Arno Penzias on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arno Allan Penzias (; born April 26, 1933) is an American
 Penzias went on to work at
Penzias went on to work at Team / Arno Penzias
/ref>
The first part of an article authored by Arno Penzias that was published in Science Reporter magazine
The second part of an article authored by Arno Penzias entitled Ideas
A Whisper From Space
(IMDb)
Nürnberger Astronomische Gesellschaft e.V.: Web-Seite Arno-Penzias-Radioteleskop (german)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Penzias, Arno Allan 1933 births Living people Nobel laureates in Physics American Nobel laureates Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences American astronomers Jewish astronomers City College of New York alumni Columbia University alumni Columbia University staff German emigrants to the United States Jewish American scientists Jewish physicists People from Highland Park, New Jersey Kindertransport refugees Scientists at Bell Labs Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Radio astronomers Members of the United States National Academy of Engineering Brooklyn Technical High School alumni Scientists from New York (state) Fellows of the American Physical Society
physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate ca ...
, radio astronomer and Nobel laureate
The Nobel Prizes ( sv, Nobelpriset, no, Nobelprisen) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make ...
in physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which rel ...
. Along with Robert Woodrow Wilson, he discovered the cosmic microwave background radiation
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space ...
, which helped establish the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from t ...
theory of cosmology.
Early life and education
Penzias was born inMunich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, the son of Justine (née Eisenreich) and Karl Penzias, who ran a leather business. His grandparents had come to Munich from Poland and were among the leaders of the Reichenbach Strasse Shul. At age six, he and his brother Gunther were among the Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
children evacuated to Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
as part of the Kindertransport
The ''Kindertransport'' (German for "children's transport") was an organised rescue effort of children (but not their parents) from Nazi-controlled territory that took place during the nine months prior to the outbreak of the Second Worl ...
rescue operation. Some time later, including the Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1978 ''The Origin of Elements'' his parents also fled Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
for the U.S., and the family settled in the Garment District of New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
in 1940. In 1946, Penzias became a naturalized citizen
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-citizen of a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. It may be done automatically by a statute, i.e., without any effort on the part of the i ...
of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
. He graduated from Brooklyn Technical High School
Brooklyn Technical High School, commonly called Brooklyn Tech and administratively designated High School 430, is an elite public high school in New York City that specializes in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. It is one of th ...
in 1951 and after enrolling to study chemistry at the City College of New York
The City College of the City University of New York (also known as the City College of New York, or simply City College or CCNY) is a public university within the City University of New York (CUNY) system in New York City. Founded in 1847, Cit ...
, he changed majors and graduated 1954 with a degree in physics, ranked near the top of his class.
Following graduation, Penzias served for two years as a radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
officer in the U.S. Army Signal Corps. This led to a research assistantship in the Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manha ...
Radiation Laboratory, which was then heavily involved in microwave physics. Penzias worked under Charles Townes
Charles Hard Townes (July 28, 1915 – January 27, 2015) was an American physicist. Townes worked on the theory and application of the maser, for which he obtained the fundamental patent, and other work in quantum electronics associated w ...
, who later invented the maser
A maser (, an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves through amplification by stimulated emission. The first maser was built by Charles H. Townes, Jam ...
.
Next, Penzias enrolled as a graduate student at Columbia in 1956. He earned a Ph.D. in physics from Columbia University in 1962.
Career
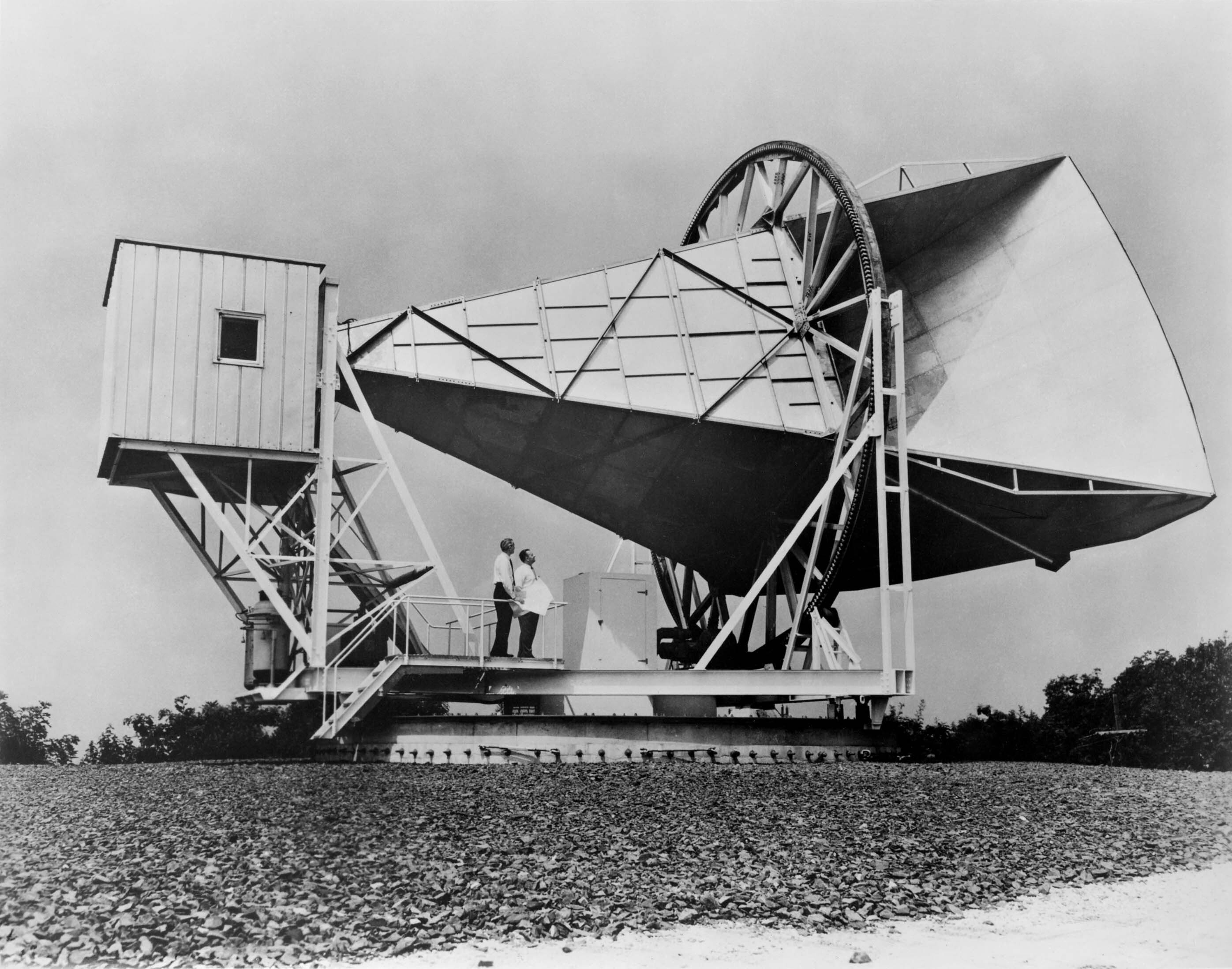
 Penzias went on to work at
Penzias went on to work at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
in Holmdel, New Jersey
Holmdel Township (usually shortened to Holmdel) is a township in Monmouth County, New Jersey, United States. The township is centrally located in the Raritan Valley region, being within the regional and cultural influence of the Raritan Bays ...
, where, with Robert Woodrow Wilson, he worked on ultra-sensitive cryogenic microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different fre ...
receivers, intended for radio astronomy observations. In 1964, on building their most sensitive antenna/receiver system, the pair encountered radio noise which they could not explain. It was far less energetic than the radiation given off by the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked ey ...
, and it was isotropic, so they assumed their instrument was subject to interference by terrestrial sources. They tried, and then rejected, the hypothesis that the radio noise emanated from New York City. An examination of the microwave horn antenna
A horn antenna or microwave horn is an antenna that consists of a flaring metal waveguide shaped like a horn to direct radio waves in a beam. Horns are widely used as antennas at UHF and microwave frequencies, above 300 MHz. They are ...
showed it was full of bat and pigeon droppings (which Penzias described as "white dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the m ...
material"). After the pair removed the dung buildup the noise remained. Having rejected all sources of interference, Penzias contacted Robert Dicke
Robert Henry Dicke (; May 6, 1916 – March 4, 1997) was an American astronomer and physicist who made important contributions to the fields of astrophysics, atomic physics, cosmology and gravity. He was the Albert Einstein Professor in Scien ...
, who suggested it might be the background radiation predicted by some cosmological theories. The pair agreed with Dicke to publish side-by-side letters in the Astrophysical Journal, with Penzias and Wilson describing their observations and Dicke suggesting the interpretation as the cosmic microwave background radiation
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space ...
(CMB), the radio remnant of the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from t ...
. This allowed astronomers to confirm the Big Bang, and to correct many of their previous assumptions about it.
He was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, ...
and the National Academy of Sciences in 1975. Penzias and Wilson received the 1978 Nobel Prize, sharing it with Pyotr Leonidovich Kapitsa (Kapitsa's work on Low-temperature physics
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cr ...
was unrelated to Penzias and Wilson's). In 1977, the two had received the Henry Draper Medal of the National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nat ...
. In 1979, Penzias received the Golden Plate Award of the American Academy of Achievement
The American Academy of Achievement, colloquially known as the Academy of Achievement, is a non-profit educational organization that recognizes some of the highest achieving individuals in diverse fields and gives them the opportunity to meet o ...
. He is also the recipient of The International Center in New York's Award of Excellence. In 1998, he was awarded the IRI Medal from the Industrial Research Institute
Innovation Research Interchange (IRI) is a division of the National Association of Manufacturers, a nonprofit association based in Washington, D. C., United States. IRI was founded as a private non-profit in 1938 and merged with the NAM in 2022. ...
.
On April 26, 2019 the Nürnberger Astronomische Gesellschaft e.V. (NAG) inaugurated the 3-m radio telescope at the Regiomontanus-Sternwarte, the public observatory of Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
, and dedicated this instrument to Arno Penzias.
Penzias has been a resident of Highland Park, New Jersey
Highland Park is a borough in Middlesex County, New Jersey, United States in the New York City metropolitan area. The borough is located on the northern banks of the Raritan River, in the Raritan Valley region. As of the 2020 United States Cen ...
. He has a son, David, and two daughters, Mindy Penzias Dirks, PhD, and Rabbi Shifra (Laurie) Weiss-Penzias. He currently serves as a venture partner at New Enterprise Associates
New Enterprise Associates (NEA) is an American-based venture capital firm. NEA focuses investment stages ranging from seed stage through growth stage across an array of industry sectors. With ~$25 billion in committed capital, NEA is one of the w ...
./ref>
Works
* * * * * Cite Video , BBC/WGBH BOSTON , NOVA #519 , A Whisper From Space , Copyright 1978 , Available With Permission , Consolidated Aircraft - Ronkonkoma, New YorkSee also
* Discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation *List of Jewish Nobel laureates
Nobel Prizes have been awarded to over 900 individuals, of whom at least 20% were Jews.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
The number of Jews receiving Nobel prizes has been the subject of some attention.*
*
*"Jews rank high among winners of Nobel, but why ...
References
External links
* including the Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1978 ''The Origin of Elements''The first part of an article authored by Arno Penzias that was published in Science Reporter magazine
The second part of an article authored by Arno Penzias entitled Ideas
A Whisper From Space
(IMDb)
Nürnberger Astronomische Gesellschaft e.V.: Web-Seite Arno-Penzias-Radioteleskop (german)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Penzias, Arno Allan 1933 births Living people Nobel laureates in Physics American Nobel laureates Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences American astronomers Jewish astronomers City College of New York alumni Columbia University alumni Columbia University staff German emigrants to the United States Jewish American scientists Jewish physicists People from Highland Park, New Jersey Kindertransport refugees Scientists at Bell Labs Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Radio astronomers Members of the United States National Academy of Engineering Brooklyn Technical High School alumni Scientists from New York (state) Fellows of the American Physical Society