|
586 BC Deaths
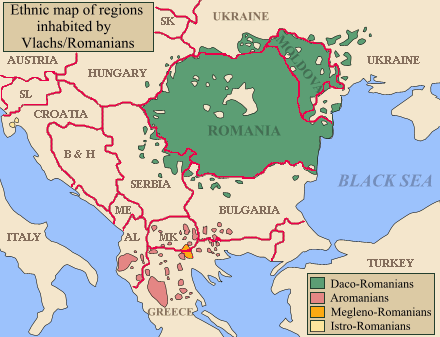
__NOTOC__ Year 586 ( DLXXXVI) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 586 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – Emperor Maurice rejects a peace proposal of the Persians, in exchange for renewed payments in gold. * Battle of Solachon: A Byzantine army under command of Philippicus defeats the Sassanid Persians, near Dara. * The Avars besiege Thessalonica ( Central Macedonia), the second city of the Byzantine Empire.History of the Byzantine Empire from DCCXVI to MLVII, George Finlay, p. 316 * The Vlachs are first mentioned in a Byzantine chronicle (approximate date). Europe * April 21 – King Liuvigild dies at Toledo after an 18-year reign, and is succeeded by his second son Reccared I. * Slavs advance to the gat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
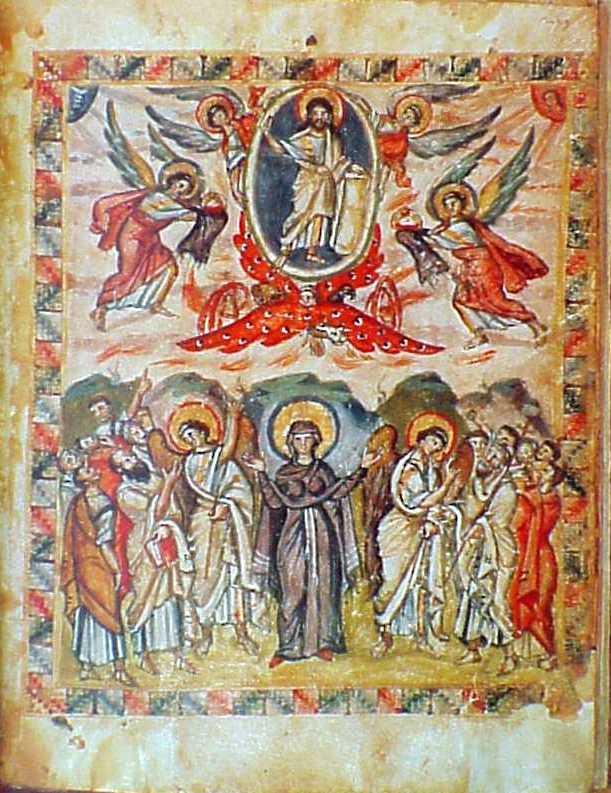
Rabbula Gospels
The Rabbula Gospels, or Rabula Gospels, (Florence, Biblioteca Medicea Laurenziana, cod. Plut. I, 56) is a 6th-century illuminated Syriac Gospel Book. One of the finest Byzantine works produced in Asia, and one of the earliest Christian manuscripts with large miniatures, it is distinguished by the miniaturist's predilection for bright colours, movement, drama, and expressionism. Coming from a period from in which little art survived, and which saw great development in Christian iconography, the manuscript has a significant place in art history, and is very often referred to. Recent scholarship has suggested that the manuscript completed in 586 was later partly overpainted by restorers and bound together with miniatures from other sources in the 15th or 16th century. Description The Gospel was completed in 586 at Monastery of St. John of Zagba (Syriac: , ), which, although traditionally thought to have been in Northern Mesopotamia, is now thought to have been in the hinterland b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crucifixion Of Jesus
The crucifixion and death of Jesus occurred in 1st-century Judea, most likely in AD 30 or AD 33. It is described in the four canonical gospels, referred to in the New Testament epistles, attested to by other ancient sources, and considered an established historical event. There is no consensus among historians on the details. Christopher M. Tuckett in ''The Cambridge companion to Jesus'' edited by Markus N. A. Bockmuehl 2001 Cambridge Univ Press pp. 123–124 In the canonical gospels, Jesus is arrested and tried by the Sanhedrin, and then by Pontius Pilate, who sentences him to flagellation and finally crucifixion by the Roman Empire.''The Cradle, the Cross, and the Crown: An Introduction to the New Testament'' by Andreas J. Köstenberger, L. Scott Kellum 2009 pp. 104–108Evans, Craig A. (2001). ''Jesus and His Contemporaries: Comparative Studies'' p. 316 Jesus was stripped of his clothing and offered vinegar mixed with myrrh or gall (likely posca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratiaria
Ratiaria (or: Raetiaria, Retiaria, Reciaria, Razaria; bg, Рациария; el, Ραζαρία μητρόπολις;) was a city founded by the Moesians, a Daco-Thracian tribe, in the 4th century BC, along the river Danube. In Roman times it was named '' Colonia Ulpia Traiana Ratiaria''. It is located 2 km west of the present village of Archar in Vidin Province, northwestern Bulgaria. The closest modern cities are Vidin (27 km. to the north west) and Lom (28 km. to the east). An archaeological museum for the site has recently been established in Dimovo. History Ratiaria was conquered by the Dacians of Burebista and later by the Romans. There was a gold mine in the city, which was exploited by the Thracians. The city may have owed its success to the goldsmiths. The earliest involvement of the Romans occurred in 75 BC when Gaius Scribonius Curio, prefect of Macedonia, entered this territory to ward off the Scordisci, the Dardani and the Daci. In 29 BC, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonia Ulpia Oescus
Oescus, Palatiolon or Palatiolum ( bg, Улпия Ескус, ) was an important ancient city on the Danube river in Ancient Rome, Roman Moesia. It later became known as ''Ulpia Oescus''. It lay northwest of the modern Bulgarian city of Pleven, near the village of Gigen. For a short time it was linked by the longest and most famous stone bridge across the Danube, Constantine's Bridge (Danube), Constantine's Bridge, with the ancient city of Sucidava (modern-day Corabia, Romania). The city seems to have at one point reached a area of 280,000 m2 and a population of 100,000. Archaeological excavations have brought to light parts of the ancient city and are continuing. Etymology The name of the Roman town comes from the river Oescus (today Iskar (river), Iskar). It probably meant "water" in the local Thracian language, Thracian dialect. History The Greek geographer Claudius Ptolemy (ca. 90–168 AD) described Ulpia Oescus as a city of the Triballi, an independent ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danubian Limes
The Danubian Limes (german: Donaulimes), or Danube Limes, refers to the Roman military frontier or ''limes'' which lies along the River Danube in the present-day German state of Bavaria, in Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Bulgaria and Romania. The Danube was not always or everywhere used by the Romans as the military frontier which was moved north or south in some locations according to military conquests, but it was maintained in many places as a fairly permanent defensive structure for long periods. The border was reinforced with numerous watchtowers, legion camps (''castra'') and forts (''castella''). Due to the boggy and dendritic nature of the Danube's river banks no border ramparts were built, unlike the Neckar-Odenwald Limes in Germany. The camps were built in the mid-1st century. Later, under Trajan, the camps, which had originally only been surrounded by earthen embankments, were enclosed by stone walls. A Roman road, the Danube Way ( la, Via Istrum) was la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, Βαρχονίτες, Varchonítes), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine sources, and the Apar ( otk, 𐰯𐰺) to the Göktürks (). They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century. The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars of the Caucasus, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars might or might not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and destruction in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century the peninsula was known as the Morea ( grc-x-byzant, Μωρέας), (Morèas) a name still in colloquial use in its demotic Greek, demotic form ( el, Μωριάς, links=no), (Moriàs). The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions of Greece, administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica (region), Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably diverse both genetically and culturally, and relations between them � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reccared I
Reccared I (or Recared; la, Flavius Reccaredus; es, Flavio Recaredo; 559 – December 601; reigned 586–601) was Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania. His reign marked a climactic shift in history, with the king's renunciation of Arianism in favour of Catholicism in 587. Reign Reccared was the younger son of King Leovigild by his first wife. Like his father, Reccared had his capital at Toledo. The Visigothic kings and nobles were traditionally Arian Christians, while the Hispano-Roman population were Roman Catholics. The Catholic bishop Leander of Seville was instrumental in converting the elder son and heir of Leovigild, Hermenegild, to Catholicism. Leander supported his rebellion and was exiled for his role. When King Leovigild died, within a few weeks of April 21, 586, bishop Leander was swift to return to Toledo. The new king had been associated with his father in ruling the kingdom and was acclaimed king by the Visigothic nobles without opposition. In January 58 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toledo, Spain
Toledo ( , ) is a city and municipality of Spain, capital of the province of Toledo and the ''de jure'' seat of the government and parliament of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. Toledo was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1986 for its extensive monumental and cultural heritage. Located on the banks of the Tagus in central Iberian Peninsula, Iberia, Toledo is known as the "City of the Three Cultures" for the cultural influences of Christians, Muslims, and Jews throughout its history. It was the capital, from 542 to 725 CE, of the Visigothic kingdom, which followed the fall of the Roman Empire. Toledo was also the location of historic events such as the Councils of Toledo and was labelled the "Imperial City" due to the fact that it was the main venue of the court of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in Spain. The city, seat of a powerful archdiocese for much of its history, has a Gothic Cathedral, the ''Cathedral of Toledo, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |