|
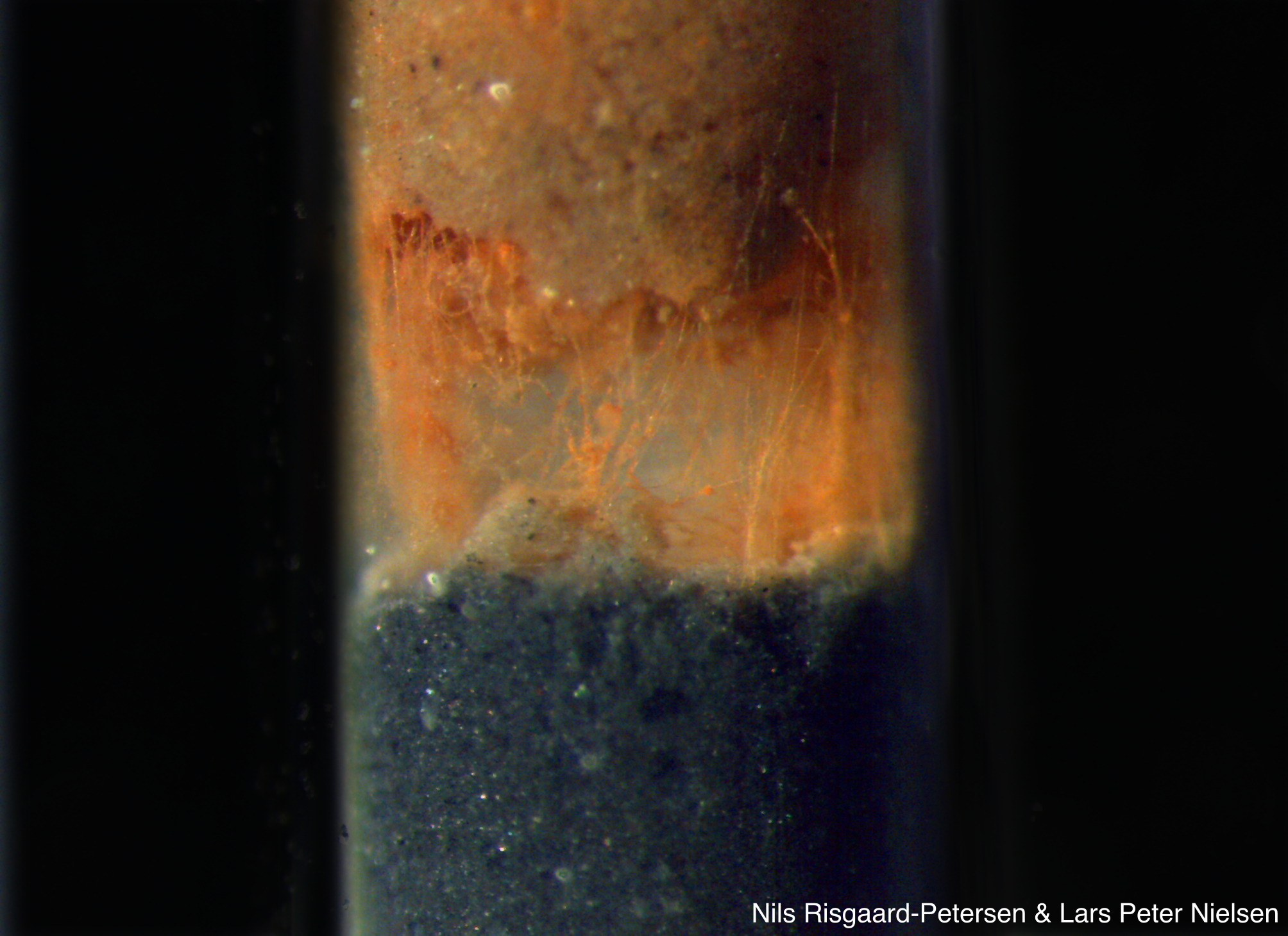
Cable Bacteria
Cable bacteria are filamentous bacteria that conduct electricity across distances over 1 cm in sediment and groundwater aquifers. Cable bacteria allow for long-distance electron transport, which connects electron donors to electron acceptors, connecting previously separated oxidation and reduction reactions. Cable bacteria couple the reduction of oxygen or nitrate at the sediment's surface to the oxidation of sulfide in the deeper, anoxic, sediment layers. Discovery Long-distance electrical conductance in sediment was first observed in 2010 as a spatial separation of sulfide oxidation and oxygen reduction in marine sediment that was interrupted and re-established at a rate faster than could be explained by chemical diffusion. It was later found that this electrical conductance could be observed across a non-conductive layer of glass microspheres, where the only possible conductive structures were filamentous bacteria belonging to the family Desulfobulbaceae. The conductivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cable Bacteria In Sediment
Cable may refer to: Mechanical * Nautical cable, an assembly of three or more ropes woven against the weave of the ropes, rendering it virtually waterproof * Wire rope, a type of rope that consists of several strands of metal wire laid into a helix ** Arresting cable, part of a system used to rapidly decelerate an aircraft as it lands ** Bowden cable, a mechanical cable for transmitting forces * Rope generally, especially a thick, heavy ("cable laid") variety Transmission * Electrical cable, an assembly of one or more wires which may be insulated, used for transmission of electrical power or signals ** Coaxial cable, an electrical cable comprising an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, coated or surrounded by a tubular conducting shield ** Power cable, a cable used to transmit electrical power ** Submarine communications cable, a cable laid on the sea bed to carry telecommunication signals between land-based stations * Fiber-optic cable, a cable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microorganisms
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from μικρός, mikrós, "small" and βίος, bíos, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradable Electronics
Biodegradable electronics are electronic circuits and devices with a limited lifetime owing to their tendency to biodegrade. Such devices are proposed to represent useful medical implant, and temporary communication sensors. Organic electronic devices as compostable material platforms have been fabricated on aluminum foil and paper to accommodate these expanded functionalities. In one embodiment of this idea, paper films were utilized as a combination substrate and gate dielectric for use with pentacene-based active layers. This idea was expanded upon to create complete circuits using foldable paper-based substrates. Silk coatings could underpin an electronic devices because it melts away when the device is no longer needed. One test device, a heating circuit powered by beaming radio waves at it, was implanted under the skin of a rat with a wound. After the wound had healed, the implant simply melts away. The US military research agency DARPA funded research on building a tiny di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Spill
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into the ocean or coastal waters, but spills may also occur on land. Oil spills may be due to releases of crude oil from tankers, offshore platforms, drilling rigs and wells, as well as spills of refined petroleum products (such as gasoline, diesel) and their by-products, heavier fuels used by large ships such as bunker fuel, or the spill of any oily refuse or waste oil. Oil spills penetrate into the structure of the plumage of birds and the fur of mammals, reducing its insulating ability, and making them more vulnerable to temperature fluctuations and much less buoyant in the water. Cleanup and recovery from an oil spill is difficult and depends upon many factors, including the type of oil spilled, the temperature of the water (affecting evapor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Fuel Cells
Microbial fuel cell (MFC) is a type of bioelectrochemical fuel cell system that generates electric current by diverting electrons produced from the microbial oxidation of reduced compounds (also known as fuel or electron donor) on the anode to oxidized compounds such as oxygen (also known as oxidizing agent or electron acceptor) on the cathode through an external electrical circuit. MFCs can be grouped into two general categories: mediated and unmediated. The first MFCs, demonstrated in the early 20th century, used a mediator: a chemical that transfers electrons from the bacteria in the cell to the anode. Unmediated MFCs emerged in the 1970s; in this type of MFC the bacteria typically have electrochemically active redox proteins such as cytochromes on their outer membrane that can transfer electrons directly to the anode. In the 21st century MFCs have started to find commercial use in wastewater treatment. History The idea of using microbes to produce electricity was conceived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are common in wetlands, where they are responsible for marsh gas, and in the digestive tracts of animals such as ruminants and many humans, where they are responsible for the methane content of belching in ruminants and flatulence in humans. In marine sediments, the biological production of methane, also termed methanogenesis, is generally confined to where sulfates are depleted, below the top layers. Moreover, methanogenic archaea populations play an indispensable role in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Others are extremophiles, found in environments such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of Earth's crust, kilometers below the surface. Physical description Methanogens are coccoid (spherical shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Reducing Bacteria
Sulfate-reducing microorganisms (SRM) or sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) are a group composed of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfate-reducing archaea (SRA), both of which can perform anaerobic respiration utilizing sulfate () as terminal electron acceptor, reducing it to hydrogen sulfide (H2S). Therefore, these sulfidogenic microorganisms "breathe" sulfate rather than Allotropes of oxygen, molecular oxygen (O2), which is the terminal electron acceptor reduced to water (H2O) in Anaerobic respiration, aerobic respiration. Most sulfate-reducing microorganisms can also reduce some other oxidized inorganic sulfur Chemical compound, compounds, such as sulfite (), dithionite (), thiosulfate (), trithionate (), tetrathionate (), Allotropes of sulfur, elemental sulfur (S8), and polysulfides (). Depending on the context, "sulfate-reducing microorganisms" can be used in a broader sense (including all species that can reduce any of these sulfur compounds) or in a narrower sense (inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
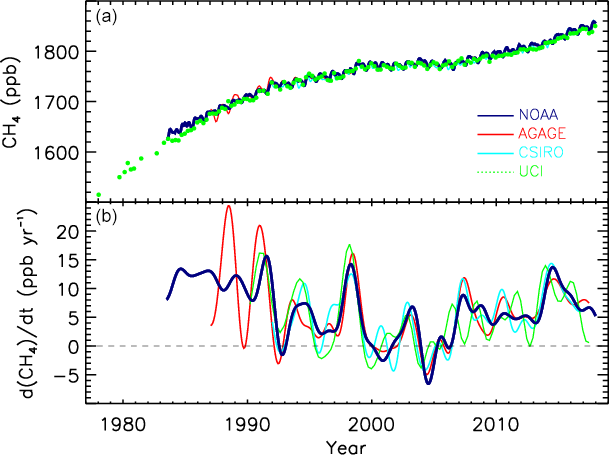
Methane Emissions
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of methane released globally was from human activities, while natural sources contributed about 40% (230 million tons). Reducing methane emissions by capturing and utilizing the gas can produce simultaneous environmental and economic benefits. Since the Industrial Revolution, methane concentrations in the atmosphere have more than doubled, and about 20 percent of the warming the planet has experienced can be attributed to the gas. About one-third (33%) of anthropogenic emissions are from gas release during the extraction and delivery of fossil fuels; mostly due to gas venting and gas leaks from both active fossil fuel infrastructure and orphan wells. Russia is the world's top methane emitter from oil and gas. Animal agriculture is a similarly lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phytoplankton productivity". Water bodies with very low nutrient levels are termed oligotrophic and those with moderate nutrient levels are termed mesotrophic. Advanced eutrophication may also be referred to as dystrophic and hypertrophic conditions. Eutrophication can affect freshwater or salt water systems. In freshwater ecosystems it is almost always caused by excess phosphorus. In coastal waters on the other hand, the main contributing nutrient is more likely to be nitrogen, or nitrogen and phosphorus together. This depends on the location and other factors. When occurring naturally, eutrophication is a very slow process in which nutrients, especially phosphorus compounds and organic matter, accumulate in water bodies. These nutrients deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The underground mine gas term for foul-smelling hydrogen sulfide-rich gas mixtures is ''stinkdamp''. Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of purified hydrogen sulfide in 1777. The British English spelling of this compound is hydrogen sulphide, a spelling no longer recommended by the Royal Society of Chemistry or the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic to humans and most other animals by inhibiting cellular respiration in a manner similar to hydrogen cyanide. When it is inhaled or it or its salts are ingested in high amounts, damage to organs occurs rapidly with symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to convulsions and death. Despite this, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the " Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |