|
CCoV-HuPn-2018
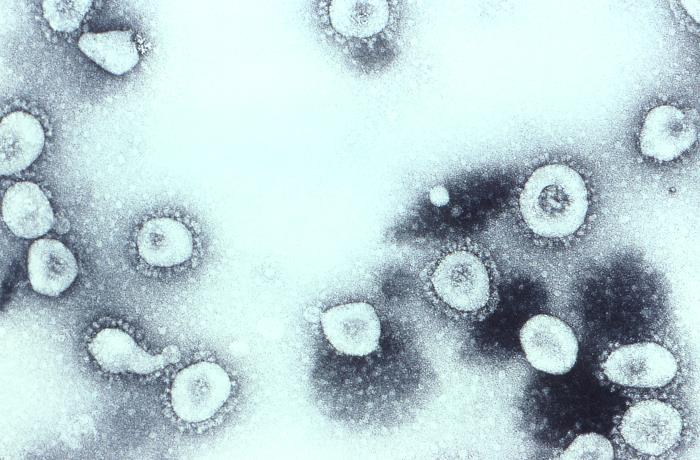
Canine coronavirus HuPn-2018, or CCoV-HuPn-2018, is a virus first discovered in a surveillance study in Sarawak, Malaysia, in hospitalized human pneumonia patients. It may be the eighth coronavirus known to cause disease in humans, but no human-to-human transmission has been seen. This is a canine-feline recombinant alphacoronavirus (genotype II) related to the CCoV-II strain of ''Alphacoronavirus 1'' with part of the FCoV in S2 domain and a specific 12 amino acids deletion Deletion or delete may refer to: Computing * File deletion, a way of removing a file from a computer's file system * Code cleanup, a way of removing unnecessary variables, data structures, cookies, and temporary files in a programming language * ... in the N protein. References {{Coronaviridae Animal virology Alphacoronaviruses Zoonoses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphacoronavirus
Alphacoronaviruses (Alpha-CoV) are members of the first of the four genera (''Alpha''-, '' Beta-'', '' Gamma-'', and '' Delta-'') of coronaviruses. They are positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses that infect mammals, including humans. They have spherical virions with club-shaped surface projections formed by trimers of the spike protein, and a viral envelope. Alphacoronaviruses are in the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'' of the family ''Coronaviridae''. Both the ''Alpha''- and ''Betacoronavirus'' lineages descend from the bat viral gene pool. Alphacoronaviruses were previously known as "phylogroup 1 coronaviruses". The Alphacoronavirus genus is very diverse, particularly in bats. Most bat originating strains haven't been successfully isolated and cultured in laboratory. Alphacoronaviruses infecting other mammal species have been much better studied, see List of Coronavirus live isolates. Etymology The name alphacoronavirus is derived from Ancient Greek ἄλφα ( álp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canine Coronavirus
Canine coronavirus (CCoV) is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which is a member of the species ''Alphacoronavirus 1.'' It causes a highly contagious intestinal disease worldwide in dogs. The infecting virus enters its host cell by binding to the APN receptor. It was discovered in 1971 in Germany during an outbreak in sentry dogs. The virus is a member of the genus ''Alphacoronavirus'' and subgenus ''Tegacovirus''. Canine enteric coronavirus Pathology The virus invades and replicates in the villi of the small intestine. Intestinal disease may be related to virus-induced apoptosis (programmed cell death) of cells of the epithelial mucosa of the small intestine. Canine coronavirus was originally thought to cause serious gastrointestinal disease, but now most cases are considered to be very mild or without symptoms. A more serious complication of canine coronavirus occurs when the dog is also infected with canine parvovirus. Coronavirus infection of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarawak
Sarawak (; ) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia. The largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak is located in northwest Borneo Island, and is bordered by the Malaysian state of Sabah to the northeast, Kalimantan (the Indonesian portion of Borneo) to the south, and Brunei in the north. The capital city, Kuching, is the largest city in Sarawak, the economic centre of the state, and the seat of the Sarawak state government. Other cities and towns in Sarawak include Miri, Malaysia, Miri, Sibu, and Bintulu. As of 2021, the population of Sarawak was estimated to be around 2.45 million. Sarawak has an equatorial climate with tropical rainforests and abundant animal and plant species. It has several prominent cave systems at Gunung Mulu National Park. Rajang River is the longest river in Malaysia; Bakun Dam, one of the largest dams in Southeast Asia, is located on one of its tributaries, the Balui River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime Malaysia–Thailand border, border with Thailand and Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia, and a maritime border with the Philippines and Vietnam. Kuala Lumpur is the national capital, the country's largest city, and the seat of the Parliament of Malaysia, legislative branch of the Government of Malaysia, federal government. The nearby Planned community#Planned capitals, planned capital of Putrajaya is the administrative capital, which represents the seat of both the Government of Malaysia#Executive, executive branch (the Cabine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold (which is also caused by other viruses, predominantly rhinoviruses), while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis. Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'', in the family ''Coronaviridae'', order '' Nidovirales'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, one of the largest among RNA viruses. They have characteristic club-shaped spikes that project from their surface, which in electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant Virus
A recombinant virus may occur naturally or be produced by recombining pieces of DNA using recombinant DNA technology. Synthetic recombination This may be used to produce viral vaccines or gene therapy vectors. Natural recombination The term is also used to refer to naturally occurring recombination between virus genomes in a cell infected by more than one virus strain. This occurs either by Homologous recombination of the nucleic acid strands or by reassortment of genomic segments. Both these and mutation within the virus have been suggested as ways in which influenza and other viruses evolve. An example of a recombinant virus is Western equine encephalitis virus (WEE), which is a recombinant virus between two other closely related yet distinct encephalitis viruses. In addition, reassortment is most important for pandemic influenza viruses. See also * Reassortment * Mutation In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous. Genotype contributes to phenotype, the observable traits and characteristics in an individual or organism. The degree to which genotype affects phenotype depends on the trait. For example, the petal color in a pea plant is exclusively determined by genotype. The petals can be purple or white depending on the alleles present in the pea plant. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphacoronavirus 1
''Alphacoronavirus 1'' is a species of coronavirus that infects cats, dogs and pigs. It includes the virus strains feline coronavirus, canine coronavirus, and transmissible gastroenteritis virus.'''' It is an Viral envelope, enveloped, positive-strand RNA virus which is able to enter its host cell by binding to the Alanine aminopeptidase, APN receptor. Member viruses were first recognised as viruses that caused transmissible gastroenteritis in pigs in 1965. It was originally named ''porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus'' in 1976. After subsequent discovery of ''canine coronavirus'' in dogs and ''feline coronavirus'' in cats, the three virus species were merged into a single species in 2009. The strain Canine coronavirus HuPn-2018, canine coronavirus-HuPn-2018 has been identified in a small number of human cases. Discovery In the mid-1940s there was an outbreak of pig disease in US, called transmissible gastroenteritis, which was characterised mainly by diarrhoea and vomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FCoV
Feline coronavirus (FCoV) is a positive-stranded RNA virus that infects cats worldwide. It is a coronavirus of the species ''Alphacoronavirus 1'' which includes canine coronavirus (CCoV) and porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus (TGEV). It has two different forms: feline enteric coronavirus (FECV) that infects the intestines and feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV) that causes the disease feline infectious peritonitis (FIP). Feline coronavirus is typically shed in feces by healthy cats and transmitted by the fecal-oral route to other cats. In environments with multiple cats, the transmission rate is much higher compared to single-cat environments. The virus is insignificant until mutations cause the virus to be transformed from FECV to FIPV. FIPV causes feline infectious peritonitis, for which treatment is generally symptomatic and palliative only. The drug GS-441524 shows promise as an antiviral treatment for FIP, but at the moment it is only available on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deletion (genetics)
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Some chromosomes have fragile spots where breaks occur which result in the deletion of a part of chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiations, chemicals. When a chromosome breaks, a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as deletion or a deficiency. For synapsis to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop. The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single base flipping in the template DNA, followed by template DNA strand sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein
The nucleocapsid (N) protein is a protein that packages the positive-sense RNA genome of coronaviruses to form ribonucleoprotein structures enclosed within the viral capsid. The N protein is the most highly expressed of the four major coronavirus structural proteins. In addition to its interactions with RNA, N forms protein-protein interactions with the coronavirus membrane protein (M) during the process of viral assembly. N also has additional functions in manipulating the cell cycle of the host cell. The N protein is highly immunogenic and antibodies to N are found in patients recovered from SARS and Covid-19. History The coronavirus from Wuhan, China was first identified in January 2020. A patient in the state of Washington was given a diagnosis of coronavirus infection on 20 January. A group of scientists based at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia isolated the virus from nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs and were able to characterize th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |