|
Ryanodine Receptor
Ryanodine receptors (RyR for short) form a class of intracellular calcium channels in various forms of excitable animal tissue like muscles and neurons. There are three major isoforms of the ryanodine receptor, which are found in different tissues and participate in different signaling pathways involving calcium release from intracellular organelles. The RYR2 ryanodine receptor isoform is the major cellular mediator of calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) in animal cells. Etymology The ryanodine receptors are named after the plant alkaloid ryanodine which shows a high affinity to them. Isoforms There are multiple isoforms of ryanodine receptors: * RyR1 is primarily expressed in skeletal muscle * RyR2 is primarily expressed in myocardium (heart muscle) * RyR3 is expressed more widely, but especially in the brain. * Non-mammalian vertebrates typically express two RyR isoforms, referred to as RyR-alpha and RyR-beta. * Many invertebrates, including the model organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
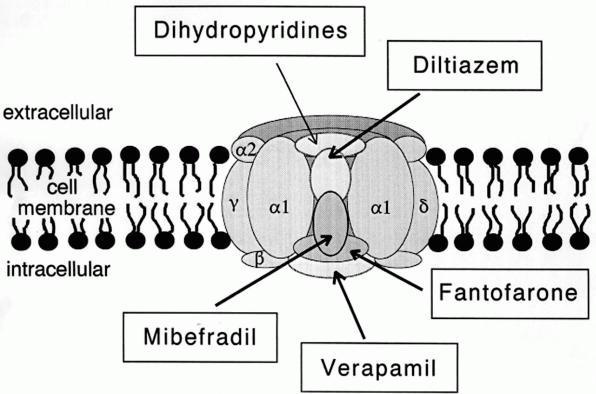 |
Calcium Channel
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels. Comparison tables The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated. Voltage-gated Ligand-gated *the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (in vasoconstriction) ** P2X receptors Page 479 Pharmacology L-type calcium channel blockers are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
RYR1
Ryanodine receptor 1 (RYR-1) also known as skeletal muscle calcium release channel or skeletal muscle-type ryanodine receptor is one of a class of ryanodine receptors and a protein found primarily in skeletal muscle Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of m .... In humans, it is encoded by the ''RYR1'' gene. Function RYR1 functions as a calcium in biology, calcium release channel in the Endoplasmic reticulum#Sarcoplasmic reticulum, sarcoplasmic reticulum, as well as a connection between the sarcoplasmic reticulum and the transverse tubule. RYR1 is associated with the dihydropyridine receptor (L-type calcium channels) within the sarcolemma of the T-tubule, which opens in response to depolarization, and thus effectively means that the RYR1 channel opens in response to depolar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Calcium Spark
A calcium spark is the microscopic release of calcium ( Ca2+) from a store known as the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), located within muscle cells. This release occurs through an ion channel within the membrane of the SR, known as a ryanodine receptor (RyR), which opens upon activation. This process is important as it helps to maintain Ca2+ concentration within the cell. It also initiates muscle contraction in skeletal and cardiac muscles and muscle relaxation in smooth muscles. Ca2+ sparks are important in physiology as they show how Ca2+ can be used at a subcellular level, to signal both local changes, known as local control, as well as whole cell changes. Activation As mentioned above, Ca2+ sparks depend on the opening of ryanodine receptors, of which there are three types: * Type 1 – found mainly in skeletal muscle * Type 2 – found mainly in the heart * Type 3 – found mainly in the brain Opening of the channel allows Ca2+ to pass from the SR, into the cell. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
L-type Calcium Channel
The L-type calcium channel (also known as the dihydropyridine channel, or DHP channel) is part of the high-voltage activated family of voltage-dependent calcium channel. "L" stands for long-lasting referring to the length of activation. This channel has four isoforms: Cav1.1, Cav1.2, Cav1.3, and Cav1.4. L-type calcium channels are responsible for the excitation- contraction coupling of skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscle, and for aldosterone secretion in endocrine cells of the adrenal cortex. They are also found in neurons, and with the help of L-type calcium channels in endocrine cells, they regulate neurohormones and neurotransmitters. They have also been seen to play a role in gene expression, mRNA stability, neuronal survival, ischemic-induced axonal injury, synaptic efficacy, and both activation and deactivation of other ion channels. In cardiac myocytes, the L-type calcium channel passes inward Ca2+ current (ICaL) and triggers calcium release from the sarcoplasmic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Dihydropyridine Receptor
Cav1.1 also known as the calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1S subunit, (CACNA1S), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CACNA1S'' gene. It is also known as CACNL1A3 and the dihydropyridine receptor (DHPR, so named due to the blocking action DHP has on it). Function This gene encodes one of the five subunits of the slowly inactivating L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel in skeletal muscle cells. Mutations in this gene have been associated with hypokalemic periodic paralysis, thyrotoxic periodic paralysis and malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Cav1.1 is a voltage-dependent calcium channel found in the transverse tubule of muscles. In skeletal muscle it associates with the ryanodine receptor RyR1 of the sarcoplasmic reticulum via a mechanical linkage. It senses the voltage change caused by the end-plate potential from nervous stimulation and propagated by sodium channels as action potentials to the T-tubules. It was previously thought that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
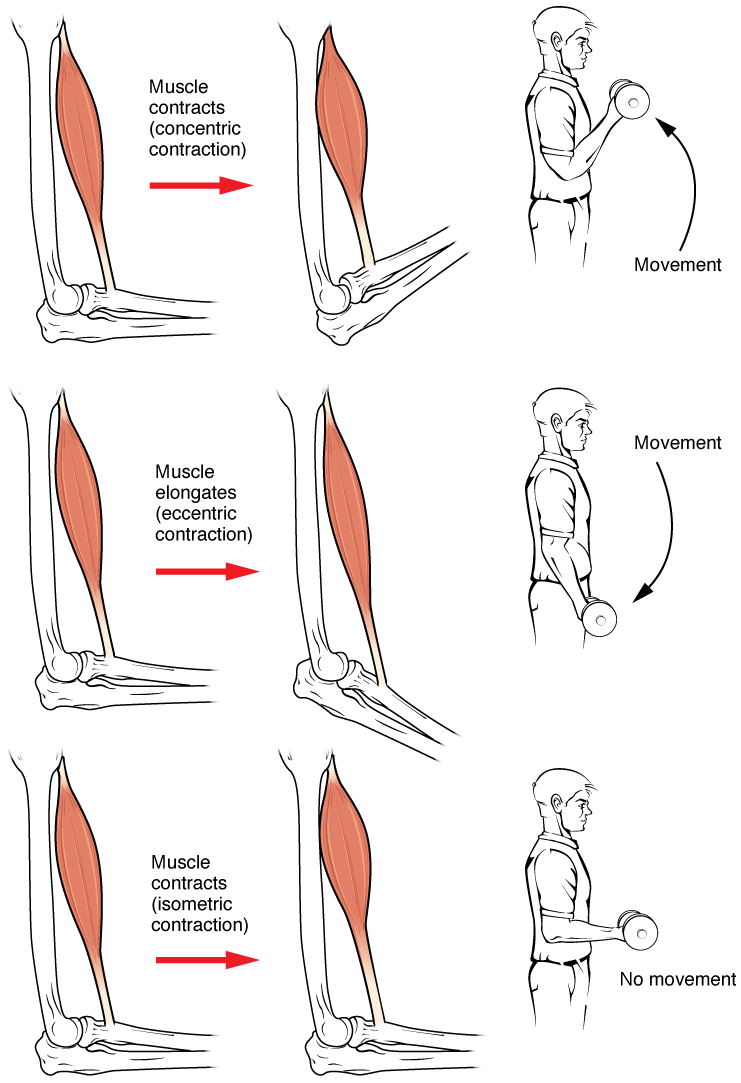 |
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the interaction of two types of filaments which are the thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are two strands of actin coiled around each, and thick filaments consist of mostly elongated proteins called myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils which are important organelles in the skeletal muscle system. Muscle contraction can also be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells that is similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in other cells. The main function of the SR is to store calcium ions (Ca2+). Calcium ion levels are kept relatively constant, with the concentration of calcium ions within a cell being 10,000 times smaller than the concentration of calcium ions outside the cell. This means that small increases in calcium ions within the cell are easily detected and can bring about important cellular changes (the calcium is said to be a second messenger). Calcium is used to make calcium carbonate (found in chalk) and calcium phosphate, two compounds that the body uses to make teeth and bones. This means that too much calcium within the cells can lead to hardening (calcification) of certain intracellular structures, including the mitochondria, leading to cell death. Therefore, it is vital that calcium ion levels are controlled tightly, and can be released in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Calcium In Biology
Calcium ions (Ca2+) contribute to the physiology and biochemistry of organisms' cells. They play an important role in signal transduction pathways, where they act as a second messenger, in neurotransmitter release from neurons, in contraction of all muscle cell types, and in fertilization. Many enzymes require calcium ions as a cofactor, including several of the coagulation factors. Extracellular calcium is also important for maintaining the potential difference across excitable cell membranes, as well as proper bone formation. Plasma calcium levels in mammals are tightly regulated, electronic-book electronic- with bone acting as the major mineral storage site. Calcium ions, Ca2+, are released from bone into the bloodstream under controlled conditions. Calcium is transported through the bloodstream as dissolved ions or bound to proteins such as serum albumin. Parathyroid hormone secreted by the parathyroid gland regulates the resorption of Ca2+ from bone, reabsorption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
RYR3
Ryanodine receptor 3 is one of a class of ryanodine receptors and a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RYR3'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is both a calcium channel and a receptor for the plant alkaloid ryanodine. RYR3 and RYR1 control the resting calcium ion concentration in skeletal muscle Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of m .... See also * Ryanodine receptor References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Ion channels EF-hand-containing proteins {{gene-15-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |