|
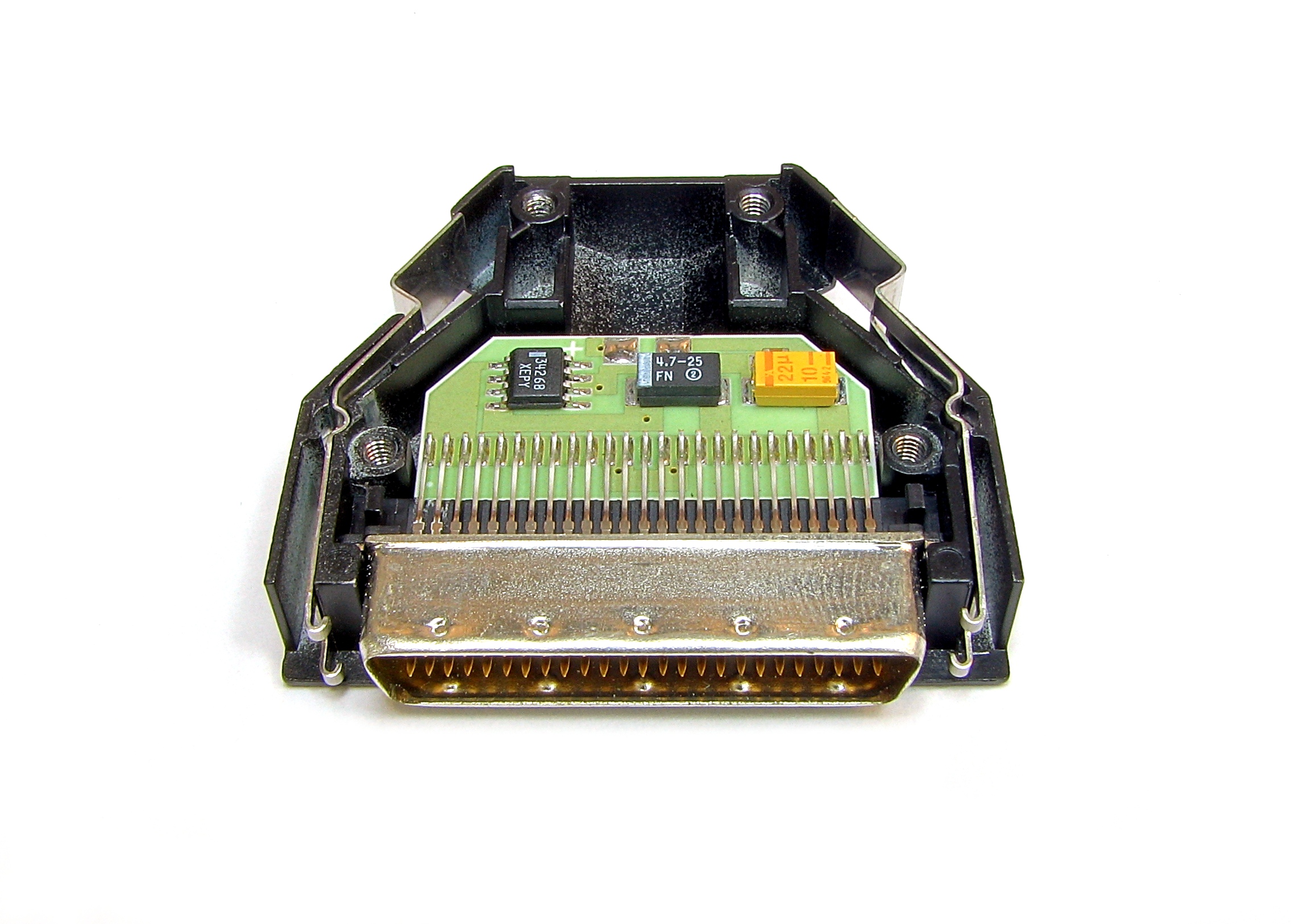
Cable Modems
A cable modem is a type of network bridge that provides bi-directional data communication via radio frequency channels on a hybrid fibre-coaxial (HFC), radio frequency over glass (RFoG) and coaxial cable infrastructure. Cable modems are primarily used to deliver broadband Internet access in the form of cable Internet, taking advantage of the high bandwidth of a HFC and RFoG network. They are commonly deployed in the Americas, Asia, Australia, and Europe. History MITRE Cablenet Internet Experiment Note (IEN) 96IEN 96 - The Cablenet Project (1979) describes an early RF cable modem system. From pages 2 and 3 of IEN 96: T ... |
ARRIS CM820B DOCSIS Cable Modem
In architecture, an arris is the sharp edge formed by the intersection of two surfaces, such as the corner of a Concrete Masonry Unit, masonry unit; the edge of a timber in timber framing; the junction between two planes of plaster or any intersection of divergent architectural details. The term also refers to the raised edges which separate the fluting (architecture), flutings in a Doric order, Doric column. The origin of the term ''arris'' is from the Latin , meaning the beard of grain, beard or the ear (botany), ear of grain or the bone of a fish. See also arête. An arris rail is a structural element, whose cross section is a 45 degree isosceles right angled triangle. Arris rails are usually made of wood, and are manufactured by cutting a length of square-section timber lengthwise diagonally. They are used for structures which require joining two timbers at right angles; for example, connecting wooden posts and beams. Another common use is for the horizontal rails of ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Signal
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal. In music production, carrier signals can be controlled by a modulating signal to change the sound property of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the ''carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. The carrier is higher in frequency than the modulation signal. In radio communication the modulated carrier is transmitted through space as a radio wave to a radio receiver. Another purpose is to transmit multiple channels of information through a single communication medium, using frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). For example in cable television which uses FDM, many carrier signals, each modulated with a different television channel, are transported through a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Topology
A tree topology, or star-bus topology, is a hybrid network topology in which star networks are interconnected via bus networks. Tree networks are hierarchical, and each node In general, a node is a localized swelling (a "knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex). Node may refer to: In mathematics * Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph *Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines ... can have an arbitrary number of child nodes. Regular tree networks A regular tree network's topology is characterized by two parameters: the branching, d, and the number of generations, G. The total number of the nodes, N, and the number of peripheral nodes N_p, are given by : N= \frac,\quad N_p=d^G Random tree networks Three parameters are crucial in determining the statistics of random tree networks, first, the branching probability, second the maximum number of allowed progenies at each branching point, and third the maximum number of generatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Topology
Network topology is the arrangement of the elements ( links, nodes, etc.) of a communication network. Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and control radio networks, industrial fieldbusses and computer networks. Network topology is the topological structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically. It is an application of graph theory wherein communicating devices are modeled as nodes and the connections between the devices are modeled as links or lines between the nodes. Physical topology is the placement of the various components of a network (e.g., device location and cable installation), while logical topology illustrates how data flows within a network. Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, or signal types may differ between two different networks, yet their logical topologies may be identical. A network’s physical topology is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Amplifier
In electronics, a distribution amplifier, or simply distribution amp or DA, is a device that accepts a single input signal and provides this same signal to multiple isolated outputs. These devices allow a signal to be distributed to multiple destinations without ground loops or signal degradation. They are used for a number of common engineering tasks, including multiple amplification, cable television, splitting monitor and front of house mixes, and "tapping" a signal prior to sending it through effects units to preserve a "dry" signal for later experimentation. Audio distribution amplifier An Audio Distribution Amplifier also known as: a press feed; a pool feed; a media feed; press box; or an ADA, takes a single audio feed, usually a line input, but it may be a microphone input, and outputs multiple line or microphone outputs. This can be done using a passive feed, where the signal is split among the outputs, or as an active feed where the outputs are amplified. The primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simplex Communication
Simplex communication is a communication channel that sends information in one direction only."Simplex" ''The IEEE Authoritative Dictionary of Standard Terms, 7th Ed.'', 2000, Inst. of Electrical and Electronic Engineers, p.1053 The International Telecommunication Union definition is a communications channel that operates in one direction at a time, but that may be reversible; this is termed half duplex in other contexts. A duplex communication channel requires two simplex channels operating in opposite directions at the same time. For example, in TV and radio broadcasting, information flows only from the transmitter site to multiple receivers. A pair of walkie-talkie two-way radios provide a simplex circuit in the ITU sense; only one party at a time can talk, while the other listens until it can hear an opportunity to transmit. The transmission medium (the radio signal over the air) can carry information in only one direction. The old Western Union company used the term simpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Termination
In electronics, electrical termination is the practice of ending a transmission line with a device that matches the characteristic impedance of the line. Termination prevents signals from reflecting off the end of the transmission line. Reflections at the ends of unterminated transmission lines cause distortion which can produce ambiguous digital signal levels and mis-operation of digital systems. Reflections in analog signal systems cause such effects as video ghosting, or power loss in radio transmitter transmission lines. Transmission lines Signal termination often requires the installation of a terminator at the beginning and end of a wire or cable to prevent an RF signal from being reflected back from each end, causing interference, or power loss. The terminator is usually placed at the end of a transmission line or daisy chain bus (such as in SCSI), and is designed to match the AC impedance of the cable and hence minimize signal reflections, and power losses. Less com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cable Television Headend
A cable television headend is a master facility for receiving television signals for processing and distribution over a cable television system. A headend facility may be staffed or unstaffed and is typically surrounded by some type of security fencing. The building is typically sturdy and purpose-built to provide security, cooling, and easy access for the electronic equipment used to receive and re-transmit video over the local cable infrastructure. One can also find head ends in power-line communication (PLC) substations and Internet communications networks. Reception Nearly all cable TV systems carry subscription content that is relayed from a satellite in geosynchronous orbit. Encrypted to prevent unauthorized use, this content is uplinked from one or more earth stations operated by various content delivery companies. The content is then analog or digitally modulated and transmitted through the cable network (the OSP or "OutSide Plant") to subscriber homes by means of coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-wire Circuit
In telecommunication, a four-wire circuit is a two-way circuit using two paths so arranged that the respective signals are transmitted in one direction only by one path and in the other direction by the other path. The four-wire circuit gets its name from the fact that is uses four conductors to create two complete electrical circuits, one for each direction. The two separate circuits (channels) allow full- duplex operation with low crosstalk. In telephony a four-wire circuit was historically used to transport and switch baseband audio signals in the phone company telephone exchange before the advent of digital modulation and the electronic switching system eliminated baseband audio from the telco plant except for the local loop. The local loop is a two-wire circuit for one reason only: to save copper. Using half the number of copper wire conductors per circuit means that the infrastructure cost for wiring each circuit is halved. Although a lower quality circuit, the local loop al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminal (telecommunication)
In the context of telecommunications, a terminal is a device which ends a telecommunications link and is the point at which a signal enters or leaves a network. Examples of terminal equipment include telephones, fax machines, computer terminals, printers and workstations. An end instrument is a piece of equipment connected to the wires at the end of a telecommunications link. In telephony, this is usually a telephone connected to a local loop. End instruments that relate to data terminal equipment include printers, computers, barcode readers, automated teller machines (ATMs) and the console ports of routers. See also * Communication endpoint * Data terminal equipment * End system * Host (network) * Node (networking) * Terminal equipment In telecommunication, the term terminal equipment has the following meanings: * Communications equipment at either end of a communications link, used to permit the stations involved to accomplish the mission for which the link was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |