|
Bacillus Phages
A Bacillus phage is a member of a group of bacteriophages known to have bacteria in the genus '' Bacillus'' as host species. These bacteriophages have been found to belong to the families '' Myoviridae'', '' Siphoviridae'', '' Podoviridae'', or '' Tectiviridae''. The genus Bacillus includes the model organism, ''B. subtilis'', and two widely known human pathogens, ''B. anthracis'' and ''B. cereus''. Other strains of '' Bacillus'' bacteria that phage are known to infect include ''B. megaterium'', ''B. mycoides'', ''B. pseudomycoides'', B. thuringiensis, and ''B. weihenstephanensis''. More than 1,455 bacillus phage have been discovered from many different environments and areas around the world. Only 164 of these phages have been completely sequenced as of December 16, 2021. Genome diversity Bacillus phage are classified based on their genome sequences. The total sequence length ranges from 7,826 (in phage pMC8) to 509,170 bp (in phage pHS181) with the GC content of these phage be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophages
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biomass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Phage Cluster Dot-Plot
''Bacillus'' (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum '' Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacilli'' is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. ''Bacillus'' species can be either obligate aerobes which are dependent on oxygen, or facultative anaerobes which can survive in the absence of oxygen. Cultured ''Bacillus'' species test positive for the enzyme catalase if oxygen has been used or is present. ''Bacillus'' can reduce themselves to oval endospores and can remain in this dormant state for years. The endospore of one species from Morocco is reported to have survived being heated to 420 °C. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients: the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. They are not true spores (i.e., not an offspring). Endospore f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Phage Phi29
''Bacillus virus Φ29'' (bacteriophage Φ29) is a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) bacteriophage with a prolate icosahedral head and a short tail that belongs to the genus ''Salasvirus'', order '' Caudovirales'', and family ''Salasmaviridae''. They are in the same order as phages PZA, Φ15, BS32, B103, M2Y (M2), Nf, and GA-1. First discovered in 1965, the Φ29 phage is the smallest '' Bacillus'' phage isolated to date and is among the smallest known dsDNA phages. Φ29 has a unique DNA packaging motor structure that employs prohead packaging RNA (pRNA) to guide the translocation of the phage genome during replication. This novel structure system has inspired ongoing research in nanotechnology, drug delivery, and therapeutics. In nature, the Φ29 phage infects '' Bacillus subtilis'', a species of gram-positive, endospore-forming bacteria that is found in soil, as well as the gastrointestinal tracts of various marine and terrestrial organisms, including human beings. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalyze the chemical reaction : deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNAn pyrophosphate + DNAn+1. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the three prime (3')-end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell's DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each daughter cell. In this way, genetic information is passed down from generation to generation. Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
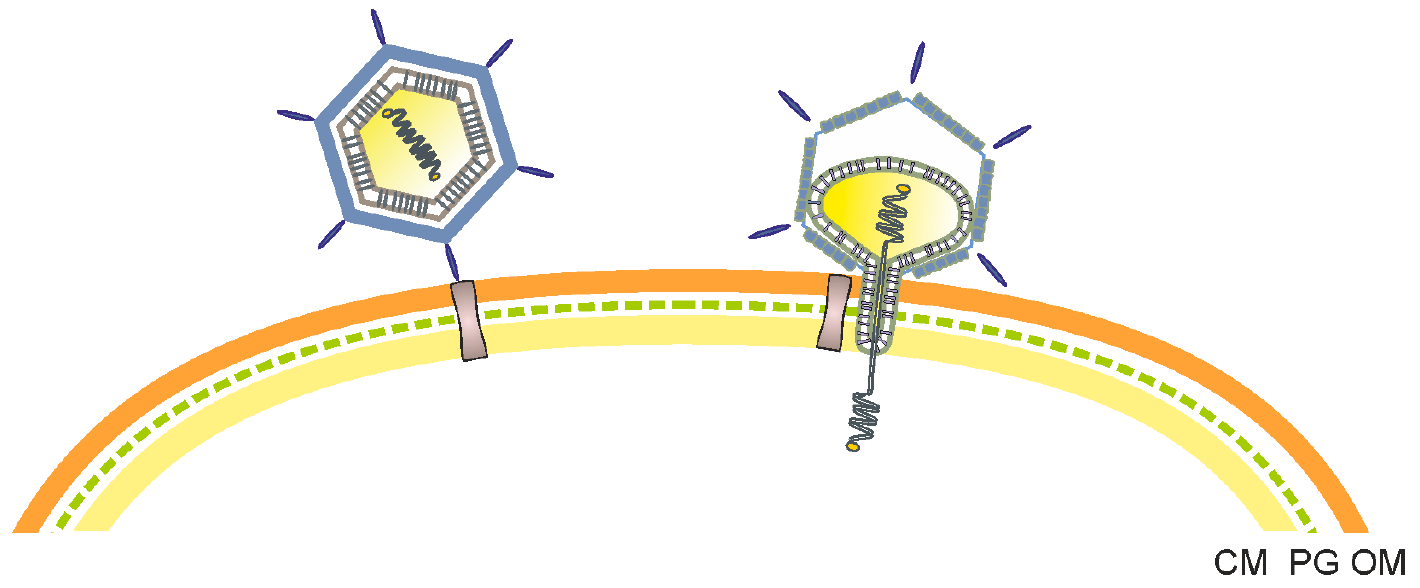
Tectivirus
''Tectiviridae'' is a family of viruses with 10 species in five genera. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. Tectiviruses have no head-tail structure, but are capable of producing tail-like tubes of ~ 60×10 nm upon adsorption or after chloroform treatment. The name is derived from Latin ''tectus'' (meaning 'covered'). Virology The virions of ''Tectiviridae'' species are non-enveloped, icosahedral and display a pseudo T=25 symmetry. The capsid has two layers. The outer layer is a protein structure of 240 capsid proteins trimers, and the inner one is a proteinaceous lipid membrane which envelopes the virus genome. Apical spikes extending about 20 nanometers (nm) protrude from the icosahedrons vertices. The genome is a single molecule of linear double-stranded DNA of 15 kilo bases in length, and has 30 open reading frames. It forms a tightly packed coil and encodes several structural proteins. It encodes about 30 proteins that are transcribed in operons. At least 9 structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Pumilus
''Bacillus pumilus'' is a Gram-positive, aerobic, spore-forming bacillus commonly found in soil. ''Bacillus pumilus'' spores—with the exception of mutant strain ATCC 7061—generally show high resistance to environmental stresses, including UV light exposure, desiccation, and the presence of oxidizers such as hydrogen peroxide. Strains of ''B. pumilus'' found at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory were found to be particularly resistant to hydrogen peroxide. A strain of ''B. pumilus'' isolated from black tiger shrimp (''Penaeus monodon'') was found to have high salt tolerance and to inhibit the growth of marine pathogens, including ''Vibrio alginolyticus'', when cultured together. Genome and cell structure ''Bacillus pumilus'' contains one circular chromosome including about 4000 genes and 3600-3900 proteins with varying length in the range of 3.7 to 3.8 Mbp. 41% of the DNA base pairs in ''B. pumilus'' are G-C. The cellular structure of ''B. pumilus'' is similar to other ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
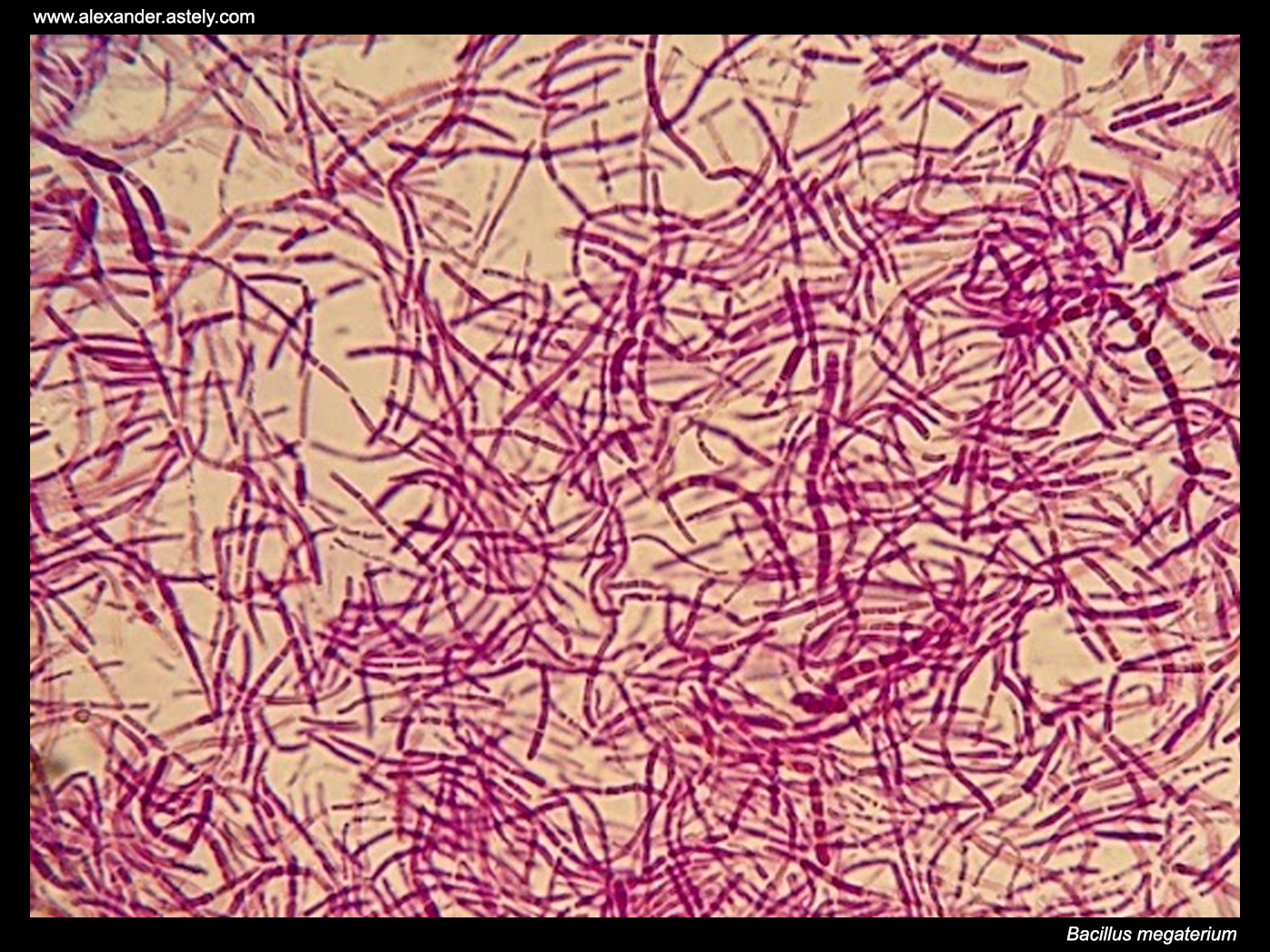
Bacillus Megaterium
''Bacillus megaterium'' is a rod-like, Gram-positive, mainly aerobic spore forming bacterium found in widely diverse habitats.De Vos, P. ''et al.'' Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology: Volume 3: The Firmicutes. ''Springer'' (2009) It has a cell length of up to 4 µm and a diameter of 1.5 µm, which is quite large for a bacteria. The cells often occur in pairs and chains, where the cells are joined together by polysaccharides on the cell walls. In the 1960s, prior to the utilization of ''Bacillus subtilis'' for this purpose, ''B. megaterium'' was the main model organism among Gram-positive bacteria for intensive studies on biochemistry, sporulation and bacteriophages. Recently, its popularity has started increasing in the field of biotechnology for its recombinant protein production capacity.Bunk, B. ''et al.'' A short story about a big magic bug. ''Bioengineered Bugs'' 1:85–91 (2010) This species has been recently transferred into the genus ''Priestia''. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Sporothermodurans
''Bacillus sporothermodurans'' is a species of bacteria notable for producing highly heat-resistant endospores, hence its name. It is strictly aerobic. Its type strain is M215 (DSMZ 10599). This species has been recently transferred into the genus ''Heyndrickxia ''Heyndrickxia'' is a genus of gram-positive rod-shaped bacteria (except for ''Heyndrickxia'' ''sporothermodurans'', which stains gram-negative) in the family ''Bacillaceae'' within the order ''Bacillales''. The type species for this genus is '' ...''. The correct nomenclature is ''Heyndrickxia sporothermodurans.'' References Further reading * * * * External links *Type strain of ''Bacillus sporothermodurans'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase sporothermodurans Bacteria described in 1996 {{bacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as ''Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control of mosq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus
''Bacillus'' (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum ''Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacilli'' is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. ''Bacillus'' species can be either obligate aerobes which are dependent on oxygen, or facultative anaerobes which can survive in the absence of oxygen. Cultured ''Bacillus'' species test positive for the enzyme catalase if oxygen has been used or is present. ''Bacillus'' can reduce themselves to oval endospores and can remain in this dormant state for years. The endospore of one species from Morocco is reported to have survived being heated to 420 °C. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients: the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. They are not true spores (i.e., not an offspring). Endospore formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Cereus
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness due to their spore-forming nature, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals, and even exhibit mutualism with certain plants. ''B. cereus'' bacteria may be anaerobes or facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus ''Bacillus'', can produce protective endospores. They have a wide range of virulence factors, including phospholipase C, cereulide, sphingomyelinase, metalloproteases, and cytotoxin K, many of which are regulated via quorum sensing. ''B. cereus'' strains exhibit flagellar motility. The ''Bacillus cereus'' group comprises seven closely related species: ''B. cereus'' ''sensu stricto'' (referred to herein as ''B. cereus''), '' B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Anthracis
''Bacillus anthracis'' is a gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium that causes anthrax, a deadly disease to livestock and, occasionally, to humans. It is the only permanent ( obligate) pathogen within the genus ''Bacillus''. Its infection is a type of zoonosis, as it is transmitted from animals to humans. It was discovered by a German physician Robert Koch in 1876, and became the first bacterium to be experimentally shown as a pathogen. The discovery was also the first scientific evidence for the germ theory of diseases. ''B. anthracis'' measures about 3 to 5 μm long and 1 to 1.2 μm wide. The reference genome consists of a 5,227,419 bp circular chromosome and two extrachromosomal DNA plasmids, pXO1 and pXO2, of 181,677 and 94,830 bp respectively, which are responsible for the pathogenicity. It forms a protective layer called endospore by which it can remain inactive for many years and suddenly becomes infective under suitable environmental conditions. Because of the resilie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |