|
CMB
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space. It is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination when the first atoms were formed. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark (see: Olbers' paradox). However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background brightness, or glow, almost uniform, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale form. These models offer a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The overall uniformity of the Universe, known as the flatness problem, is explained through cosmic inflation: a sudden and very rapid expansion of space during the earliest moments. However, physics currently lacks a widely accepted theory of quantum gravity that can successfully model the earliest conditions of the Big Bang. Crucially, these models are compatible with the Hubble–Lemaître law—the observation that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmologists
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate.For an overview, see Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed those physical laws to be understood. Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond the Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
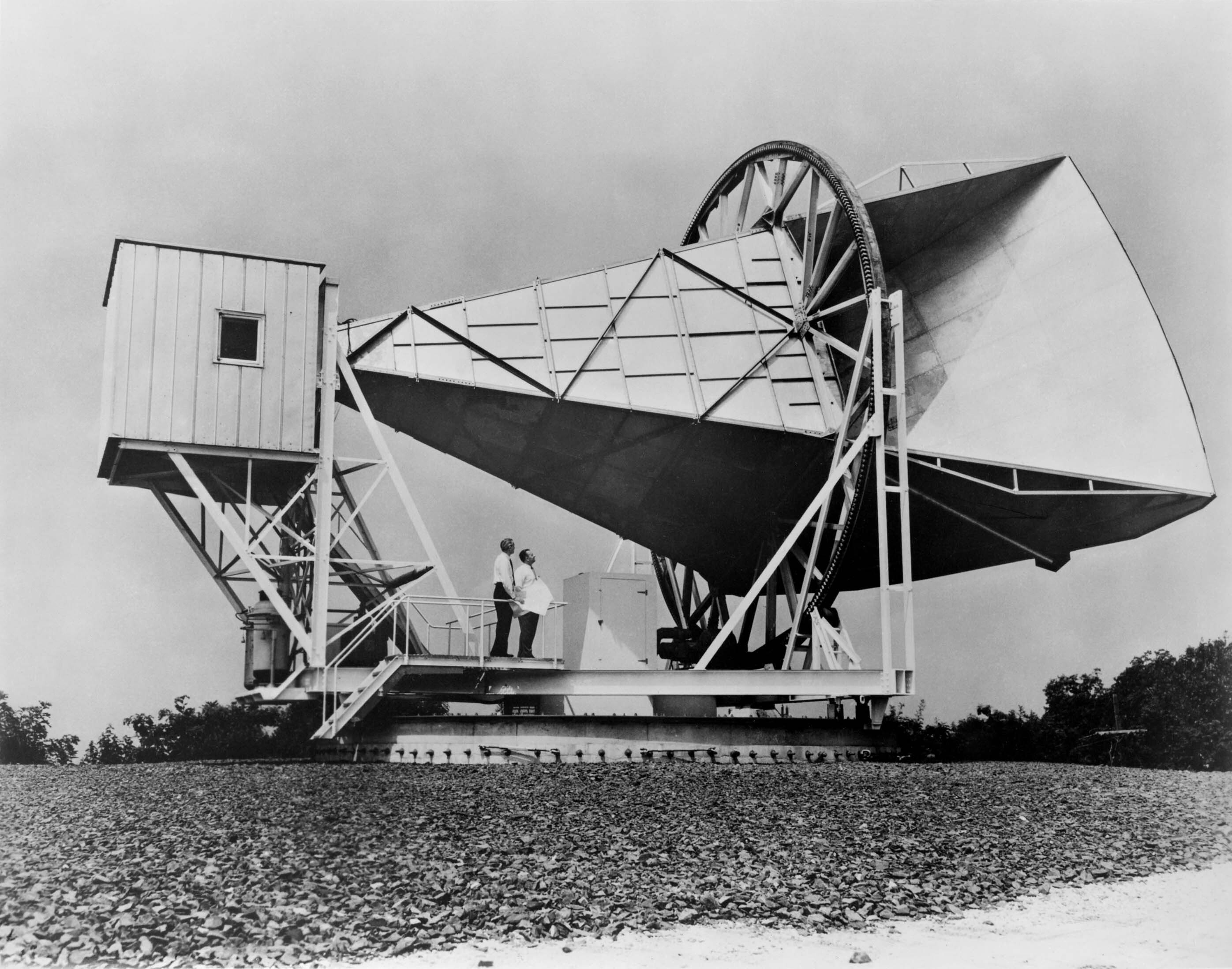
Discovery Of Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
The discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation constitutes a major development in modern physical cosmology. In 1964, US physicist Arno Allan Penzias and radio-astronomer Robert Woodrow Wilson discovered the CMB, estimating its temperature as 3.5 K, as they experimented with the Holmdel Horn Antenna. The new measurements were accepted as important evidence for a hot early Universe ( big bang theory) and as evidence against the rival steady state theory as theoretical work around 1950D.W. Sciama - https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-94-009-0655-6_1 Accessed 13 August 2018 showed the need for a CMB for consistency with the simplest relativistic universe models. In 1978, Penzias and Wilson were awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics for their joint measurement. There had been a prior measurement of the cosmic background radiation (CMB) by Andrew McKellar in 1941 at an effective temperature of 2.3 K using CN stellar absorption lines observed by W. S. Adams. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ranges as microwaves; the above broad definition includes both Ultra high frequency, UHF and Extremely high frequency, EHF (millimeter wave) bands. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 0.3 m and 3 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire Super high frequency, SHF band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. Frequencies in the microwave range are often referred to by their Radio band#IEEE, IEEE radar band designations: S band, S, C band (IEEE), C, X band, X, Ku band, Ku, K band (IEEE), K, or Ka band, Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' is not meant to suggest a wavelength in the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olbers' Paradox
Olbers's paradox, also known as the dark night sky paradox, is an argument in astrophysics and physical cosmology that says that the darkness of the night sky conflicts with the assumption of an infinite and eternal static universe. In the hypothetical case that the universe is static, homogeneous at a large scale, and populated by an infinite number of stars, any line of sight from Earth must end at the surface of a star and hence the night sky should be completely illuminated and very bright. This contradicts the observed darkness and non-uniformity of the night. The darkness of the night sky is one of the pieces of evidence for a dynamic universe, such as the Big Bang model. That model explains the observed non-uniformity of brightness by invoking expansion of the universe, which increases the wavelength of visible light originating from the Big Bang to microwave scale via a process known as ''redshift''. The resulting microwave radiation background has wavelengths much l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch Of Recombination
In cosmology, recombination refers to the epoch during which charged electrons and protons first became bound to form electrically neutral hydrogen atoms. Recombination occurred about 370,000 yearsRecombination time frames: * Edward L. Wright'Javascript Cosmology Calculator(last modified 23 July 2018). With a default H_0 = (based on ), the calculated age of the universe with a redshift of ''z'' = is in agreement with Olive and Peacock (about 370,000 years). * : "Going forward in time now, the temperature declined, and at ''T''∼3000 K, few of the photons in the radiation field, even in its high-energy tail, had the energy required to ionize a hydrogen atom. Most of the electrons and protons then recombined. Once this happened, at a time ''t''rec = 380,000 yr after the Big Bang, the major source of opacity disappeared, and the Universe became transparent to radiation of most frequencies." * : "The million dollar question is now, 'when did recombination happen? ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric Expansion Of Space
The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between any two given gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself changes. The universe does not expand "into" anything and does not require space to exist "outside" it. This expansion involves neither space nor objects in space "moving" in a traditional sense, but rather it is the metric (which governs the size and geometry of spacetime itself) that changes in scale. As the spatial part of the universe's spacetime metric increases in scale, objects become more distant from one another at ever-increasing speeds. To any observer in the universe, it appears that all of space is expanding, and that all but the nearest galaxies (which are bound by gravity) recede at speeds that are proportional to their distance from the observer. While objects within space cannot travel faster than light, this limitation does not apply to the effects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombination (cosmology)
In cosmology, recombination refers to the epoch during which charged electrons and protons first became bound to form electrically neutral hydrogen atoms. Recombination occurred about 370,000 yearsRecombination time frames: * Edward L. Wright'Javascript Cosmology Calculator(last modified 23 July 2018). With a default H_0 = (based on ), the calculated age of the universe with a redshift of ''z'' = is in agreement with Olive and Peacock (about 370,000 years). * : "Going forward in time now, the temperature declined, and at ''T''∼3000 K, few of the photons in the radiation field, even in its high-energy tail, had the energy required to ionize a hydrogen atom. Most of the electrons and protons then recombined. Once this happened, at a time ''t''rec = 380,000 yr after the Big Bang, the major source of opacity disappeared, and the Universe became transparent to radiation of most frequencies." * : "The million dollar question is now, 'when did recombination ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Woodrow Wilson
Robert Woodrow Wilson (born January 10, 1936) is an American astronomer who, along with Arno Allan Penzias, discovered cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) in 1964. The pair won the 1978 Nobel Prize in Physics for their discovery. While doing tests and experiments with the Holmdel Horn Antenna at Bell Labs in Holmdel Township, New Jersey, Wilson and Penzias discovered a source of noise in the atmosphere that they could not explain. After removing all potential sources of noise, including pigeon droppings on the antenna, the noise was finally identified as CMB, which served as important corroboration of the Big Bang theory. In 1970, Wilson led a team that made the first detection of a rotational spectral line of carbon monoxide (CO) in an astronomical object, the Orion Nebula, and eight other galactic sources. Subsequently, CO observations became the standard method of tracing cool molecular interstellar gas, and detection of CO was the foundational event for the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Body
A black body or blackbody is an idealized physical object, physical body that absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence. The name "black body" is given because it absorbs all colors of light. A black body also emits black-body radiation. In contrast, a white body is one with a "rough surface that reflects all incident rays completely and uniformly in all directions." A black body in thermal equilibrium (that is, at a constant temperature) emits electromagnetic black-body radiation. The radiation is emitted according to Planck's law, meaning that it has a frequency spectrum, spectrum that is determined by the temperature alone (see figure at right), not by the body's shape or composition. An ideal black body in thermal equilibrium has two main properties: #It is an ideal emitter: at every frequency, it emits as much or more thermal radiative energy as any o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often used interchangeably. However, an astronomical body or celestial body is a single, tightly bound, contiguous entity, while an astronomical or celestial ''object'' is a complex, less cohesively bound structure, which may consist of multiple bodies or even other objects with substructures. Examples of astronomical objects include planetary systems, star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies, while asteroids, moons, planets, and stars are astronomical bodies. A comet may be identified as both body and object: It is a ''body'' when referring to the frozen nucleus of ice and dust, and an ''object'' when describing the entire comet with its diffuse coma and tail. History Astronomical objects such as stars, planets, nebulae, asteroids and comet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arno Penzias
Arno Allan Penzias (; born April 26, 1933) is an American physicist, radio astronomer and Nobel laureate in physics. Along with Robert Woodrow Wilson, he discovered the cosmic microwave background radiation, which helped establish the Big Bang theory of cosmology. Early life and education Penzias was born in Munich, Germany, the son of Justine (née Eisenreich) and Karl Penzias, who ran a leather business. His grandparents had come to Munich from Poland and were among the leaders of the Reichenbach Strasse Shul. At age six, he and his brother Gunther were among the Jewish children evacuated to Britain as part of the Kindertransport rescue operation. Some time later, including the Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1978 ''The Origin of Elements'' his parents also fled Nazi Germany for the U.S., and the family settled in the Garment District of New York City in 1940. In 1946, Penzias became a naturalized citizen of the United States. He graduated from Brooklyn Technical High School in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |