|
Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley (, ; Bekaa, Biqâ, Becaa) is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon and its most important farming region. Industry, especially the country's agricultural industry, also flourishes in Beqaa. The region broadly corresponds to the Coele-Syria of classical antiquity. The Beqaa is located about east of Beirut. The valley is situated between Mount Lebanon to the west and the Anti-Lebanon mountains to the east. It is the northern continuation of the Jordan Rift Valley, and thus part of the Great Rift Valley, which stretches from Syria to the Red Sea. Beqaa Valley is long and wide on average. It has a Mediterranean climate of wet, often snowy winters and dry, warm summers. Climate The region receives limited rainfall, particularly in the north, because Mount Lebanon creates a rain shadow that blocks precipitation coming from the sea. The northern section has an average annual rainfall of , compared to in the central valley. Nevertheless, two rivers originate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasarnaba
Kasarnaba () is a town in Baalbek District, Baalbek-Hermel Governorate, Lebanon famous for its hilly terrain and traditional agricultural practices. Geography The town is located at the shoulder of The Western Lebanese Mountain Range just to the East of Mount Sanine specifically and it overlooks the central parts of Beqaa Valley. History A Roman Temple is found in this town, called " Castra El Banaat". In 1838, Eli Smith noted Kasarnaba's population to be predominantly Metawileh. People in Kasarnaba are traditionally farmers famous for growing vineyards and wild rose flowers for rosewater extraction, in addition to many other traditional Horticultural crops some of which are listed below. In 1994 Mustafa Dirani was abducted by Israeli forces from his home in Kasarnaba. He was held (without charge) by Israel until 2004. Traditional Crops - Grapes - Cherries - Apricots - Common Fig - Roses (for Rosewater) - Tobacco Landscape Kasarnaba has many hills creating d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
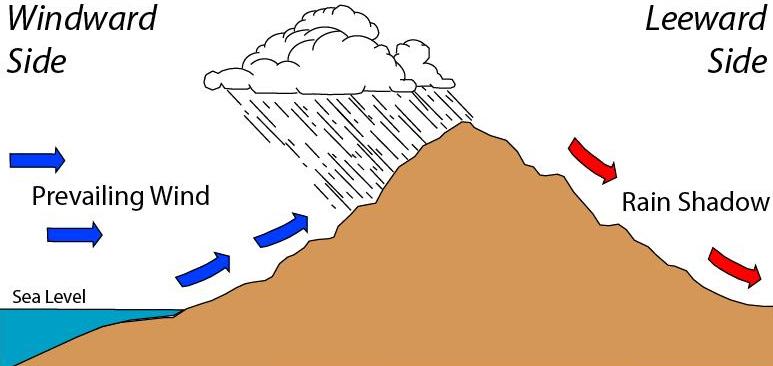
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing sea breeze, onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is orographic lift, driven upslope towards the summit, peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to Precipitation, precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing Foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of arid, dry climate region behind the ridge, mountain crests. This climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit tree, fruit- or nut (fruit), nut-producing trees that are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of large gardens, where they serve an aesthetic as well as a productive purpose. A fruit garden is generally synonymous with an orchard, although it is set on a smaller, non-commercial scale and may emphasize berry shrubs in preference to fruit trees. Most temperate-zone orchards are laid out in a regular grid, with a grazed or mown lawn, grass or bare soil base that makes maintenance and fruit gathering easy. Most modern commercial orchards are planted for a single variety of fruit. While the importance of introducing biodiversity is recognized in forest plantations, introducing genetic diversity in orchard plantations by interspersing other trees might offer benefits. Genetic diversity in an orchard would provide resili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vineyard
A vineyard ( , ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines. Many vineyards exist for winemaking; others for the production of raisins, table grapes, and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyards are often characterised by their , a French term loosely translating as "a sense of place" that refers to the specific geographical and geological characteristics of grapevine plantations, which may be imparted to the wine itself. History The earliest evidence of wine production dates from between 6000 and 5000 BC. Wine making technology improved considerably with the ancient Greeks but it was not until the end of the Roman Empire that cultivation techniques as we know them were common throughout Europe. In medieval Europe the Catholic Church was a staunch supporter of wine, which was necessary for the celebration of the Mass (liturgy), Mass. During the lengthy instability of the Middle Ages, the monasteries m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
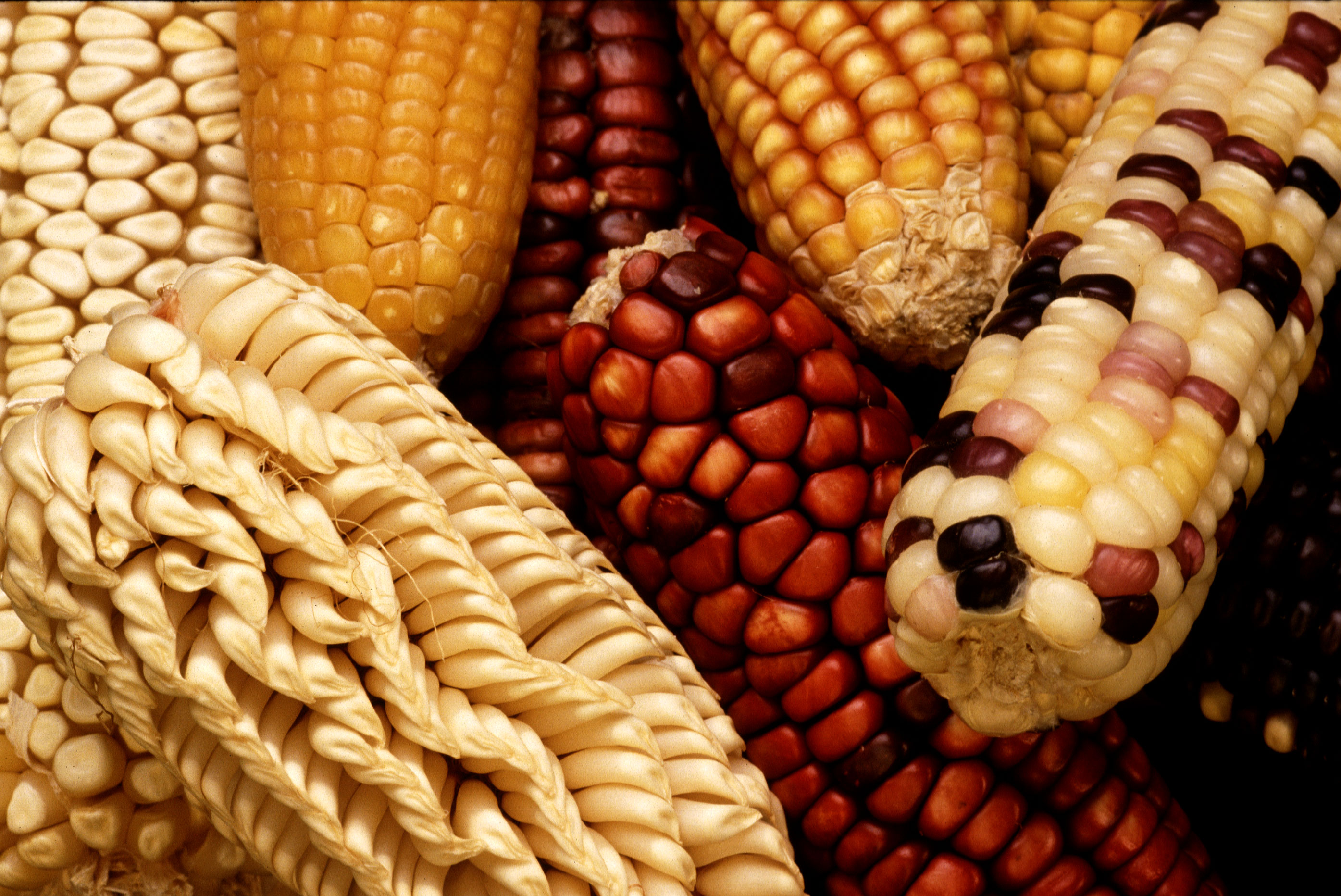
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomadic Pastoralism
Nomadic pastoralism, also known as nomadic herding, is a form of pastoralism in which livestock are herded in order to seek for fresh pastures on which to graze. True nomads follow an irregular pattern of movement, in contrast with transhumance, where seasonal pastures are fixed. However, this distinction is often not observed and the term 'nomad' used for both—and in historical cases the regularity of movements is often unknown in any case. The herded livestock include cattle, water buffalo, yaks, llamas, sheep, goats, reindeer, horses, donkeys or camels, or mixtures of species. Nomadic pastoralism is commonly practiced in regions with little arable land, typically in the developing world, especially in the steppe lands north of the agricultural zone of Eurasia. Pastoralists often trade with sedentary agrarians, exchanging meat for grains; however, they have been known to raid. Of the estimated 30–40 million nomadic pastoralists worldwide, most are found in central A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arable Land
Arable land (from the , "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for the purposes of agricultural statistics, the term often has a more precise definition: A more concise definition appearing in the Eurostat glossary similarly refers to actual rather than potential uses: "land worked (ploughed or tilled) regularly, generally under a system of crop rotation". In Britain, arable land has traditionally been contrasted with pasturable land such as heaths, which could be used for sheep-rearing but not as farmland. Arable land is vulnerable to land degradation and some types of un-arable land can be enriched to create useful land. Climate change and biodiversity loss are driving pressure on arable land. By country According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, in 2013, the world's arable land amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in Western AsiaGasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. p. 5: "... today the term ''Levantine'' can describe shared cultural products, such as Levantine cuisine or Levantine archaeology". .Steiner & Killebrew, p9: "The general limits ..., as defined here, begin at the Plain of 'Amuq in the north and extend south until the Wâdī al-Arish, along the northern coast of Sinai. ... The western coastline and the eastern deserts set the boundaries for the Levant ... The Euphrates and the area around Jebel el-Bishrī mark the eastern boundary of the northern Levant, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccation, desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |