|
CPEB
CPEB, or cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein, is a highly conserved RNA-binding protein that promotes the elongation of the polyadenine tail of messenger RNA. CPEB most commonly activates the target RNA for translation, but can also act as a repressor, dependent on its phosphorylation state. In animals, CPEB is expressed in several alternative splicing isoforms that are specific to particular tissues and functions, including the self-cleaving Mammalian CPEB3 ribozyme. CPEB was first identified in ''Xenopus'' oocytes and associated with meiosis; a role has also been identified in the spermatogenesis of '' Caenorhabditis elegans''. CPEB is involved in closed-loop regulation of mRNAs that keeps them inactive. The closed-loop structure between the 3'UTR and 5'UTR inhibits translation. This has been observed in ''Xenopus laevis'' in which eIF4E bound to the 5' cap interacts with Maskin bound to CPEB on the 3' UTR creating translationally inactive transcripts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammalian CPEB3 Ribozyme
The mammalian CPEB3 ribozyme is a self cleaving non-coding RNA located in the second intron of the CPEB3 gene which belongs to a family of genes regulating messenger RNA polyadenylation. This ribozyme is highly conserved and found only in mammals. The CPEB3 ribozyme is structurally and biochemically related to the human hepatitis delta virus ribozyme The hepatitis delta virus (HDV) ribozyme is a non-coding RNA found in the hepatitis delta virus that is necessary for viral replication and is the only known human virus that utilizes ribozyme activity to infect its host. The ribozyme acts to pr .... Other HDV-like ribozymes have been identified and confirmed to be active ''in vitro'' in a number of eukaryotes. References External links * Non-coding RNA Ribozymes RNA splicing {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element
The cytoplasmic polyadenylation element (CPE) is a sequence element found in the 3' untranslated region of messenger RNA. While several sequence elements are known to regulate cytoplasmic polyadenylation, CPE is the best characterized. The most common CPE sequence is UUUUAU, though there are other variations. Binding of CPE binding proteinCPEB to this region promotes the extension of the existing polyadenine tail and, in general, activation of the mRNA for protein translation. This elongation occurs after the mRNA has been exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. A longer poly(A) tail attracts more cytoplasmic polyadenine binding proteins (PABPs) which interact with several other cytoplasmic proteins that encourage the mRNA and the ribosome to associate. The lengthening of the poly(A) tail thus has a role in increasing translational efficiency of the mRNA. The polyadenine tails are extended from approximately 40 bases to 150 bases. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation should be distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature mRNA for translation. In many bacteria, the poly(A) tail promotes degradation of the mRNA. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression. The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene terminates. The 3′-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3′ end. In some genes these proteins add a poly(A) tail at one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing. The poly(A) tail is important for the nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It is not known what causes a normal protein to misfold, but the resulting abnormal three-dimensional structure confers infectious properties by collapsing nearby protein molecules into the same shape. The word ''prion'' is derived from the term, "proteinaceous infectious particle". In comparison to all other known infectious agents such as viroids, viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites, all of which contain nucleic acids ( DNA, RNA, or both), the hypothesized role of a protein as an infectious agent stands in contrast. Prion isoforms of the prion protein (PrP), whose specific function is uncertain, are hypothesized as the cause of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), including scrapie in sheep, chronic wasting disease ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PolyA Tail
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature mRNA for translation. In many bacteria, the poly(A) tail promotes degradation of the mRNA. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression. The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene terminates. The 3′-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3′ end. In some genes these proteins add a poly(A) tail at one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing. The poly(A) tail is important for the nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5'UTR
The 5′ untranslated region (also known as 5′ UTR, leader sequence, transcript leader, or leader RNA) is the region of a messenger RNA (mRNA) that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of translation of a transcript by differing mechanisms in viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. While called untranslated, the 5′ UTR or a portion of it is sometimes translated into a protein product. This product can then regulate the translation of the main coding sequence of the mRNA. In many organisms, however, the 5′ UTR is completely untranslated, instead forming a complex secondary structure to regulate translation. The 5′ UTR has been found to interact with proteins relating to metabolism, and within the 5′ UTR. In addition, this region has been involved in transcription regulation, such as the sex-lethal gene in ''Drosophila''. Regulatory elements within 5′ UTRs have also been linked to mRNA export. General structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3' UTR
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally influence gene expression. During gene expression, an mRNA molecule is transcribed from the DNA sequence and is later translated into a protein. Several regions of the mRNA molecule are not translated into a protein including the 5' cap, 5' untranslated region, 3′ untranslated region and poly(A) tail. Regulatory regions within the 3′-untranslated region can influence polyadenylation, translation efficiency, localization, and stability of the mRNA. The 3′-UTR contains both binding sites for regulatory proteins as well as microRNAs (miRNAs). By binding to specific sites within the 3′-UTR, miRNAs can decrease gene expression of various mRNAs by either inhibiting translation or directly causing degradation of the transcript. The 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3'UTR
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally influence gene expression. During gene expression, an mRNA molecule is transcribed from the DNA sequence and is later translated into a protein. Several regions of the mRNA molecule are not translated into a protein including the 5' cap, 5' untranslated region, 3′ untranslated region and poly(A) tail. Regulatory regions within the 3′-untranslated region can influence polyadenylation, translation efficiency, localization, and stability of the mRNA. The 3′-UTR contains both binding sites for regulatory proteins as well as microRNAs (miRNAs). By binding to specific sites within the 3′-UTR, miRNAs can decrease gene expression of various mRNAs by either inhibiting translation or directly causing degradation of the transcript. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditions) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
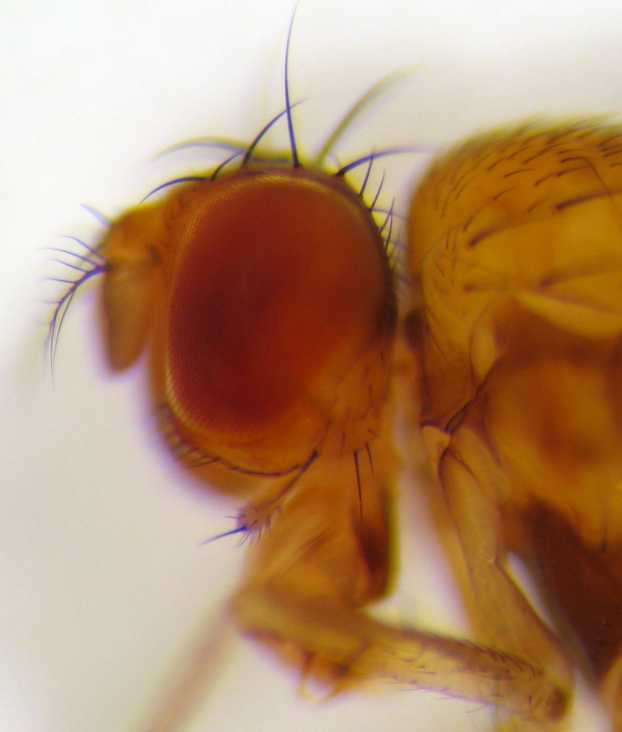
Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies (sometimes referred to as "true fruit flies"); tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly. One species of ''Drosophila'' in particular, '' D. melanogaster'', has been heavily used in research in genetics and is a common model organism in developmental biology. The terms "fruit fly" and "''Drosophila''" are often used synonymously with ''D. melanogaster'' in modern biological literature. The entire genus, however, contains more than 1,500 species and is very diverse in appearan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplysia Californica
The California sea hare (''Aplysia californica'') is a species of sea slug in the sea hare family, Aplysiidae.Rosenberg, G.; Bouchet, P. (2011). Aplysia californica J. G. Cooper, 1863. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=240765 on 2012-03-31 It is found in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California in the United States and northwestern Mexico. Distribution ''A. californica'' is found along the coast of California, United States, and northwestern Mexico (including the Gulf of California). ''Aplysia'' species inhabit the photic zone to graze on algae, mainly the intertidal, usually not deeper than . Description The maximum length recorded for the California sea hare is when crawling, thus fully extended, although most adult specimens are half this size or smaller. Adult animals can weigh up to . A closely related species, ''Aplysia vaccaria'', the black sea hare, can grow to be larger still. A California ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |