|
C1s
Complement component 1s (, '' C1 esterase'', ''activated complement C1s'', ''complement C overbar 1r'', ''C1s'') is a protein involved in the complement system The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and at .... C1s is part of the C1 complex. In humans, it is encoded by the ''C1S'' gene. C1s cleaves C4 and C2, which eventually leads to the production of the classical pathway C3-convertase. See also * C1q - another part of the C1 complex * C1r - another part of the C1 complex * MASP-2 - a protein similar to C1s, part of the lectin pathway References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * Complement system EC 3.4.21 {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Component 1r
Complement C1r subcomponent (, ''activated complement C1r'', ''C overbar 1r esterase'', ''C1r'') is a protein involved in the complement system of the innate immune system. In humans, C1r is encoded by the ''C1R'' gene. C1r along with C1q and C1s form the C1 complex, which is the first component of the serum complement system. C1r is an enzyme that activates C1s to its active form, by proteolysis, proteolytic cleavage. Clinical significance *Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Periodontal type is associated with mutations in the ''CR1'' gene Function C1r has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with C1s. C1r proteolysis, cleaves C1s to form the active form of C1s. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * Complement system EC 3.4.21 {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C1 Esterase
C1, C01, C.I or C-1 may refer to: Arts and media * C1, a note-octave in music * C1 Television, a Mongolian television channel * Schecter C-1 Hellraiser FR, a guitar model * A Yamaha grand piano model * "C1", a slang expression in the video game '' Counter-Strike'', used to express agreement Biology and medicine Anatomy * Cervical vertebra 1, the first cervical vertebrae of the vertebral column * Cervical spinal nerve 1, a spinal nerve of the cervical segment Biochemistry * C1 complex, the first component of the classical complement pathway * C1 domain, an important secondary messenger protein domain * C1-inhibitor, a human serine protease inhibitor * C1 regulatory sequence for the insulin gene * Apolipoprotein C1, a human lipoprotein * Chlorophyll c1, a form of chlorophyll * Cytochrome C1, a precursor protein to Cytochrome C * Proanthocyanidin C1, a type of polyphenolic compound * Prostaglandin C1, a form of prostaglandins Other uses in biology and medicine * C1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
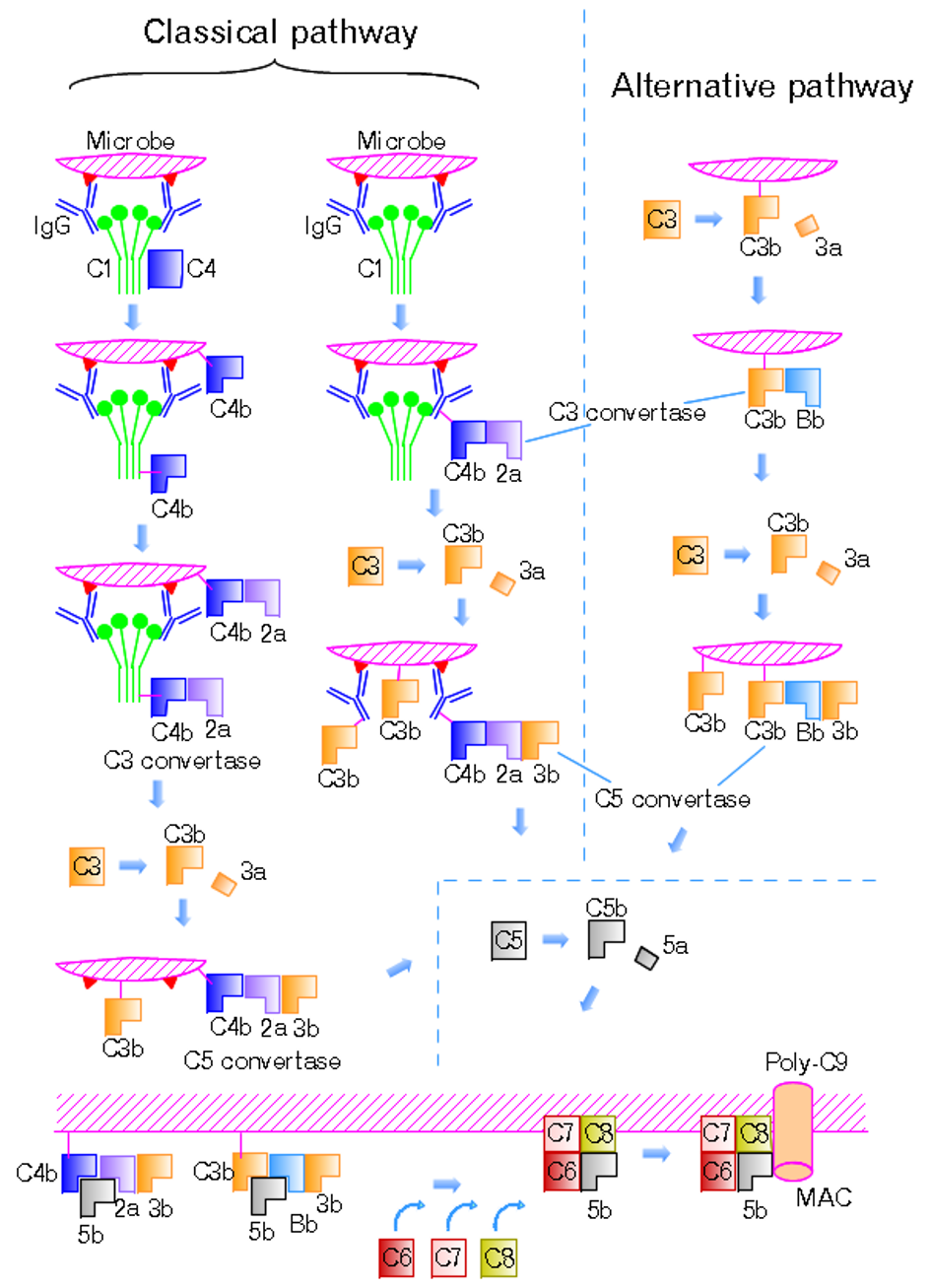
Complement System
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and attack the pathogen's cell membrane. It is part of the innate immune system, which is not adaptable and does not change during an individual's lifetime. The complement system can, however, be recruited and brought into action by antibodies generated by the adaptive immune system. The complement system consists of a number of small proteins that are synthesized by the liver, and circulate in the blood as inactive precursors. When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end result of this ''complement activation'' or ''complement fixation'' cascade is stimulation of phagocytes to clear foreign and damaged materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C1 Complex
The C1 complex (''complement component 1'', ''C1'') is a protein complex involved in the complement system. It is the first component of the classical complement pathway and is composed of the subcomponents C1q, C1r and C1s. Structure The C1 complex is composed of 1 molecule of C1q, 2 molecules of C1r and 2 molecules of C1s, or ''C1qr2s2''. Function Activation of the C1 complex initiates the classical complement pathway. This occurs when C1q binds to antigen-antibody complexes. The antibodies IgM or certain subclasses of IgG complexed with antigens are able to initiate the complement system: a single pentameric IgM can initiate the pathway, while several monomeric IgG molecules are needed. C1q can also be activated in other ways, for example by binding to pentraxins such as C-reactive protein or directly to the surface of pathogens. Such binding of C1q leads to conformational changes in the C1q molecule, which activates the associated C1r molecules. Active C1r cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Component 4
Complement component 4 (C4), in humans, is a protein involved in the intricate complement system, originating from the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system. It serves a number of critical functions in immunity, tolerance, and autoimmunity with the other numerous components. Furthermore, it is a crucial factor in connecting the recognition pathways of the overall system instigated by antibody-antigen (Ab-Ag) complexes to the other effector proteins of the innate immune response. For example, the severity of a dysfunctional complement system can lead to fatal diseases and infections. Complex variations of it can also lead to schizophrenia. The C4 protein was thought to derive from a simple two-locus allelic model, which however has been replaced by a much more sophisticated multimodular RCCX gene complex model which contain long and short forms of the C4A or C4B genes usually in tandem RCCX cassettes with copy number variation, that somewhat parallels variation in the levels of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Component 2
Complement C2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''C2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is part of the classical pathway of the complement system, acting as a multi-domain serine protease. Deficiency of C2 has been associated with certain autoimmune diseases. Function In the classical and lectin pathways of complement activation, formation of the C3-convertase and C5-convertases requires binding of C2 to an activated surface-bound C4b in the presence of Mg2+; the resultant C4bC2 complex is cleaved by C1s Complement component 1s (, '' C1 esterase'', ''activated complement C1s'', ''complement C overbar 1r'', ''C1s'') is a protein involved in the complement system The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune s ... or MASP2 into C2a and C2b. It is thought that cleavage of C2 by C1s, while bound to C4b, results in a conformational rotation of C2b whereas the released C2a fragment may retain most of its original structure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Complement Pathway
The classical complement pathway is one of three pathways which activate the complement system, which is part of the immune system. The classical complement pathway is initiated by antigen-antibody complexes with the antibody isotypes IgG and IgM. Following activation, a series of proteins are recruited to generate C3 convertase (C4b2b, historically referred C4b2a), which cleaves the C3 protein. The C3b component of the cleaved C3 binds to C3 convertase (C4b2b) to generate C5 convertase (C4b2b3b), which cleaves the C5 protein. The cleaved products attract phagocytes to the site of infection and tags target cells for elimination by phagocytosis. In addition, the C5 convertase initiates the terminal phase of the complement system, leading to the assembly of the membrane attack complex ( MAC). The membrane attack complex creates a pore on the target cell's membrane, inducing cell lysis and death. The classical complement pathway can also be activated by apoptotic cells, ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C3-convertase
C3 convertase (''C4bC2b'', formerly ''C4b2a'') belongs to family of serine proteases and is necessary in innate immunity as a part of the complement system which eventuate in opsonisation of particles, release of inflammatory peptides, C5 convertase formation and cell lysis. C3 convertase can be used to refer to the form produced in the alternative pathway (C3bBb) or the classical and lectin pathways (C4bC2b, formerly C4b2a). Once formed, both C3 convertases will catalyze the proteolytic cleavage of C3 into C3a and C3b (hence the name "C3-convertase"). The smaller fragment called C3a serves to increase vascular permeability and promote extravasation of phagocytes, while the larger C3b fragment can be used as an opsonin or bind to either type of C3 convertase to form the trimolecular C5 convertase to activate C5 for the membrane attack complex. Formation C3 convertase formation can occur in three different pathways: the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Droga Klasyczna
''Droga'' (Polish for 'road') was a monthly magazine dedicated to literary and social topics. It was published in Nazi-occupied Warsaw from December 1943 to April 1944. Its founders were Ewa Pohoska and Juliusz Garztecki. See also * List of magazines in Poland The following is a list of notable current and defunct magazines in Poland. In the country, there are also English-language magazines in addition to those published in Polish.1943 establishments in Poland 1944 disestablishments in Poland Defunct literary magazines published in Poland [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Component 1q
The complement component 1q (or simply C1q) is a protein complex involved in the complement system, which is part of the innate immune system. C1q together with C1r and C1s form the C1 complex. Antibodies of the adaptive immune system can bind antigen, forming an antigen-antibody complex. When C1q binds antigen-antibody complexes, the C1 complex becomes activated. Activation of the C1 complex initiates the classical complement pathway of the complement system. The antibodies IgM and all IgG subclasses except IgG4 are able to initiate the complement system. Structure C1q is a 400 kDa protein formed from 18 peptide chains in 3 subunits of 6. Each 6 peptide subunit consists of a Y-shaped pair of triple peptide helices joined at the stem and ending in a globular non-helical head. The 80-amino acid helical component of each triple peptide contain many Gly-X-Y sequences, where X and Y are proline, isoleucine, or hydroxylysine; they, therefore, strongly resemble collagen f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |