|
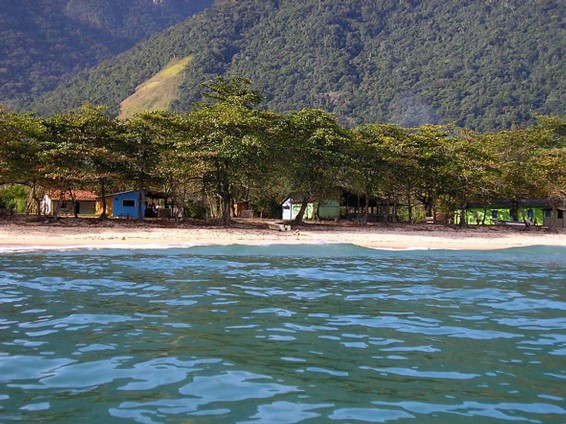
Caiçaras Em Paraty
Caiçaras () are the traditional inhabitants of the coastal regions of the Southeast Brazil, southeastern and South Region, Brazil, southern Brazil. They form a distinct group of people, Mixed-race Brazilian, descended from Africans, indigenous people, and Europeans. Their traditional way of life based on subsistence agriculture, hunting and fishing is threatened by real estate speculation, restrictive laws and declining fish stocks. Origins The name ''caiçara'' comes from the Tupi language ''ka'aysá'' (or ''ka'aysara''), a rustic fence made of tree branches. The fences would surround a village, or would be used for trapping fish. Over time it came to be used for the huts built on the beaches, and then for the inhabitants. The people are of mixed African, indigenous, and European origins. Their origins and customs are similar to the caipiras who live further inland. In literature the caiçaras are represented as traditional, primitive, isolated and self-sufficient fishing peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caiçaras Em Paraty
Caiçaras () are the traditional inhabitants of the coastal regions of the Southeast Brazil, southeastern and South Region, Brazil, southern Brazil. They form a distinct group of people, Mixed-race Brazilian, descended from Africans, indigenous people, and Europeans. Their traditional way of life based on subsistence agriculture, hunting and fishing is threatened by real estate speculation, restrictive laws and declining fish stocks. Origins The name ''caiçara'' comes from the Tupi language ''ka'aysá'' (or ''ka'aysara''), a rustic fence made of tree branches. The fences would surround a village, or would be used for trapping fish. Over time it came to be used for the huts built on the beaches, and then for the inhabitants. The people are of mixed African, indigenous, and European origins. Their origins and customs are similar to the caipiras who live further inland. In literature the caiçaras are represented as traditional, primitive, isolated and self-sufficient fishing peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coati
Coatis, also known as coatimundis (), are members of the family Procyonidae in the genera ''Nasua'' and ''Nasuella''. They are diurnal mammals native to South America, Central America, Mexico, and the southwestern United States. The name "coatimundi" comes from the Tupian languages of Brazil, where it means "lone coati". Locally in Belize, the coati is known as "quash". Physical characteristics Adult coatis measure from head to the base of the tail, which can be as long as their bodies. Coatis are about tall at the shoulder and weigh between , about the size of a large house cat. Males can become almost twice as large as females and have large, sharp canine teeth. The measurements above relate to the white-nosed and South America coatis. The two mountain coatis are smaller. All coatis share a slender head with an elongated, flexible, slightly upward-turned nose, small ears, dark feet, and a long, non-prehensile tail used for balance and signaling. Ring-tailed coatis have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caipira
A Caipira () is an ethnic group native to Paulistânia, cultural area in Brazil, the term "''caipira''", of origin in the Paulista General language, probably influenced by the terms "''kai'pira''", "''ka'apir''", "''ka'a pora''" or "''kopira''", from the Tupi language, originally designates, since Brazilian colonial times, the inhabitant of the countryside, the "bush cutter". The caipira reached, mainly, due to the cycle of bandeirism and tropeirism, populations of the former Captaincy of São Vicente (later Captaincy of São Paulo), which today are the states of Santa Catarina, Paraná, São Paulo, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Goiás, Mato Grosso, Tocantins, Rondônia and Rio Grande do Sul, as well as parts of south of Rio de Janeiro state, such as Paraty, which was part of São Paulo until 1727 and parts of Uruguay that were disputed with Spain. The term "caipira" is often used in Brazil in a pejorative, ethnocentric and stereotyped way for inland populations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribeirinhos
The ribeirinhos are a traditional population in South America, who live near rivers. Their main activities are fishing and Agriculture, farming on a small scale, for their own use. They usually live in Stilt house, pile dwelling and travel by motor boats called Voadeira, voadeiras. According to the Joshua Project, there are approximately 7,105,000 ribeirinho people in Brazil. The Brazilian government has formally recognized their existence since 2007. See also *Cholos pescadores *Montubio *Caiçaras *Indigenous peoples in Brazil References Ethnic groups in Brazil Rivers {{Brazil-culture-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
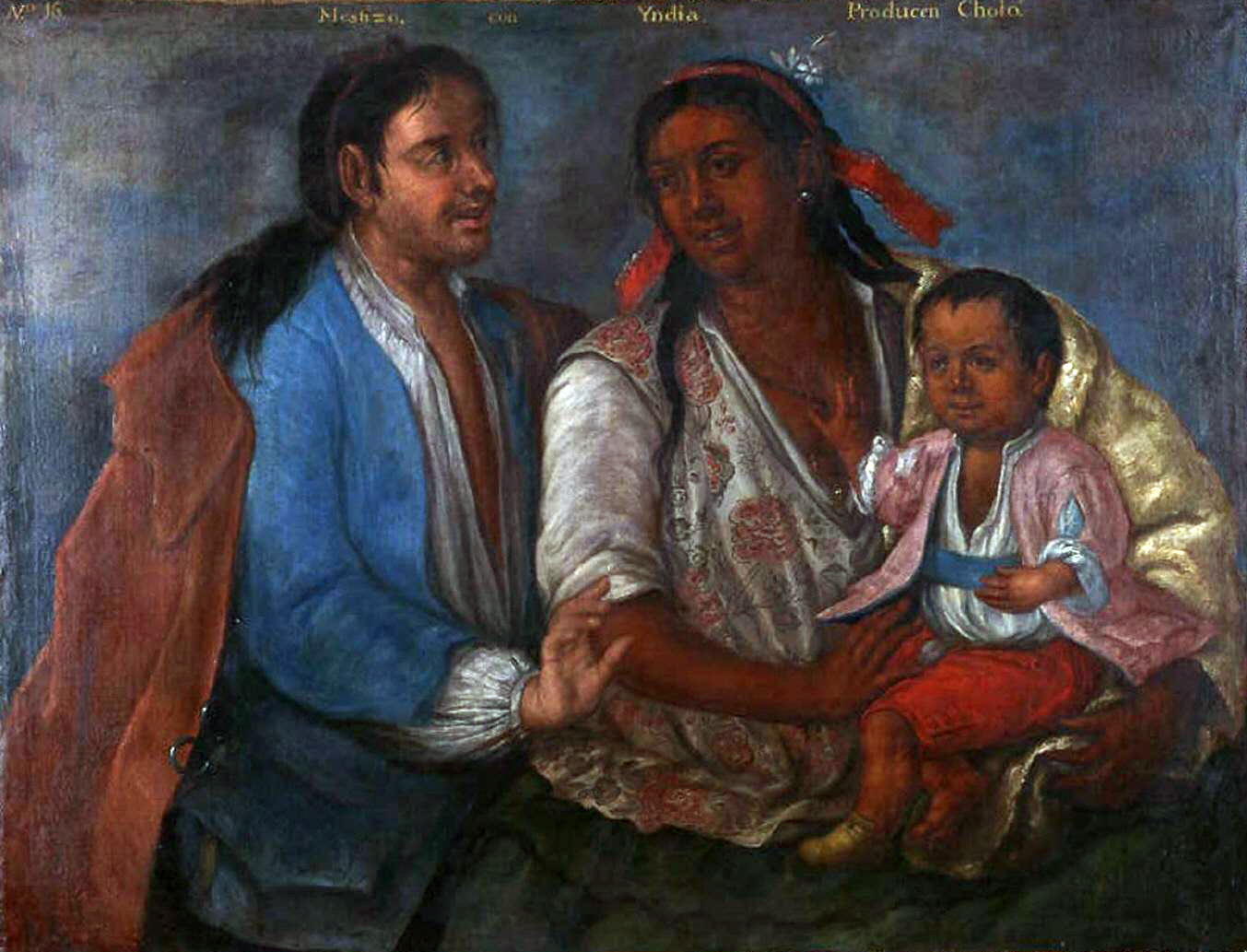
Cholo Pescador
''Cholo'' () is a loosely defined Spanish term that has had various meanings. Its origin is a somewhat derogatory term for people of mixed-blood heritage in the Spanish Empire in Latin America and its successor states as part of ''castas'', the informal ranking of society by heritage. ''Cholo'' no longer necessarily refers only to ethnic heritage, and is not always meant negatively. ''Cholo'' can signify anything from its original sense as a person with one Amerindian parent and one ''Mestizo'' parent, "gangster" in Mexico, an insult in some South American countries (similar to chulo in Spain), or a "person who dresses in the manner of a certain subculture" in the United States as part of the cholo subculture. Historical usage In his work ''Vocabulario en Lengua Castellana y Mexicana'' (1571), Fray Alonso de Molina reports that the word "cholo" or "xolo" derives from Nahuatl and means "paje, moço, criado o esclavo" ("page, waiter, servant o slave"). The term's use to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toucan
Toucans (, ) are members of the Neotropical near passerine bird family Ramphastidae. The Ramphastidae are most closely related to the American barbets. They are brightly marked and have large, often colorful bills. The family includes five genera and over forty different species. Toucans are arboreal and typically lay 2–4 white eggs in their nests. They make their nests in tree hollows and holes excavated by other animals such as woodpeckers—the toucan bill has very limited use as an excavation tool. When the eggs hatch, the young emerge completely naked, without any down. Toucans are resident breeders and do not migrate. Toucans are usually found in pairs or small flocks. They sometimes fence with their bills and wrestle, which scientists hypothesize they do to establish dominance hierarchies. In Africa and Asia, hornbills occupy the toucans' ecological niche, an example of convergent evolution. Taxonomy and systematics The name of this bird group is derived from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-fronted Piping Guan
The black-fronted piping guan or jacutinga in Brazilian Portuguese (''Pipile jacutinga'') is a bird in the chachalaca, guan, and curassow family Cracidae. It is found in Argentina, Brazil, and Paraguay.del Hoyo, J., G. M. Kirwan, and C. J. Sharpe (2020). Black-fronted Piping-Guan (''Pipile jacutinga''), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.bfpgua1.01 retrieved September 25, 2021 Taxonomy and systematics The taxonomies of the International Ornithological Committee (IOC), ''The Clements Checklist of Birds of the World'', and '' Handbook of the Birds of the World'' treat the black-fronted piping guan as one of four species in genus Pipile.Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, S. M. Billerman, T. A. Fredericks, J. A. Gerbracht, D. Lepage, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2021. The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinamou
Tinamous () form an order of birds called Tinamiformes (), comprising a single family called Tinamidae (), divided into two distinct subfamilies, containing 46 species found in Mexico, Central America, and South America. The word "tinamou" comes from the Galibi term for these birds, ''tinamu''. Tinamous have traditionally been regarded as the sister group of the flightless ratites, but recent work places them well within the ratite radiation, implying basal ratites could fly. Tinamous first appear in the fossil record in the Miocene epoch. They are generally sedentary, ground-dwelling and, though not flightless, when possible avoid flight in favour of hiding or running away from danger. They are found in a variety of habitats, ranging from semi-arid alpine grasslands to tropical rainforests. The two subfamilies are broadly divided by habitat, with the Nothurinae referred to as steppe or open country tinamous, and the Tinaminae known as forest tinamous. Although some species are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peccary
A peccary (also javelina or skunk pig) is a medium-sized, pig-like hoofed mammal of the family Tayassuidae (New World pigs). They are found throughout Central and South America, Trinidad in the Caribbean, and in the southwestern area of North America. They usually measure between in length, and a full-grown adult usually weighs about . They represent the closest relatives of the family Suidae, which contains pigs and relatives. Together Tayassuidae and Suidae are grouped in the Suina within the Artiodactyla (even toed ungulates). Peccaries are social creatures that live in herds. They eat roots, grubs, and a variety of foods. They can identify each other by their strong odors. A group of peccaries that travel and live together is called a "squadron". A squadron of peccaries averages between six and nine members. Peccaries first appeared in North America during the Miocene, and migrated into South America during the Pliocene-Pleistocene as part of the Great American Interchange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capybara
The capybaraAlso called capivara (in Brazil), capiguara (in Bolivia), chigüire, chigüiro, or fercho (in Colombia and Venezuela), carpincho (in Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay) and ronsoco (in Peru). or greater capybara (''Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris'') is a giant cavy rodent native to South America. It is the largest living rodent and a member of the genus ''Hydrochoerus''. The only other extant member is the lesser capybara (''Hydrochoerus isthmius''). Its close relatives include guinea pigs and rock cavies, and it is more distantly related to the agouti, the chinchilla, and the nutria. The capybara inhabits savannas and dense forests, and lives near bodies of water. It is a highly social species and can be found in groups as large as 100 individuals, but usually live in groups of 10–20 individuals. The capybara is hunted for its meat and hide and also for grease from its thick fatty skin. It is not considered a threatened species. Etymology Its common name is derived fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillo
Armadillos (meaning "little armored ones" in Spanish) are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. Nine extinct genera and 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of different environments. Armadillos are characterized by a leathery armor shell and long, sharp claws for digging. They have short legs, but can move quite quickly. The average length of an armadillo is about , including its tail. The giant armadillo grows up to and weighs up to , while the pink fairy armadillo has a length of only . When threatened by a predator, ''Tolypeutes'' species frequently roll up into a ball; they are the only species of armadillo capable of this. Etymology The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeast Brazil
The Southeast Region of Brazil ( pt, Região Sudeste do Brasil; ) is composed of the states of Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. It is the richest region of the country, responsible for approximately 60% of the Brazilian GDP, as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais are the three richest states of Brazil, the top three Brazilian states in terms of GDP. The Southeast of Brazil also has the highest GDP per capita among all Brazilian regions. The Southeast region leads the country in population, urban population, population density, vehicles, industries, universities, airports, ports, highways, hospitals, schools, houses and many other areas. Geography *São Paulo Heart of the largest continued remnant of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest, the Ribeira Valley is a Natural Heritage of Humanity, granted heritage as a Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO. One of the biggest attractions is the biologic and ecosystems diversity, where approximately 400 species of bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |