|
Caesar (Byzantine Title)
Caesar ( English Caesars; Latin ''Caesares''; in Greek: ''Kaîsar'') is a title of imperial character. It derives from the ''cognomen'' of Julius Caesar, a Roman dictator. The change from being a familial name to a title adopted by the Roman emperors can be traced to AD 68, following the fall of the Julio–Claudian dynasty. Origins The first known individual to bear the ''cognomen'' of "Caesar" was Sextus Julius Caesar, who is likewise believed to be the common ancestor of all subsequent Julii Caesares. Sextus' great-grandson was the dictator Gaius Julius Caesar. After he seized control of the Roman Republic following his war against the Senate, he adopted the title of ''dictator perpetuo'' ("dictator in perpetuity"), a title he only held for about a month before he was assassinated in 44 BC. Julius Caesar's death did not lead to the restoration of the Republic, and instead led to the rise of the Second Triumvirate, composed by three dictators including Jul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and subsequently became dictator from 49 BC until his assassination in 44 BC. He played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Crassus and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass power as were opposed by the within the Roman Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the frequent support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the Gallic Wars, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both invaded Britain and built a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
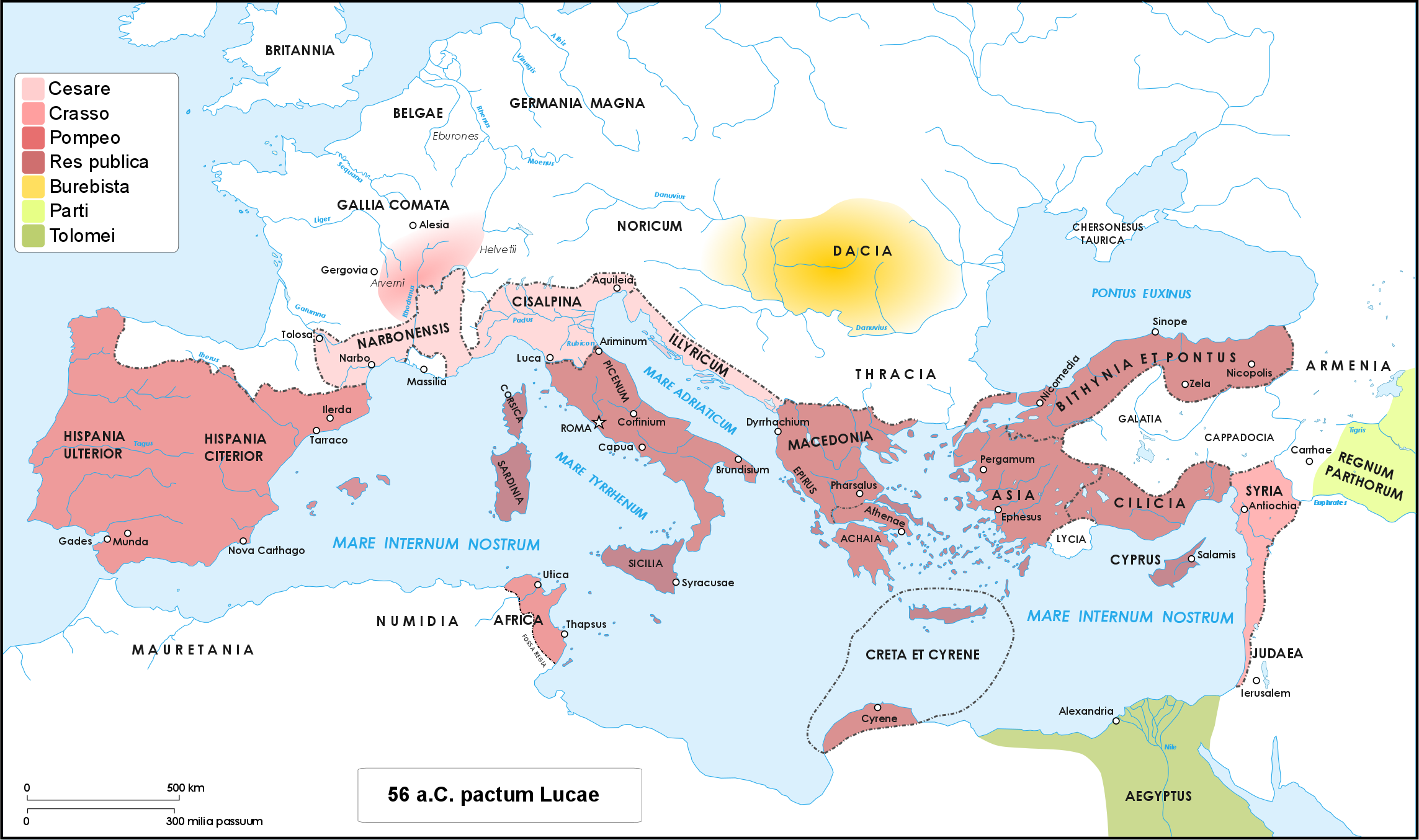
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julio-Claudian Dynasty
, native_name_lang=Latin, coat of arms=Great_Cameo_of_France-removebg.png, image_size=260px, caption= The Great Cameo of France depicting emperors Augustus, Tiberius, Claudius and Nero, type= Ancient Roman dynasty, country= Roman Empire, estates=* Imperial Palaces of the Palatine Hill * House of Augustus * Villa of Livia * Gardens of Maecenas * ''Domus Aurea'' * ''Domus Transitoria'' * Villa of Nero * ''Villa Jovis'', parent house=, titles= Roman emperor Pharaoh of Egypt Prince of the Senate Greatest Priest of Rome Father of the Country , styles=" Imperator""Caesar""Augustus", founded=, founder=Augustus, final ruler=Nero, other_families=, deposition= (deposed by Galba), ethnicity= Ancient Roman, religion=Roman Religion Imperial cult The Julio-Claudian dynasty comprised the first five Roman emperors: Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero. This line of emperors ruled the Roman Empire, from its formation (under Augustus, in 27 BC) until the last of the line, empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Antonia Minor at Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, where his father was stationed as a military legate. He was the first Roman emperor to be born outside Italia (Roman Empire), Italy. Nonetheless, Claudius was an Italian of Sabine origins. As he had a limp and slight deafness due to sickness at a young age, he was ostracized by his family and was excluded from public office until his Roman consul, consulship (which was shared with his nephew, Caligula, in 37). Claudius's infirmity probably saved him from the fate of many other nobles during the purges throughout the reigns of Tiberius and Caligula, as potential enemies did not see him as a serious threat. His survival led to him being declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard after Caligula's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father was the politician Tiberius Claudius Nero and his mother was Livia Drusilla, who would eventually divorce his father, and marry the future-emperor Augustus in 38 BC. Following the untimely deaths of Augustus' two grandsons and adopted heirs, Gaius and Lucius Caesar, Tiberius was designated Augustus' successor. Prior to this, Tiberius had proved himself an able diplomat, and one of the most successful Roman generals: his conquests of Pannonia, Dalmatia, Raetia, and (temporarily) parts of Germania laid the foundations for the empire's northern frontier. Early in his career, Tiberius was happily married to Vipsania, daughter of Augustus' friend, distinguished general and intended heir, Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa. They had a son, Drusus Jul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praenomen
The ''praenomen'' (; plural: ''praenomina'') was a personal name chosen by the parents of a Roman child. It was first bestowed on the ''dies lustricus'' (day of lustration), the eighth day after the birth of a girl, or the ninth day after the birth of a boy. The praenomen would then be formally conferred a second time when girls married, or when boys assumed the '' toga virilis'' upon reaching manhood. Although it was the oldest of the ''tria nomina'' commonly used in Roman naming conventions, by the late republic, most praenomina were so common that most people were called by their praenomina only by family or close friends. For this reason, although they continued to be used, praenomina gradually disappeared from public records during imperial times. Although both men and women received praenomina, women's praenomina were frequently ignored, and they were gradually abandoned by many Roman families, though they continued to be used in some families and in the countryside. Backgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperator
The Latin word ''imperator'' derives from the stem of the verb la, imperare, label=none, meaning 'to order, to command'. It was originally employed as a title roughly equivalent to ''commander'' under the Roman Republic. Later it became a part of the titulature of the Roman Emperors as part of their cognomen. The English word ''emperor'' derives from ''imperator'' via fro, Empereür. The Roman emperors themselves generally based their authority on multiple titles and positions, rather than preferring any single title. Nevertheless, ''imperator'' was used relatively consistently as an element of a Roman ruler's title throughout the Principate and the Dominate. ''Imperatores'' in the ancient Roman Kingdom When Rome was ruled by kings, to be able to rule, the king had to be invested with the full regal authority and power. So, after the comitia curiata, held to elect the king, the king also had to be conferred the imperium. ''Imperatores'' in the Roman Republic In Roman Repub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen Gentilicium
The (or simply ) was a hereditary name borne by the peoples of Roman Italy and later by the citizens of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. It was originally the name of one's (family or clan) by patrilineal descent. However, as Rome expanded its frontiers and non-Roman peoples were progressively granted citizenship and concomitant , the latter lost its value in indicating patrilineal ancestry. For men, the was the middle of the ("three names"), after the and before the . For women, the was often the only name used until the late Republic. For example, three members of gens ''Julia'' were Gaius ''Julius'' Caesar and his sisters ''Julia'' Major and ''Julia'' Minor ("Julia the elder" and "Julia the younger"). History The ''nomen gentilicium'', or "gentile name" designated a Roman citizen as a member of a ''gens''. A ''gens'', which may be translated as "race", "family", or "clan", constituted an extended Roman family, all of whom shared the same ''nomen'', and claim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus (title)
''Augustus'' (plural ''Augusti''; , ; "majestic", "great" or "venerable") was an ancient Roman title given as both name and title to Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus (often referred to simply as Augustus), Rome's first Emperor. On his death, it became an official title of his successor, and was so used by Roman emperors thereafter. The feminine form '' Augusta'' was used for Roman empresses and other female members of the Imperial family. The masculine and feminine forms originated in the time of the Roman Republic, in connection with things considered divine or sacred in traditional Roman religion. Their use as titles for major and minor Roman deities of the Empire associated the Imperial system and Imperial family with traditional Roman virtues and the divine will, and may be considered a feature of the Roman Imperial cult. In Rome's Greek-speaking provinces, "Augustus" was translated as ''Sebastos'' (Σεβαστός, "venerable"), or Hellenised as ''Augoustos'' (); these tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Naming Conventions
Over the course of some fourteen centuries, the Romans and other peoples of Italy employed a system of nomenclature that differed from that used by other cultures of Europe and the Mediterranean Sea, consisting of a combination of personal and family names. Although conventionally referred to as the ''tria nomina'', the combination of praenomen, nomen, and cognomen that have come to be regarded as the basic elements of the Roman name in fact represent a continuous process of development, from at least the seventh century BC to the end of the seventh century AD. The names that developed as part of this system became a defining characteristic of Roman civilization, and although the system itself vanished during the Early Middle Ages, the names themselves exerted a profound influence on the development of European naming practices, and many continue to survive in modern languages. Overview The distinguishing feature of Roman nomenclature was the use of both personal names and regular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Principate, which is the first phase of the Roman Empire, and Augustus is considered one of the greatest leaders in human history. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult as well as an era associated with imperial peace, the ''Pax Romana'' or ''Pax Augusta''. The Roman world was largely free from large-scale conflict for more than two centuries despite continuous wars of imperial expansion on the empire's frontiers and the year-long civil war known as the "Year of the Four Emperors" over the imperial succession. Originally named Gaius Octavius, he was born into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian ''gens'' Octavia. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was named in Caesar' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Triumvirate
The Second Triumvirate was an extraordinary commission and magistracy created for Mark Antony, Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, and Octavian to give them practically absolute power. It was formally constituted by law on 27 November 43 BC with a term of five years; it was renewed in 37 BC for another five years before expiring in 32 BC. Constituted by the ''lex Titia'', the triumvirs were given broad powers to make or repeal legislation, issue judicial punishments without due process or right of appeal, and appoint all other magistrates. The triumvirs also split the Roman world into three sets of provinces. The triumvirate, formed in the aftermath of a conflict between Antony and the senate, emerged as a force to reassert Caesarian control over the western provinces and wage war on the ''liberatores'' led by the men who assassinated Julius Caesar. After proscriptions, purging the senatorial and equestrian orders, and a brutal civil war, the ''liberatores'' were defea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |