|
CAPZA2
F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-2 also known as CapZ-alpha2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CAPZA2'' gene. Structure CapZ-alpha2 is a 33.0 kDa protein composed of 286 amino acids. ''CAPZA2'' is located on human chromosome 7, position q31.2-q31.3. The primary sequence of CapZ-alpha2 contains three C-terminal, regularly spaced leucines at positions 258, 262 and 266 found in consensus sequence of KxxxLxxE/DLxxALxxK/R that are critical for actin binding; these residues are conserved within the CapZ-beta isoform. CapZ-alpha2 is 85% identical to CapZ-alpha1, and differ by a small number of key amino acids; 21 amino acid differences perpetrate isoform specificity. CapZ-alpha2 is expressed in a variety of tissues, including cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle, where it caps sarcomeric actin at Z-discs; the ratio of CapZ-alpha2 to CapZ-alpha1 varies significantly among different tissues. Function CapZ binds the barbed end of actin filaments and prevents addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
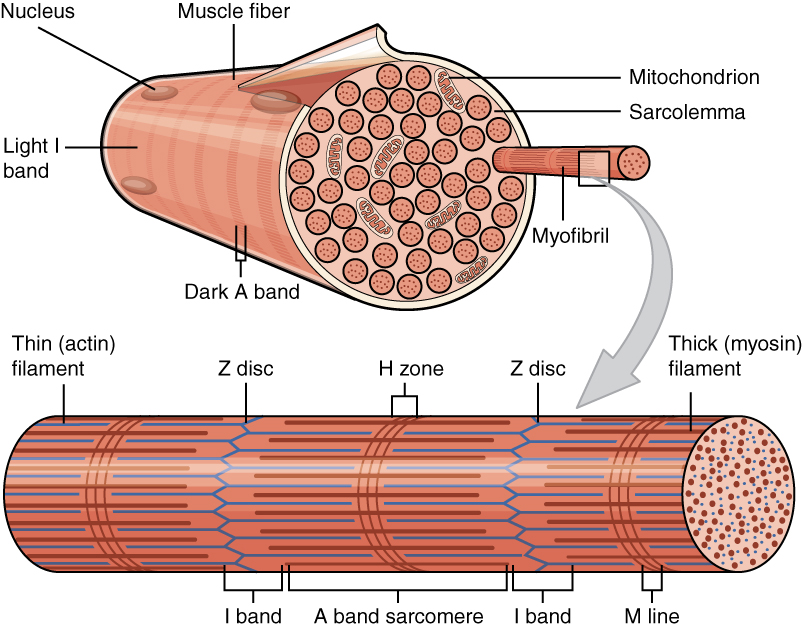
Myofilament
Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the ''contractile proteins'' and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act together in muscle contraction, and in order of size are a thick one of mostly myosin, a thin one of mostly actin, and a very thin one of mostly titin. Types of muscle tissue are striated skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, obliquely striated muscle (found in some invertebrates), and non-striated smooth muscle. Various arrangements of myofilaments create different muscles. Striated muscle has transverse bands of filaments. In obliquely striated muscle, the filaments are staggered. Smooth muscle has irregular arrangements of filaments. Structure There are three different types of myofilaments: thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thick filaments consist primarily of a type of myosin, a motor protein – myosin II. Each thick filament is approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACTA1
Actin, alpha skeletal muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ACTA1'' gene. Actin alpha 1 which is expressed in skeletal muscle is one of six different actin isoforms which have been identified. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha actins are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. Skeletal actin gene expression Skeletal alpha actin expression is induced by stimuli and conditions known to cause muscle formation. Such conditions result in fusion of committed cells (satellite cells) into myotubes, to form muscle fibers. Skeletal actin itself, when expressed, causes expression of several other "myogenic genes", which are essential to muscle formation. One key transcription factor that activates skeletal actin gene expression is Serum Response Factor ("SRF"), a protein that binds to specific sites on the promoter DNA of the actin gene. SRF may bring a number of other proteins to the promoter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Microarray
A DNA microarray (also commonly known as DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains picomoles (10−12 moles) of a specific DNA sequence, known as '' probes'' (or ''reporters'' or '' oligos''). These can be a short section of a gene or other DNA element that are used to hybridize a cDNA or cRNA (also called anti-sense RNA) sample (called ''target'') under high-stringency conditions. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected and quantified by detection of fluorophore-, silver-, or chemiluminescence-labeled targets to determine relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences in the target. The original nucleic acid arrays were macro arrays approximately 9 cm × 12 cm and the first computerized image based analysis was published in 1981. It was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
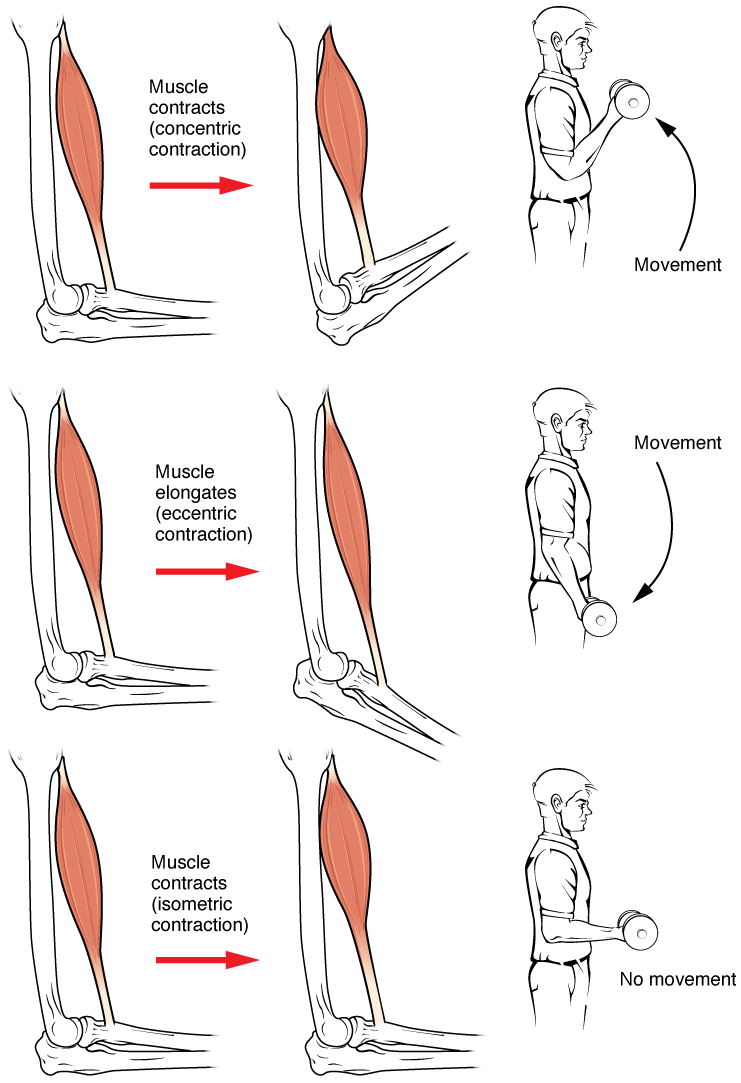
Eccentric Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the interaction of two types of filaments which are the thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are two strands of actin coiled around each, and thick filaments consist of mostly elongated proteins called myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils which are important organelles in the skeletal muscle system. Muscle contraction can also be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYL2
Myosin regulatory light chain 2, ventricular/cardiac muscle isoform (MLC-2) also known as the regulatory light chain of myosin (RLC) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYL2'' gene. This cardiac ventricular RLC isoform is distinct from that expressed in skeletal muscle (MYLPF), smooth muscle (MYL12B) and cardiac atrial muscle ( MYL7). Ventricular myosin light chain-2 (MLC-2v) refers to the ventricular cardiac muscle form of myosin light chain 2 (Myl2). MLC-2v is a 19-KDa protein composed of 166 amino acids, that belongs to the EF-hand Ca2+ binding superfamily. MLC-2v interacts with the neck/tail region of the muscle thick filament protein myosin to regulate myosin motility and function. Structure Cardiac, ventricular RLC is an 18.8 kDa protein composed of 166 amino acids. RLC and the second ventricular light chain, essential light chain (ELC, MYL3), are non-covalently bound to IQXXXRGXXXR motifs in the 9 nm S1-S2 lever arm of the myosin head, both alpha ( M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNNT2
Cardiac muscle troponin T (cTnT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNNT2'' gene. Cardiac TnT is the tropomyosin-binding subunit of the troponin complex, which is located on the thin filament of striated muscles and regulates muscle contraction in response to alterations in intracellular calcium ion concentration. The TNNT2 gene is located at 1q32 in the human chromosomal genome, encoding the cardiac muscle isoform of troponin T (cTnT). Human cTnT is an ~36-kDa protein consisting of 297 amino acids including the first methionine with an isoelectric point (pI) of 4.88. It is the tropomyosin- binding and thin filament anchoring subunit of the troponin complex in cardiac muscle cells. TNNT2 gene is expressed in vertebrate cardiac muscles and embryonic skeletal muscles. Structure Cardiac TnT is a 35.9 kDa protein composed of 298 amino acids. Cardiac TnT is the largest of the three troponin subunits (cTnT, troponin I (TnI), troponin C (TnC)) on the actin thin filame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYBPC3
The myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYBPC3'' gene. This isoform is expressed exclusively in heart muscle during human and mouse development, and is distinct from those expressed in slow skeletal muscle ( MYBPC1) and fast skeletal muscle (MYBPC2). Structure cMyBP-C is a 140.5 kDa protein composed of 1273 amino acids. cMyBP-C is a myosin-associated protein that binds at 43 nm intervals along the myosin thick filament backbone, stretching for 200 nm on either side of the M-line within the crossbridge-bearing zone (C-region) of the A band in striated muscle. The approximate stoichiometry of cMyBP-C along the thick filament is 1 per 9-10 myosin molecules, or 37 cMyBP-C molecules per thick filament. In addition to myosin, cMyBP-C also binds titin and actin. The cMyBP-C isoform expressed in cardiac muscle differs from those expressed in slow and fast skeletal muscle ( MYBPC1 and MYBPC2, respectively) by three features: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
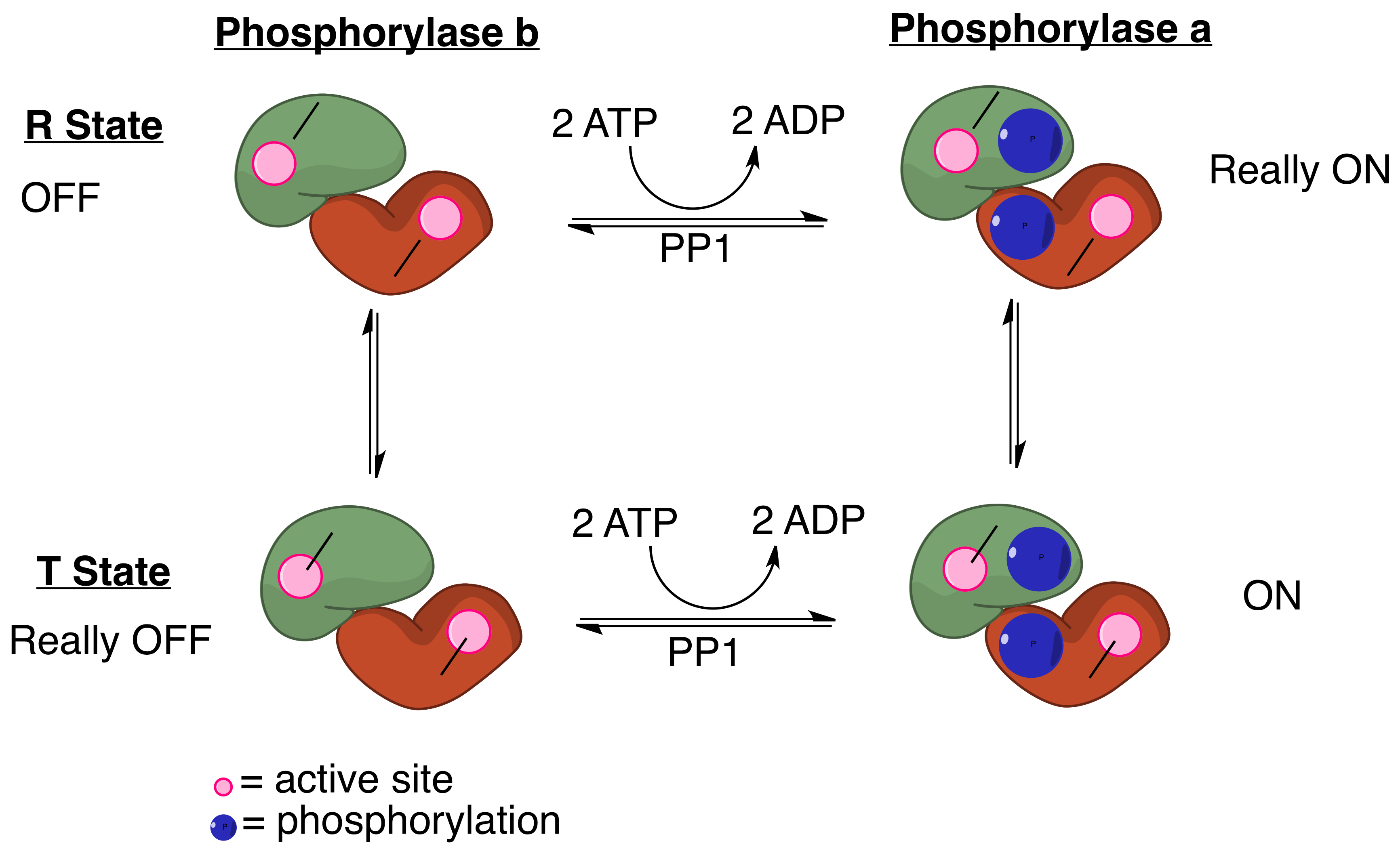
Protein Phosphatase 1
Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) belongs to a certain class of phosphatases known as protein serine/threonine phosphatases. This type of phosphatase includes metal-dependent protein phosphatases (PPMs) and aspartate-based phosphatases. PP1 has been found to be important in the control of glycogen metabolism, muscle contraction, cell progression, neuronal activities, splicing of RNA, mitosis, cell division, apoptosis, protein synthesis, and regulation of membrane receptors and channels. Structure Each PP1 enzyme contains both a catalytic subunit and at least one regulatory subunit. The catalytic subunit consists of a 30-kD single-domain protein that can form complexes with other regulatory subunits. The catalytic subunit is highly conserved among all eukaryotes, thus suggesting a common catalytic mechanism. The catalytic subunit can form complexes with various regulatory subunits. These regulatory subunits play an important role in substrate specificity as well as compartmentaliza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S100A1
Protein S100-A1, also known as S100 calcium-binding protein A1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''S100A1'' gene. S100A1 is highly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle, and localizes to Z-discs and sarcoplasmic reticulum. S100A1 has shown promise as an effective candidate for gene therapy to treat post- myocardially infarcted cardiac tissue. Structure S100A1 is a member of the S100 family of proteins expressed in cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle and brain, with highest density at Z-lines and sarcoplasmic reticulum. S100A1 contains 4 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs in its dimerized form, and can exist as either a hetero or homo dimer. The S100A1 homodimer is high affinity (nanomolar range or tighter), and is formed through hydrophobic packing of an X-type 4-helix bundle created between helices 1, 1', 4, and 4'. Protein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy structural information on the homodimeric form of this protein shows that each monomer is helical and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |