|
Cadillac Desert
''Cadillac Desert'' (1986), is a history by American Marc Reisner about land development and water policy in the western United States. Subtitled ''The American West and Its Disappearing Water'', it explores the history of the federal agencies, Bureau of Reclamation and U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and their struggles to remake the American West in ways to satisfy national settlement goals. The book concludes that the development-driven policies, formed when settling the West was the country's main concern, have had serious long-term negative effects on the environment and water quantity. The book was revised and updated in 1993. Topics discussed * Army Corps of Engineers *Bureau of Reclamation *California Aqueduct * California Water Wars *Central Arizona Project *Colorado River *Colorado River Storage Project *David Brower *Floyd Dominy *Garrison Dam * Glen Canyon Dam *Grand Coulee Dam * Hoover Dam * Klamath Diversion *Los Angeles Department of Water and Power * Manifest Dest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marc Reisner
Marc Reisner (September 14, 1948 – July 21, 2000) was an American environmentalist and writer best known for his book ''Cadillac Desert'', a history of water management in the American West. Early life He was born in Minneapolis, Minnesota, the son of a lawyer and a scriptwriter, and graduated from Earlham College in 1970. Career For a time he was on the staffs of Environmental Action and the Population Institute in Washington, D.C. Starting in 1972, he worked for seven years as a staff writer and director of communications for the Natural Resources Defense Council in New York. Writings and television work In 1979 he received an Alicia Patterson Journalism Fellowship, which enabled him to conduct research and write ''Cadillac Desert'', which was first published in 1986. According to The Guardian, ''Cadillac Desert'' illuminated the importance of water conservation in the American West with "the remarkable ability to explain entertainingly the complex, and often numbing, deals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manifest Destiny
Manifest destiny was a cultural belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American settlers were destined to expand across North America. There were three basic tenets to the concept: * The special virtues of the American people and their institutions * The mission of the United States to redeem and remake the Western United States, West in the image of the History of agrarianism#United States, agrarian Eastern United States, East * An irresistible destiny to accomplish this essential duty Historians have emphasized that "manifest destiny" was always contested; many endorsed the idea, but the large majority of Whig Party (United States), Whigs and many prominent Americans (such as Abraham Lincoln and Ulysses S. Grant) rejected the concept. Historian Daniel Walker Howe writes, "American imperialism did not represent an American consensus; it provoked bitter dissent within the national polity while the ''Whigs'' saw America's moral missio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadillac Desert (film)
''Cadillac Desert: Water and the Transformation of Nature'' is a 1997 American four-part documentary series about water, money, politics, and the transformation of nature.. The film was directed by Jon H. Else and Linda Harrar. Synopsis The film chronicles the growth of a large community in the western American desert. It brought abundance and a legacy of risk created in the United States and abroad. The first three episodes are based on Marc Reisner's book, ''Cadillac Desert'' (1986), that delves into the history of water use and misuse in the American West. It explores the triumph and disaster, heroism and intrigue, and the rivalries and bedfellows that dominate this little-known chapter of American history. The final episode is drawn from Sandra Postel's book, ''Last Oasis'' (1992), which examines the global impact of the technologies and policies that came out of the United States' manipulation of water. She demonstrates how they have created the need for conservation metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hastings West-Northwest Journal Of Environmental Law And Policy
The ''Hastings Environmental Law Journal'' is a student-run law review published at the University of California, Hastings College of the Law. Founded in 1994, the journal primarily covers environmental law and policy and related subjects with a regional focus in California, the Pacific Northwest, Alaska and Hawai'i.''Journal Information'', 21 vii (2015). History and overview The journal was established in 1994 as a regional journal "that would contribute to an integrated understanding of environmental and natural resources policy."Brian E. Gray, ''Dedication'', 14 29 (2008). The founding editors had the goal of establishing an "interdisciplinary journal" that would feature "articles by legal scholars, practicing lawyers, biologists, economists, engineers, historians, hydrologists, land and resource managers, and other professionals." It is among several regional environmental law journals to focus specifically on issues related to California and the Pacific Northwest. Althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Mulholland
William Mulholland (September 11, 1855 – July 22, 1935) was an Irish Americans, Irish American self-taught civil engineer who was responsible for building the infrastructure to provide a water supply that allowed Los Angeles to grow into the largest city in California. As the head of a predecessor to the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power, Mulholland designed and supervised the building of the Los Angeles Aqueduct, a system to move water from Owens Valley to the San Fernando Valley. The creation and operation of the aqueduct led to the disputes known as the California Water Wars. In March 1928, Mulholland's career came to an end when the St. Francis Dam failed just over 12 hours after he and his assistant gave it a safety inspection. Early life William Mulholland was born in Belfast, Ireland, part of the United Kingdom. His parents Hugh and Ellen Mulholland were Dubliners and they returned to the city a few years after William's birth. His younger brother, Hugh Jr., was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teton Dam
The Teton Dam was an earthen dam in the western United States, on the Teton River in eastern Idaho. It was built by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, one of eight federal agencies authorized to construct dams.Perrow, Charles. ''Normal Accidents''. New York: Basic Books, 1984. , pp.233–238 Located between Fremont and Madison counties, it suffered a catastrophic failure on June 5, 1976, as it was filling for the first time. The collapse of Teton Dam resulted in eleven deaths, and killed 16,000 livestock. The dam cost about $100 million to build and the federal government paid over $300 million in claims related to its failure. Total damage estimates have ranged up to $2 billion, and the dam was not rebuilt. History and geology Interest in building a dam in the eastern Snake River Plain had arisen for many years to control spring runoff and provide a more constant water supply in the summer. The area had suffered a severe drought in 1961, followed by severe flooding in 1962. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stewart Lee Udall
Stewart Lee Udall (January 31, 1920 – March 20, 2010) was an American politician and later, a federal government official. After serving three terms as a congressman from Arizona, he served as Secretary of the Interior from 1961 to 1969, under presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson. Early life and career Stewart Udall was born on January 31, 1920, in Saint Johns, Arizona, to Louisa Lee Udall (1893–1974) and Levi Stewart Udall (1891–1960). He had five siblings: Inez, Elma, Morris (Mo), Eloise, and David Burr. As a young boy Stewart worked on the family farm in St. Johns. He was remembered by his mother as a child with tremendous energy and an unquenchable curiosity. Udall attended the University of Arizona for two years until World War II. He served four years in the Air Force as an enlisted gunner on a B-24 Liberator, flying fifty missions over Western Europe from Italy with the 736th Bomb Squadron, 454th Bomb Group, for which he received the Air Medal with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snail Darter Controversy
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gastropoda that have a coiled shell that is large enough for the animal to retract completely into. When the word "snail" is used in this most general sense, it includes not just land snails but also numerous species of sea snails and freshwater snails. Gastropods that naturally lack a shell, or have only an internal shell, are mostly called ''slugs'', and land snails that have only a very small shell (that they cannot retract into) are often called ''semi-slugs''. Snails have considerable human relevance, including as food items, as pests, and as vectors of disease, and their shells are used as decorative objects and are incorporated into jewelry. The snail has also had some cultural significance, tending to be associated with lethargy. The snai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rain Follows The Plow
Rain follows the plow is the conventional name for a now-discredited theory of climatology that was popular throughout the American West and Australia during the late 19th century. The phrase was employed as a summation of the theory by Charles Dana Wilber: God speed the plow. ... By this wonderful provision, which is only man's mastery over nature, the clouds are dispensing copious rains ... he plowis the instrument which separates civilization from savagery; and converts a desert into a farm or garden. ... To be more concise, ''Rain follows the plow''. The basic premise of the theory was that human habitation and agriculture through homesteading effected a permanent change in the climate of arid and semi-arid regions, making these regions more humid. The theory was widely promoted in the 1870s as a justification for the settlement of the Great Plains, a region previously known as the "Great American Desert". It was also used to justify the expansion of wheat growing on margi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powell Geographic Expedition Of 1869
The Powell Geographic Expedition of 1869, led by American naturalist John Wesley Powell, was the first thorough cartographic and scientific investigation of long segments of the Green and Colorado rivers in the southwestern United States, including the first recorded passage of white men through the entirety of the Grand Canyon. The expedition, which lasted approximately three months during the summer of 1869, embarked from Green River Station, Wyoming Territory and traveled downstream through parts of the present-day states of Colorado and Utah before reaching the confluence of the Colorado and Virgin rivers in present-day Arizona and Nevada . Despite a series of hardships, including losses of boats and supplies, near-drownings, and the eventual departures of several crew members, the voyage produced the first detailed descriptions of much of the previously unexplored canyon country of the Colorado Plateau. Powell retraced part of the 1869 route on a second expedition in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
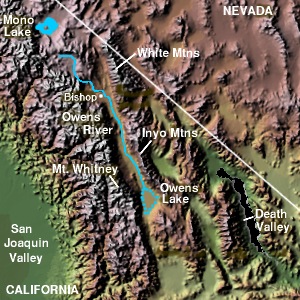
Owens Valley
Owens Valley (Numic Numic is a branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family. It includes seven languages spoken by Native American peoples traditionally living in the Great Basin, Colorado River basin, Snake River basin, and southern Great Plains. The word Numic com ...: ''Payahǖǖnadǖ'', meaning "place of flowing water") is an arid valley of the Owens River in eastern California in the United States. It is located to the east of the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada, west of the White Mountains (California), White Mountains and Inyo Mountains, and north of the Mojave Desert. It sits on the west edge of the Great Basin section, Great Basin. The mountain peaks on the West side (including Mount Whitney) reach above in elevation, while the floor of the Owens Valley is about , making the valley the deepest in the United States. The Sierra Nevada casts the valley in a rain shadow, which makes Owens Valley "the Land of Little Rain." The bed of Owens Lake, now a predominantly dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogallala Aquifer
The Ogallala Aquifer () is a shallow water table aquifer surrounded by sand, silt, clay, and gravel located beneath the Great Plains in the United States. One of the world's largest aquifers, it underlies an area of approximately in portions of eight states (South Dakota, Nebraska, Wyoming, Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, and Texas). It was named in 1898 by geologist N. H. Darton from its type locality near the town of Ogallala, Nebraska. The aquifer is part of the High Plains Aquifer System, and resides in the Ogallala Formation, which is the principal geologic unit underlying 80% of the High Plains. Large-scale extraction for agricultural purposes started after World War II due partially to center pivot irrigation and to the adaptation of automotive engines for groundwater wells. Today about 27% of the irrigated land in the entire United States lies over the aquifer, which yields about 30% of the ground water used for irrigation in the United States. The aquif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)