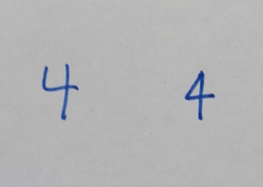|
CMOS 4000 Series
The 4000 series is a CMOS logic family of integrated circuits (ICs) first introduced in 1968 by RCA. It had a supply voltage range of 5V to 20V, which is much wider than any contemporary logic family. Almost all IC manufacturers active during this initial era fabricated models for this series. Its naming convention is still in use today. History The 4000 series was introduced as the ''CD4000 COS/MOS'' series in 1968 by RCA as a lower power and more versatile alternative to the 7400 series of transistor-transistor logic (TTL) chips. The logic functions were implemented with the newly introduced CMOS, Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor (CMOS) technology. While initially marketed with "COS/MOS" labeling by RCA (which stood for Complementary Symmetry Metal-Oxide Semiconductor), the shorter ''CMOS'' terminology emerged as the industry preference to refer to the technology. The first chips in the series were designed by a group led by Albert Medwin. Wide adoption was initiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cd4007
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as T helper cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It was discovered in the late 1970s and was originally known as leu-3 and T4 (after the OKT4 Monoclonal antibodies, monoclonal antibody that reacted with it) before being named CD4 in 1984. In humans, the CD4 protein is encoded by the ''CD4'' gene. T helper cell, CD4+ T helper cells are leukocytes, white blood cells that are an essential part of the human immune system. They are often referred to as CD4 cells, T-helper cells or T4 cells. They are called helper cells because one of their main roles is to send signals to other types of immune cells, including CD8 cytotoxic t cell, killer cells, which then destroy the infectious particle. If CD4 cells become depleted, for example in untreated HIV infection, or following immune suppressio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Decoder
In digital electronics, a binary decoder is a combinational logic circuit that converts binary information from the n coded inputs to a maximum of 2n unique outputs. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including instruction decoding, data multiplexing and data demultiplexing, seven segment displays, and as address decoders for memory and port-mapped I/O. There are several types of binary decoders, but in all cases a decoder is an electronic circuit with multiple input and multiple output signals, which converts every unique combination of input states to a specific combination of output states. In addition to integer data inputs, some decoders also have one or more "enable" inputs. When the enable input is negated (disabled), all decoder outputs are forced to their inactive states. Depending on its function, a binary decoder will convert binary information from n input signals to as many as 2n unique output signals. Some decoders have less than 2n output lines; in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary-coded Decimal
In computing and electronic systems, binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four or eight. Sometimes, special bit patterns are used for a sign or other indications (e.g. error or overflow). In byte-oriented systems (i.e. most modern computers), the term ''unpacked'' BCD usually implies a full byte for each digit (often including a sign), whereas ''packed'' BCD typically encodes two digits within a single byte by taking advantage of the fact that four bits are enough to represent the range 0 to 9. The precise 4-bit encoding, however, may vary for technical reasons (e.g. Excess-3). The ten states representing a BCD digit are sometimes called '' tetrades'' (for the nibble typically needed to hold them is also known as a tetrade) while the unused, don't care-states are named , ''pseudo-decimals'' or ''pseudo-decimal digits''. BCD's main virtue, in comparison to binary posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter (digital)
In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores (and sometimes displays) the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock. The most common type is a sequential digital logic circuit with an input line called the ''clock'' and multiple output lines. The values on the output lines represent a number in the binary or BCD number system. Each pulse applied to the clock input increments or decrements the number in the counter. A counter circuit is usually constructed of several flip-flops connected in a cascade. Counters are a very widely used component in digital circuits, and are manufactured as separate integrated circuits and also incorporated as parts of larger integrated circuits. Electronic counters An electronic counter is a sequential logic circuit that has a clock input signal and a group of output signals that represent an integer "counts" value. Upon each qualified clock edge, the circuit will incremen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D Flip-flop
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop is a device which stores a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANT Nachrichtentechnik DBT-03 - National Semiconductor CD4001BCJ-0020
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of 22,000 species have been classified. They are easily identified by their geniculate (elbowed) antennae and the distinctive node-like structure that forms their slender waists. Ants form colonies that range in size from a few dozen predatory individuals living in small natural cavities to highly organised colonies that may occupy large territories and consist of millions of individuals. Larger colonies consist of various castes of sterile, wingless females, most of which are workers (ergates), as well as soldiers (dinergates) and other specialised groups. Nearly all ant colonies also have some fertile males called "drones" and one or more fertile females called "queens" (gynes). The colonies are described as superorganisms because the ants appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4001 Pinout
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the other han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4001 Functional Diagram
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the other hand, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adder (electronics)
An adder, or summer, is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. In many computers and other kinds of microprocessor, processors adders are used in the arithmetic logic units (ALUs). They are also used in other parts of the processor, where they are used to calculate address space, addresses, database index, table indices, increment and decrement operators and similar operations. Although adders can be constructed for many number representations, such as binary-coded decimal or excess-3, the most common adders operate on binary numbers. In cases where two's complement or ones' complement is being used to represent negative numbers, it is trivial to modify an adder into an adder–subtractor. Other signed number representations require more logic around the basic adder. Binary adders Half adder The half adder adds two single binary digits ''A'' and ''B''. It has two outputs, sum (''S'') and carry (''C''). The carry signal represents an Integer overflow, overflow int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Counter
A ring counter is a type of counter composed of flip-flops connected into a shift register, with the output of the last flip-flop fed to the input of the first, making a "circular" or "ring" structure. There are two types of ring counters: * A straight ring counter, also known as a one-hot counter, connects the output of the last shift register to the first shift register input and circulates a single one (or zero) bit around the ring. * A twisted ring counter, also called switch-tail ring counter, walking ring counter, Johnson counter, or Möbius counter, connects the complement of the output of the last shift register to the input of the first register and circulates a stream of ones followed by zeros around the ring. Four-bit ring-counter sequences Properties Ring counters are often used in hardware design (e.g. ASIC and FPGA design) to create finite-state machines. A binary counter would require an adder circuit which is substantially more complex than a ring count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
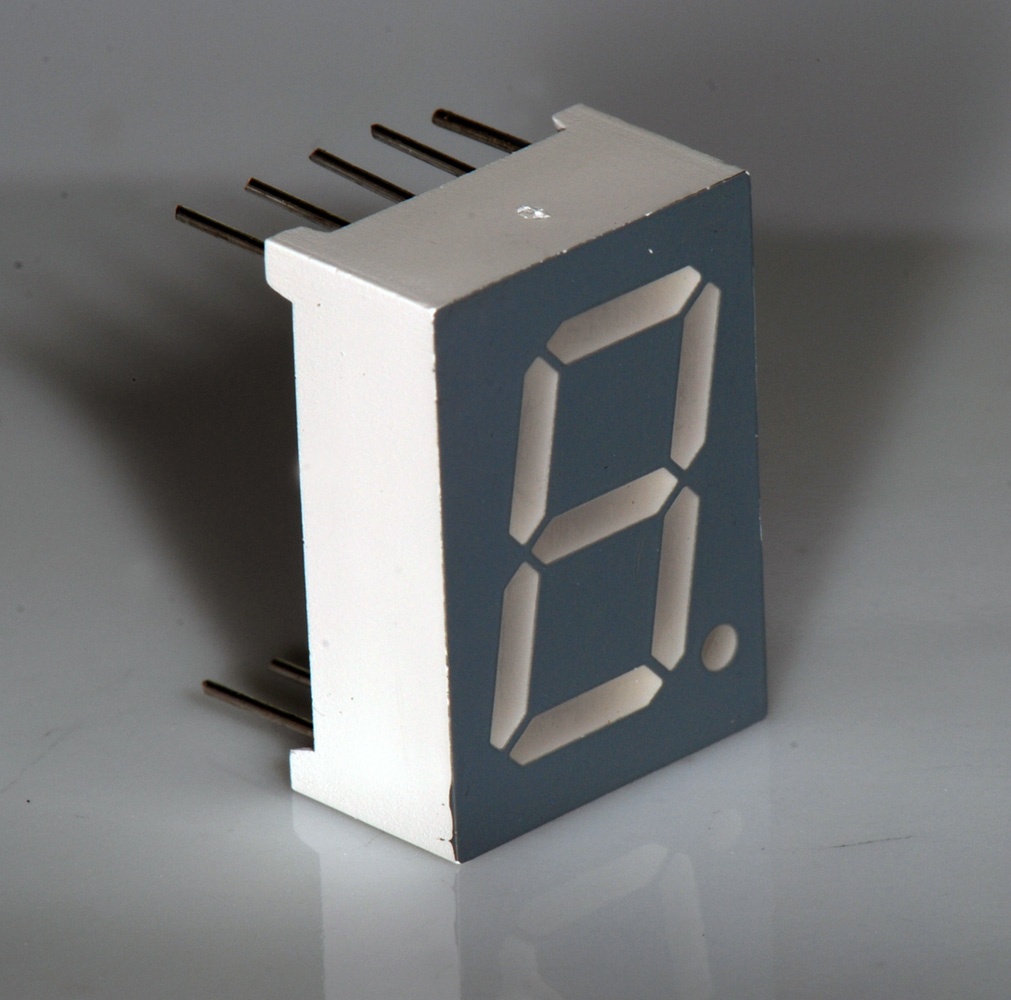
Seven-segment Display
A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, and other electronic devices that display numerical information. History Seven-segment representation of figures can be found in patents as early as 1903 (in ), when Carl Kinsley invented a method of telegraphically transmitting letters and numbers and having them printed on tape in a segmented format. In 1908, F. W. Wood invented an 8-segment display, which displayed the number 4 using a diagonal bar (). In 1910, a seven-segment display illuminated by incandescent bulbs was used on a power-plant boiler room signal panel. They were also used to show the dialed telephone number to operators during the transition from manual to automatic telephone dialing. They did not achieve widespread use until the advent of LEDs in the 1970 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |