|
CXL 1020
CXL 1020 is an experimental drug that is being investigated as a treatment for acute decompensated heart failure. CXL 1020 functions as a nitroxyl donor; nitroxyl is the reduced, protonated version of nitric oxide. Nitroxyl is capable of enhancing left ventricular contractility without increasing heart rate by modifying normal Ca2+ cycling through the sarcoplasmic reticulum as well as increasing the sensitivity of cardiac myofilaments to Ca2+. Acute decompensated heart failure Patients with acute decompensated heart failure have diminished left ventricular systolic and/or diastolic functioning. Impaired ventricular function can be a consequence of decreased sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ cycling and a corresponding decline in cardiomyocyte contraction. Reduced ventricular functioning limits the ability of the ventricles to fill with blood and pump blood to the rest of the body. Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ Cycling There are two mechanisms through which CXL 1020 is able to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Drug
An experimental drug is a medicinal product (a drug or vaccine) that has not yet received approval from governmental regulatory authorities for routine use in human or veterinary medicine. A medicinal product may be approved for use in one disease or condition but still be considered experimental for other diseases or conditions. In 2018 the United States of America signed the legislation "Right to Try", this allows individuals who fit into the criteria to try experimental drugs that are not yet deemed safe. In the United States, the body responsible for approval is the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which must grant the substance Investigational New Drug (IND) status before it can be tested in human clinical trials. IND status requires the drug's sponsor to submit an IND application that includes data from laboratory and animal testing for safety and efficacy. A drug that is made from a living organism or its products undergoes the same approval process but is called a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
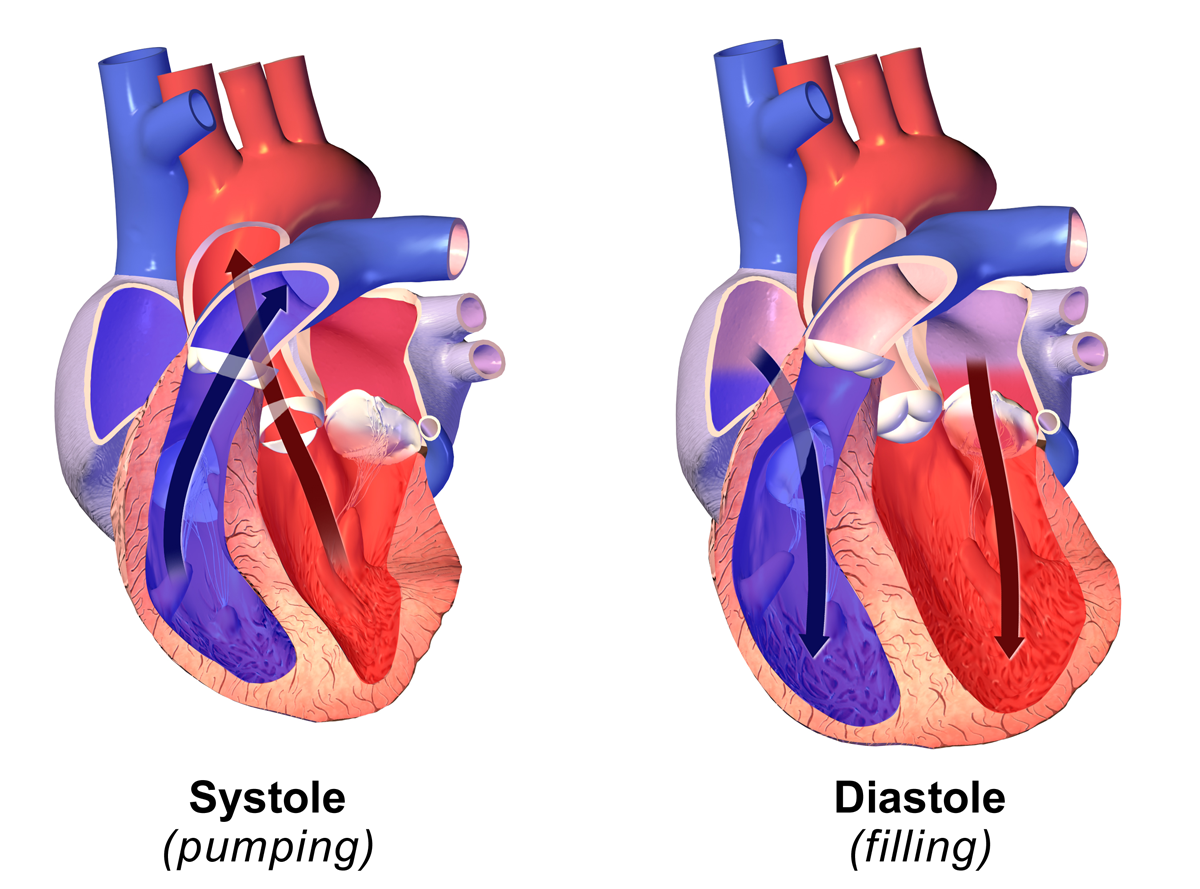
Diastolic
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles. The term originates from the Greek word (''diastolē''), meaning "dilation", from (''diá'', "apart") + (''stéllein'', "to send"). Role in cardiac cycle A typical heart rate is 75 beats per minute (bpm), which means that the cardiac cycle that produces one heartbeat, lasts for less than one second. The cycle requires 0.3 sec in ventricular systole (contraction)—pumping blood to all body systems from the two ventricles; and 0.5 sec in diastole (dilation), re-filling the four chambers of the heart, for a total of 0.8 sec to complete the cycle. Early ventricular diastole During early ventricular diastole, pressure in the two ventricles begins to drop from the peak reached during systol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryanodine Receptor 2
Ryanodine receptor 2 (RYR2) is one of a class of ryanodine receptors and a protein found primarily in cardiac muscle. In humans, it is encoded by the ''RYR2'' gene. In the process of cardiac calcium-induced calcium release, RYR2 is the major mediator for sarcoplasmic release of stored calcium ions. Structure The channel is composed of RYR2 homotetramers and FK506-binding proteins found in a 1:4 stoichiometric ratio. Calcium channel function is affected by the specific type of FK506 isomer interacting with the RYR2 protein, due to binding differences and other factors. Function The RYR2 protein functions as the major component of a calcium channel located in the sarcoplasmic reticulum that supplies ions to the cardiac muscle during systole. To enable cardiac muscle contraction, calcium influx through voltage-gated L-type calcium channels in the plasma membrane allows calcium ions to bind to RYR2 located on the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This bindi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryanodine Receptor
Ryanodine receptors (RyR for short) form a class of intracellular calcium channels in various forms of excitable animal tissue like muscles and neurons. There are three major isoforms of the ryanodine receptor, which are found in different tissues and participate in different signaling pathways involving calcium release from intracellular organelles. The RYR2 ryanodine receptor isoform is the major cellular mediator of calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) in animal cells. Etymology The ryanodine receptors are named after the plant alkaloid ryanodine which shows a high affinity to them. Isoforms There are multiple isoforms of ryanodine receptors: * RyR1 is primarily expressed in skeletal muscle * RyR2 is primarily expressed in myocardium (heart muscle) * RyR3 is expressed more widely, but especially in the brain. * Non-mammalian vertebrates typically express two RyR isoforms, referred to as RyR-alpha and RyR-beta. * Many invertebrates, including the model organisms Dros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumen (anatomy)
In biology, a lumen (plural lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine. It comes . It can refer to: *The interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows. *The interior of the gastrointestinal tract *The pathways of the bronchi in the lungs *The interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ducts *The pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vagina, splitting up in two lumina in the uterus, both of which continue through the Fallopian tubes In cell biology, a lumen is a membrane-defined space that is found inside several organelles, cellular components, or structures: *thylakoid, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondrion, or microtubule Transluminal procedures ''Transluminal procedures'' are procedures occurring through lumina, including: *Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in the lumina of, for example, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Pump (biology)
In biology, a transporter is a transmembrane protein that moves ions (or other small molecules) across a biological membrane to accomplish many different biological functions including, cellular communication, maintaining homeostasis, energy production, etc. There are different types of transporters including, pumps, uniporters, antiporters, and symporters. Active transporters or ion pumps are transporters that convert energy from various sources—including adenosine triphosphate (ATP), sunlight, and other redox reactions—to potential energy by pumping an ion up its concentration gradient. This potential energy could then be used by secondary transporters, including ion carriers and ion channels, to drive vital cellular processes, such as ATP synthesis. This page is focused mainly on ion transporters acting as pumps, but transporters can also function to move molecules through facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion does not require ATP and allows molecules, that are unable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
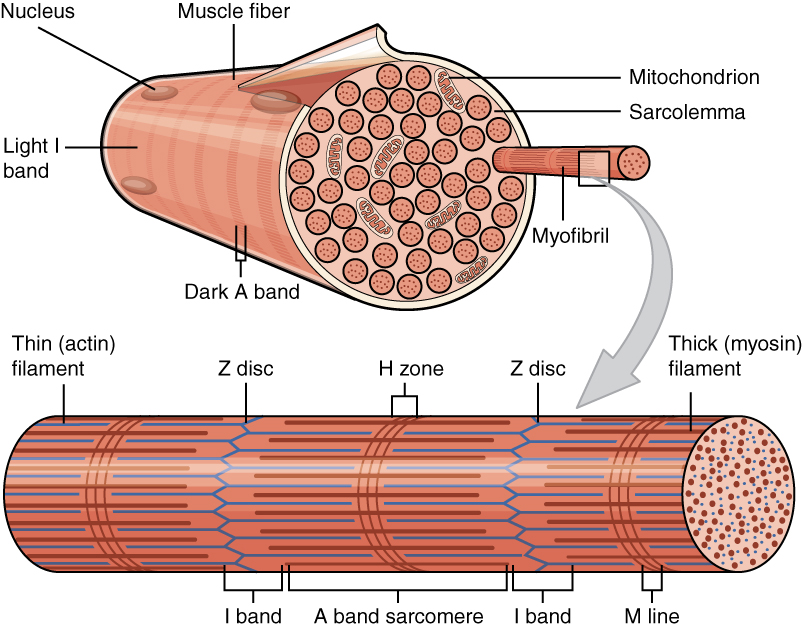
Cardiomyocyte
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's my ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Function
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium (heart), atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systole (medicine)
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and send blood to the larger, lower ventricle chambers. This flow fills the ventricles with blood, and the resulting pressure closes the valves to the atria. The ventricles now perform i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing (dyspnea), edema, leg or feet swelling, and Fatigue (medical), fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress. The condition is caused by severe congestion of multiple organs by fluid that is inadequately circulated by the failing heart. An attack of decompensation can be caused by underlying medical illness, such as myocardial infarction, an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm, infection, or thyroid disease. Treatment consists of reducing the fluid level with diuretics and improving heart function with Nitrovasodilator, nitrates, or levosimendan; other treatments such as Aquapheresis, aquapheresis ultra-filtration may also be required. Signs and symptoms Difficulty breathing, a cardinal symptom of left ventricular failure, may manifest with progressively increasing severity as the fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myofilament
Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the ''contractile proteins'' and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act together in muscle contraction, and in order of size are a thick one of mostly myosin, a thin one of mostly actin, and a very thin one of mostly titin. Types of muscle tissue are striated skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, obliquely striated muscle (found in some invertebrates), and non-striated smooth muscle. Various arrangements of myofilaments create different muscles. Striated muscle has transverse bands of filaments. In obliquely striated muscle, the filaments are staggered. Smooth muscle has irregular arrangements of filaments. Structure There are three different types of myofilaments: thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thick filaments consist primarily of a type of myosin, a motor protein – myosin II. Each thick filament is approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |