|
Burrium
Burrium was a legionary fortress in the Roman province of Britannia Superior or Roman Britain. Its remains today lie beneath the town of Usk in Monmouthshire, south east Wales. The Romans founded the fortress around AD 55, probably for the Legio XX Valeria Victrix (20th Legion) and perhaps an additional ''ala'' of 500 cavalrymen. Earth and timber defences surrounded a number of legionary barracks. The fort was key to the conquest of the Silures, a tribe very resistant to the imposition of Roman rule in Roman Wales, but in AD 66, the legion was transferred to Viroconium Cornoviorum (at Wroxeter) and their base in Wales was largely abandoned. It was briefly replaced by a works depot for iron working. The surrounding vicus seems not to have developed into a small town, although it may have had an official mansio In the Roman Empire, a ''mansio'' (from the Latin word ''mansus,'' the perfect passive participle of ''manere'' "to remain" or "to stay") was an official stopping place on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio XX Valeria Victrix
Legio XX Valeria Victrix, in English Twentieth Victorious Valeria Legion was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. The origin of the Legion's name is unclear and there are various theories, but the legion may have gained its title ''Valeria Victrix'' from a victory it achieved during the Great Illyrian revolt under the command of the general Marcus Valerius Messalla Messallinus. The legion had a boar as its emblem. History The legion was probably founded shortly after 31 BC by the emperor Augustus. XX ''Valeria victrix'' was probably part of the large Roman force that fought in the Cantabrian Wars in Hispania from 25 to 19 BC. The legion then moved to Burnum in Illyricum at the beginning of the Pannonian uprising (''Bellum Batonianum'') in AD 6. It is recorded operating against the Marcomanni in AD 6 in the army of Tiberius. In Illyria they were led by the governor of Illyricum, Marcus Valerius Messalla Messallinus, who may have given his clan (''gens'') name '' Valeria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of the Roman Empire (27 BC – AD 476). Size The size of a typical legion varied throughout the history of ancient Rome, with complements ranging from 4,200 legionaries and 300 equites (drawn from the wealthier classes – in early Rome all troops provided their own equipment) in the Republican period of Rome (the infantry were split into 10 cohorts each of four maniples of 120 legionaries), to 4,800 legionaries (in 10 cohorts of 6 centuries of 80 legionaries) during Caesar's age, to 5,280 men plus 120 auxiliaries in the Imperial period (split into 10 cohorts, nine of 480 men each, with the first cohort being double-strength at 960 men). It should be noted the above numbers are typical field strengths while "paper strength" was sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobunni; and to the west by the Demetae. Origins According to Tacitus's biography of Agricola, the Silures usually had a dark complexion and curly hair. Due to their appearance, Tacitus believed they had crossed over from Spain at an earlier date."... the swarthy faces of the Silures, the curly quality, in general, of their hair, and the position of Spain opposite their shores, attest to the passage of Iberians in old days and the occupation by them of these districts; ..." (Tacitus Annales Xi.ii, translated by M. Hutton) Jordanes, in his Origins and Deeds of the Goths, describes the Silures. "The Silures have swarthy features and are usually born with curly black hair, but the inhabitants of Caledonia have reddish hair and large loose-joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Fortifications In Monmouthshire
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμα� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansio
In the Roman Empire, a ''mansio'' (from the Latin word ''mansus,'' the perfect passive participle of ''manere'' "to remain" or "to stay") was an official stopping place on a Roman road, or ''via'', maintained by the central government for the use of officials and those on official business whilst travelling. Background The roads which traversed the Ancient World were later surveyed, developed and carefully maintained by the Romans, featuring purpose-built rest stops at regular intervals, known as ''castra''. Probably originally established as simple places of military encampment, in process of time they included barracks and magazines of provisions (''horrea'') for the troops. Over time the need arose for a more sophisticated form of shelter for travelling dignitaries and officials. The Latin term ''mansio'' is derived from ''manere'', signifying to pass the night at a place while travelling. (The word is likely to be the source of the English word mansion, though their uses are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicus (Rome)
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (plural ) designated a village within a rural area () or the neighbourhood of a larger settlement. During the Republican era, the four of the city of Rome were subdivided into . In the 1st century BC, Augustus reorganized the city for administrative purposes into 14 regions, comprising 265 . Each had its own board of officials who oversaw local matters. These administrative divisions are recorded as still in effect at least until the mid-4th century. The word "" was also applied to the smallest administrative unit of a provincial town within the Roman Empire. It is also notably used today to refer to an ''ad hoc'' provincial civilian settlement that sprang up close to and because of a nearby military fort or state-owned mining operation. Local government in Rome Each ''vicus'' elected four local magistrates ('' vicomagistri'') who commanded a sort of local police force chosen from among the people of the ''vicus'' by lot. Occasionally the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wroxeter
Wroxeter is a village in Shropshire, England, which forms part of the civil parish of Wroxeter and Uppington, beside the River Severn, south-east of Shrewsbury. ''Viroconium Cornoviorum'', the fourth largest city in Roman Britain, was sited here, and is gradually being excavated. History Roman Wroxeter, near the end of the Watling Street Roman road that ran across Romanised Celtic Britain from '' Dubris'' (Dover), was a key frontier position lying on the bank of the Severn river whose valley penetrated deep into what later became Wales following brytons fall to the Anglo Saxons, and also on a route to the south leading to the Wye valley. Archaeology has shown that the site of the later city first was established about AD 55 as a frontier post for a Thracian legionary cohort located at a fort near the Severn river crossing. A few years later a legionary fortress (''castrum'') was built within the site of the later city for the Legio XIV Gemina during their invasion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viroconium Cornoviorum
Viroconium or Uriconium, formally Viroconium Cornoviorum, was a Ancient Romans, Roman city, one corner of which is now occupied by Wroxeter, a small village in Shropshire, England, about east-south-east of Shrewsbury. At its peak, Viroconium is estimated to have been the 4th-largest Roman Empire, Roman settlement in Roman Britain, Britain, a ''civitas'' with a population of more than 15,000.Frere, ''Britannia'', p.253 The settlement probably lasted until the end of the 7th century or the beginning of the 8th. Extensive remains can still be seen. Toponym ''Viroconium'' is a latinisation of names, Latinised form of a Celtic toponymy, toponym that was linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed as Common Brittonic ''*Uiroconion'' ("[city] of ''*Uirokū''". ''*Uirokū'' ( "man-wolf") is believed to have been a Given name#Gender, masculine given name meaning "werewolf". The original capital of the local British tribe of the Cornovii was the impressive British hillforts, hillfort on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
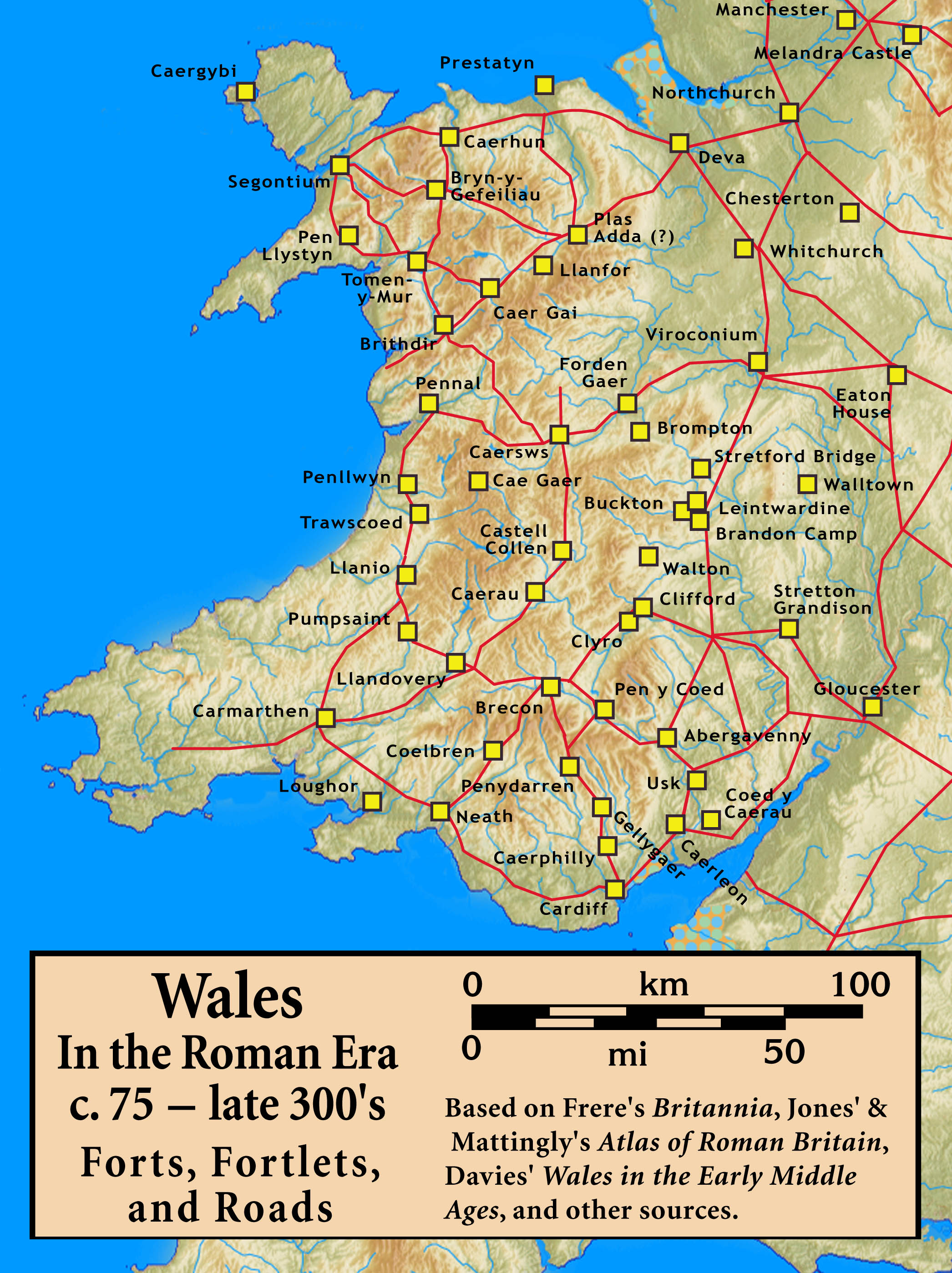
Wales In The Roman Era
The Roman era in the area of modern Wales began in 48 AD, with a military invasion by the imperial governor of Roman Britain. The conquest was completed by 78 AD, and Roman rule endured until the region was abandoned in 383 AD. The Roman Empire held a military occupation in most of Wales, except for the southern coastal region of South Wales, east of the Gower Peninsula, where there is a legacy of Romanisation in the region, and some southern sites such as Carmarthen, which was the civitas capital of the Demetae tribe. The only town in Wales founded by the Romans, Caerwent, is located in South Wales. Wales was a rich source of mineral wealth, and the Romans used their engineering technology to extract large amounts of gold, copper, and lead, as well as modest amounts of some other metals such as zinc and silver. The Roman campaigns of conquest in Wales appear in surviving ancient sources, who record in particular the resistance and ultimate conquest of two of the five na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ala (Roman Allied Military Unit)
An ''ala'' (Latin for "wing", plural: ''alae'') was the term used during the middle of the Roman Republic (338–88 BC) to denote a military formation composed of conscripts from the ''socii'', Rome's Italian military allies. A normal consular army during the period consisted of two legions, composed of only Roman citizens, and two allied ''alae''. The ''alae'' were somewhat larger than normal legions, 5,400 or 5,100 men against the legion's 4,500 men, and it contained a greater quantity of cavalry, usually 900 horsemen against the 300 supplied by the Romans. From the time of the first Roman emperor, Augustus (ruled 27 BC – AD 14), the term ''ala'' was used in the professional imperial army to denote a much smaller (ca. 500), purely cavalry unit of the non-citizen auxilia corps: see ala (Roman cavalry unit). History When the Roman armies started being composed partly of Roman citizens and partly of ''socii'' (allies from the rest of the Italian mainland), either Latini or Ita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castra
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term. In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and plural forms could refer in Latin to either a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discussion about the typologies of Roman fortifications. In English usage, ''castrum'' commonly translates to "Roman fort", "Roman camp" and "Roman fortress". However, scholastic convention tends to translate ''castrum'' as "fort", "camp", "marching camp" or "fortress". Romans used the term ''castrum'' for different sizes of camps – including large legionary fortresses, smaller forts for cohorts or for auxiliary forces, temporary encampments, and "marching" forts. The diminutive form ''castellum'' was used for fortlets, typically occupied by a detachment of a cohort or a '' centuria''. For a list of known castr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |