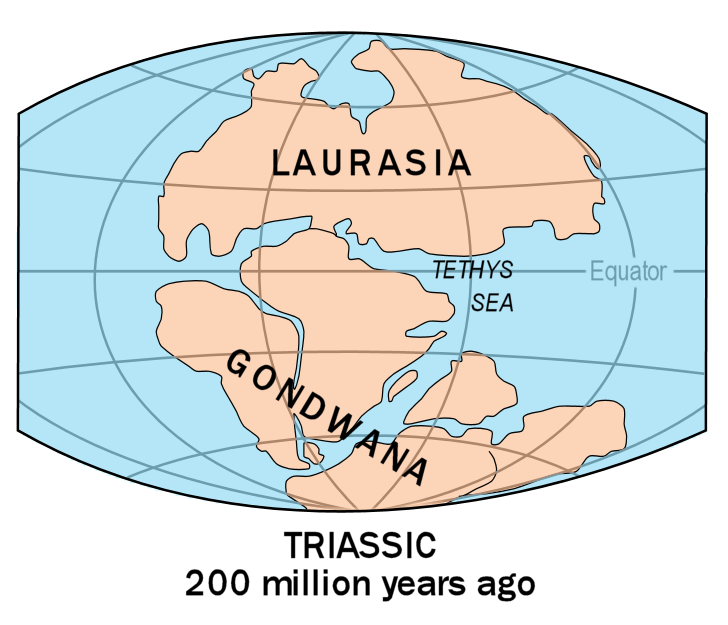
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocontinent
A paleocontinent or palaeocontinent is a distinct area of continental crust that existed as a major landmass in the geological past. There have been many different landmasses throughout Earth's time. They range in sizes, some are just a collection of small microcontinents while others are large conglomerates of crust. As time progresses and sea levels rise and fall more crust can be exposed making way for larger landmasses. The continents of the past shaped the evolution of organisms on Earth and contributed to the climate of the globe as well. As landmasses break apart, species are separated and those that were once the same now have evolved to their new climate. The constant movement of these landmasses greatly determines the distribution of organisms on Earth's surface. This is evident with how similar fossils are found on completely separate continents. Also, as continents move, mountain building events (orogenies) occur, causing a shift in the global climate as new rock is expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, Pangaea was centred on the equator and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists. Origin of the concept The name "Pangaea" is derived from Ancient Greek ''pan'' (, "all, entire, whole") and ''Gaia'' or Gaea (, "Mother Earth, land"). The concept that the continents once formed a contiguous land mass was hypothesised, with corroborating evidence, by Alfred Wegener, the originator of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leaves room for interpretation and is easier to apply to Precambrian times. To separate supercontinents from other groupings, a limit has been proposed in which a continent must include at least about 75% of the continental crust then in existence in order to qualify as a supercontinent. Supercontinents have assembled and dispersed multiple times in the geologic past (see table). According to modern definitions, a supercontinent does not exist today; the closest in existence to a supercontinent is the current Afro-Eurasian landmass, which covers approx. 57% of Earth's total land area. The last time the continental landmasses were near to one another was 336 to 175 million years ago as the supercontinent, Pangaea. The positions of continent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diachronous
In geology, a diachronism (Greek ''dia'', "through" + ''chronos'', "time" + ''-ism''), or diachronous deposit, is a sedimentary rock formation in which the material, although of a similar nature, varies in age with the place where it was deposited.Whitten F.G.A & Brooks J.R.V., (1972),''A Dictionary of Geology'', Penguin, Typically this occurs as a result of a marine transgression or regression, or the progressive development of a delta. As the shoreline advances or retreats, a succession of continuous deposits representing different environments (for example beach, shallow water, deeper water) may be left behind. Although each type of deposit (facies) may be continuous over a wide area, its age varies according to the position of the shoreline through time. An example is the sandy beds near the end of the lower Carboniferous of the west of England (the ''Drybrook sandstone'' of the Forest of Dean). Deposition of this began much later in the Bristol area than further north. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonics
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles is essential to geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is associated with the stretching and thinning of the crust or the lithosphere. This type of tectonics is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Earth
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geological change and biological evolution. The geological time scale (GTS), as defined by international convention, depicts the large spans of time from the beginning of the Earth to the present, and its divisions chronicle some definitive events of Earth history. (In the graphic, Ma means "million years ago".) Earth formed around 4.54 billion years ago, approximately one-third the age of the universe, by accretion from the solar nebula. Volcanic outgassing probably created the primordial atmosphere and then the ocean, but the early atmosphere contained almost no oxygen. Much of the Earth was molten because of frequent collisions with other bodies which led to extreme volcanism. While the Earth was in its earliest stage ( Early Earth), a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Stille
Hans Wilhelm Stille (8 October 1876 – 26 December 1966) was an influential German geologist working primarily on tectonics and the collation of tectonic events during the Phanerozoic. Stille adhered to the contracting Earth hypothesis and together with Leopold Kober he worked on the geosyncline theory to explain orogeny. Şengör (1982), p. 23 Stille's ideas emerged in the aftermath of Eduard Suess' book ''Das Antlitz der Erde'' (1883–1909). Stille's and Kober's school of thought was one of two that emerged in the post-Suess era the other being headed by Alfred Wegener and Émile Argand. This competing view rejected Earth contraction and argued for continental drift. Şengör (1982), p. 24 As Stille opposed continental drift he came to be labelled a "fixist". Şengör (1982), p. 30 Part of Stille's work dealt with massifs and sedimentary basins in Central Europe; differing from Suess' interpretations for the same area showing that between the Bohemian and Rhine massifs Mesoz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |