|
Boise National Forest
Boise National Forest is a National Forest covering of the U.S. state of Idaho. Created on July 1, 1908, from part of Sawtooth National Forest, it is managed by the U.S. Forest Service as five units: the Cascade, Emmett, Idaho City, Lowman, and Mountain Home ranger districts. The Idaho Batholith underlies most of Boise National Forest, forming the forest's Boise, Salmon River, and West mountain ranges; the forest reaches a maximum elevation of on Steel Mountain. Common land cover includes sagebrush steppe and spruce-fir forests; there are of streams and rivers and of lakes and reservoirs. Boise National Forest contains 75 percent of the known populations of Sacajawea's bitterroot, a flowering plant endemic to Idaho. The Shoshone people occupied the forest before European settlers arrived in the early 19th century. Many of the early settlers were trappers and prospectors before gold was discovered in 1862. After the 1860s Boise Basin gold rush ended, mining of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ada County, Idaho
Ada County is located in the southwestern part of Idaho, United States. As of the 2021 United States census estimate, the county had a population of 511,931, making it by far the state's most populous county; it is home to 26.8% of the state's population. The county seat and largest city is Boise, which is also the state capital. Ada County is included in the Boise metropolitan area. The Ada County Highway District has jurisdiction over all the local county and city streets, except for private roads and state roads. In the interior Pacific Northwest east of the Cascade Range, Ada County ranks second in population, behind Spokane County, Washington. History Ada County was created by the Idaho Territory legislature on December 22, 1864, partitioned from Boise County. It is named for Ada Riggs, the daughter of H.C. Riggs, a member of the legislature; he established the county and was a co-founder of Boise. Canyon County, which originally included Payette County and most of Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idaho Batholith
The Idaho Batholith is a granitic and granodioritic batholith of Cretaceous- Paleogene age that covers approximately of central Idaho and adjacent Montana. The batholith has two lobes that are separate from each other geographically and geologically. The Bitterroot lobe is the smaller lobe and the larger lobe is the Atlanta lobe. The Bitterroot lobe is in the north and is separated from the larger Atlanta lobe in the south by the Belt Supergroup metamorphic rocks that compose the Salmon River Arch. Much of the Atlanta and Bitterroot lobes are in the Idaho Batholith ecoregion. The overall intrusive event that created the Idaho batholith lasted for around 55 million years from Late Cretaceous to the Eocene (98 to 43 Ma) of magmatism and includes the younger Challis suite which is not considered to be part of the Idaho Batholith. The Challis suite intruded both the Atlanta and Bitterroot lobes of the Idaho Batholith as well as the surrounding areas to the east of the Atlant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
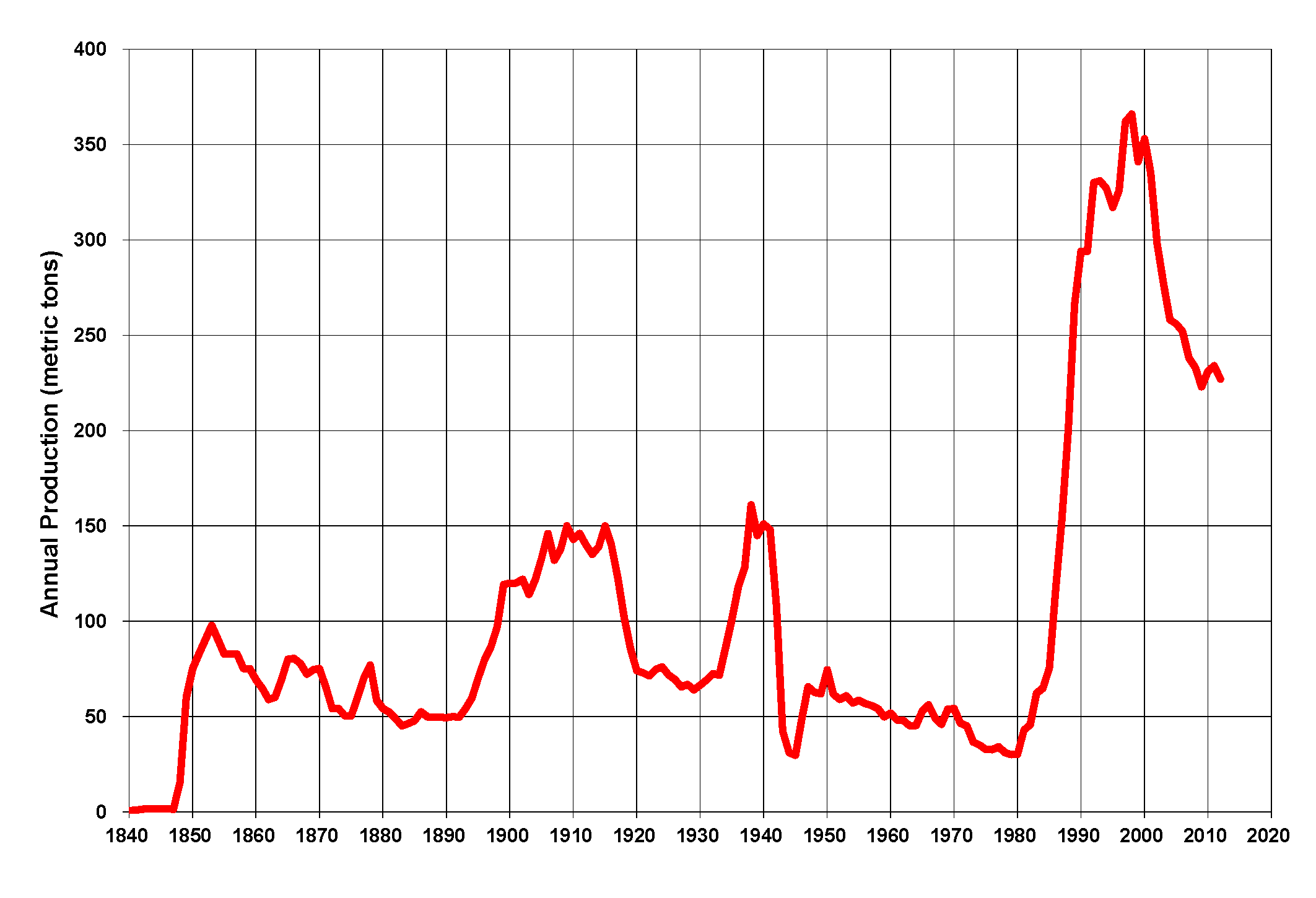
Gold Mining In The United States
Gold mining in the United States has taken place continually since the discovery of gold at the Reed farm in North Carolina in 1799. The first documented occurrence of gold was in Virginia in 1782. Some minor gold production took place in North Carolina as early as 1793, but created no excitement. The discovery on the Reed farm in 1799 which was identified as gold in 1802 and subsequently mined marked the first commercial production. The large scale production of gold started with the California Gold Rush in 1848. The closure of gold mines during World War II by the War Production Board Limitation Order No. 208 in autumn 1942 was a major impact on the production until the end of the war. US gold production greatly increased during the 1980s, due to high gold prices and the use of heap leaching to recover gold from disseminated low-grade deposits in Nevada and other states. In 2019 the United States produced 200 tonnes (6.4 million troy ounces) of gold (down from 210 tonnes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prospecting
Prospecting is the first stage of the geological analysis (followed by exploration) of a territory. It is the search for minerals, fossils, precious metals, or mineral specimens. It is also known as fossicking. Traditionally prospecting relied on direct observation of mineralization in rock outcrops or in sediments. Modern prospecting also includes the use of geologic, geophysical, and geochemical tools to search for anomalies which can narrow the search area. Once an anomaly has been identified and interpreted to be a potential prospect direct observation can then be focused on this area. In some areas a prospector must also make claims, meaning they must erect posts with the appropriate placards on all four corners of a desired land they wish to prospect and register this claim before they may take samples. In other areas publicly held lands are open to prospecting without staking a mining claim. Historical methods The traditional methods of prospecting involved combi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Trapping
Animal trapping, or simply trapping or gin, is the use of a device to remotely catch an animal. Animals may be trapped for a variety of purposes, including food, the fur trade, hunting, pest control, and wildlife management. History Neolithic hunters, including the members of the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Romania and Ukraine (c. 5500–2750 BCE), used traps to capture their prey. An early mention in written form is a passage from the self-titled book by Taoist philosopher Zhuangzi describes Chinese methods used for trapping animals during the 4th century BCE. The Zhuangzi reads, "The sleek-furred fox and the elegantly spotted leopard ... can't seem to escape the disaster of nets and traps." "Modern" steel jaw-traps were first described in western sources as early as the late 16th century. The first mention comes from Leonard Mascall's book on animal trapping. It reads, "a griping trappe made all of yrne, the lowest barre, and the ring or hoope with two clickets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon Pioneer History
Oregon pioneer history (1806–1890) is the period in the history of Oregon Country and Oregon Territory, in the present day state of Oregon and Northwestern United States. It was the era when pioneers and mountain men, primarily of European descent, traveled west across North America to explore and settle the lands west of the Rocky Mountains and north of California. Some also arrived via the Pacific Ocean, traveling by ship either around Cape Horn or by changing ships at Panama. The period begins after the explorations of the lower Columbia River by Robert Gray and George Vancouver in 1792, along with the 1804–1806 Lewis and Clark Expedition to Oregon Country, and runs until circa 1890 when railroads and urban centers created a more settled state. Territory At the beginning of the pioneer period the Oregon Country was the homeland of numerous tribes of Native Americans. Regardless, portions of the area were claimed by the United States, Great Britain, Spain, and Russia. Fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ) are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions: * Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming * Northern Shoshone: southern Idaho * Western Shoshone: Nevada, northern Utah * Goshute: western Utah, eastern Nevada They traditionally speak the Shoshoni language, part of the Numic languages branch of the large Uto-Aztecan language family. The Shoshone were sometimes called the Snake Indians by neighboring tribes and early American explorers. Their peoples have become members of federally recognized tribes throughout their traditional areas of settlement, often co-located with the Northern Paiute people of the Great Basin. Etymology The name "Shoshone" comes from ''Sosoni'', a Shoshone word for high-growing grasses. Some neighboring tribes call the Shoshone "Grass House People," based on their traditional homes made from ''sosoni''. Shoshones call themselves ''Newe'', meaning "People".Loether, Christopher"Shoshones."''Encyclopedia of the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewisia Sacajaweana
''Lewisia sacajaweana'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Montiaceae known by the common name Sacajawea's bitterroot. It is endemic to Idaho, where it is known from approximately two dozen sites, with about 75 percent of them in Boise National Forest. It is usually found at elevations ranging from to above sea level and produces white flowers shortly after snowmelt. The species is named in honor of Sacagawea, Native American guide to the Lewis and Clark Expedition The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gro .... It is part of a genus named for Meriwether Lewis of the same expedition. References sacajaweana Flora of Idaho Endemic flora of the United States {{Caryophyllales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spruce-fir Forests
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Piceoideae. Spruces are large trees, from about 20 to 60 m (about 60–200 ft) tall when mature, and have whorled branches and conical form. They can be distinguished from other members of the pine family by their needles (leaves), which are four-sided and attached singly to small persistent peg-like structures (pulvini or sterigmata) on the branches, and by their cones (without any protruding bracts), which hang downwards after they are pollinated. The needles are shed when 4–10 years old, leaving the branches rough with the retained pegs. In other similar genera, the branches are fairly smooth. Spruce are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera (moth and butterfly) species, such as the eastern spruce budworm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagebrush Steppe
Sagebrush steppe is a type of shrub-steppe, a plant community characterized by the presence of shrubs, and usually dominated by sagebrush, any of several species in the genus ''Artemisia''.Sagebrush steppe. National Park Service. This ecosystem is found in the in the United States.Sagebrush Steppe Conservation Project /ID National Lab. Wildlife Conservation Society. The most common sagebrush species in the sagebrush steppe in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel Mountain
Steel Mountain is the highest point in Boise National Forest and the second highest point in the Boise Mountains at an elevation of . It is located from Two Point Mountain, the highest point in the range and its line parent A peak's line parent is the closest higher peak on the highest ridge leading away from the peak's "key col". A col is the lowest point on the ridge between two summits and is roughly synonymous with pass, gap, saddle and notch. The highest col of ..., giving it a prominence of . References Mountains of Idaho Mountains of Elmore County, Idaho Boise National Forest {{ElmoreCountyID-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
