|
Brood XXII
Brood XXII (also known as The Baton Rouge Brood) is a brood of 13-year periodical cicadas, last seen in 2014 in a geographic region centered on Baton Rouge, Louisiana, as well as other locations in southeast Louisiana and southwest Mississippi. Periodical cicadas (''Magicicada spp.'') are often referred to as "17-year locusts" because most of the known distinct broods have a 17-year life cycle. Brood XXII is one of only three surviving broods with a 13-year cycle. The next emergence of The Baton Rouge Brood is expected in 2027. Position among other broods of cicadas Every 13 years, Brood XXII tunnels ''en masse'' to the surface of the ground, mates, lays eggs, and then dies off in several weeks. In 1907, the entomologist C. L. Marlatt postulated the existence of 30 different broods of periodical cicadas: 17 distinct broods with a 17-year life cycle, to which he assigned Roman numerals I through XVII (with emerging years 1893 through 1909); plus 13 broods with a 13-year cycle, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
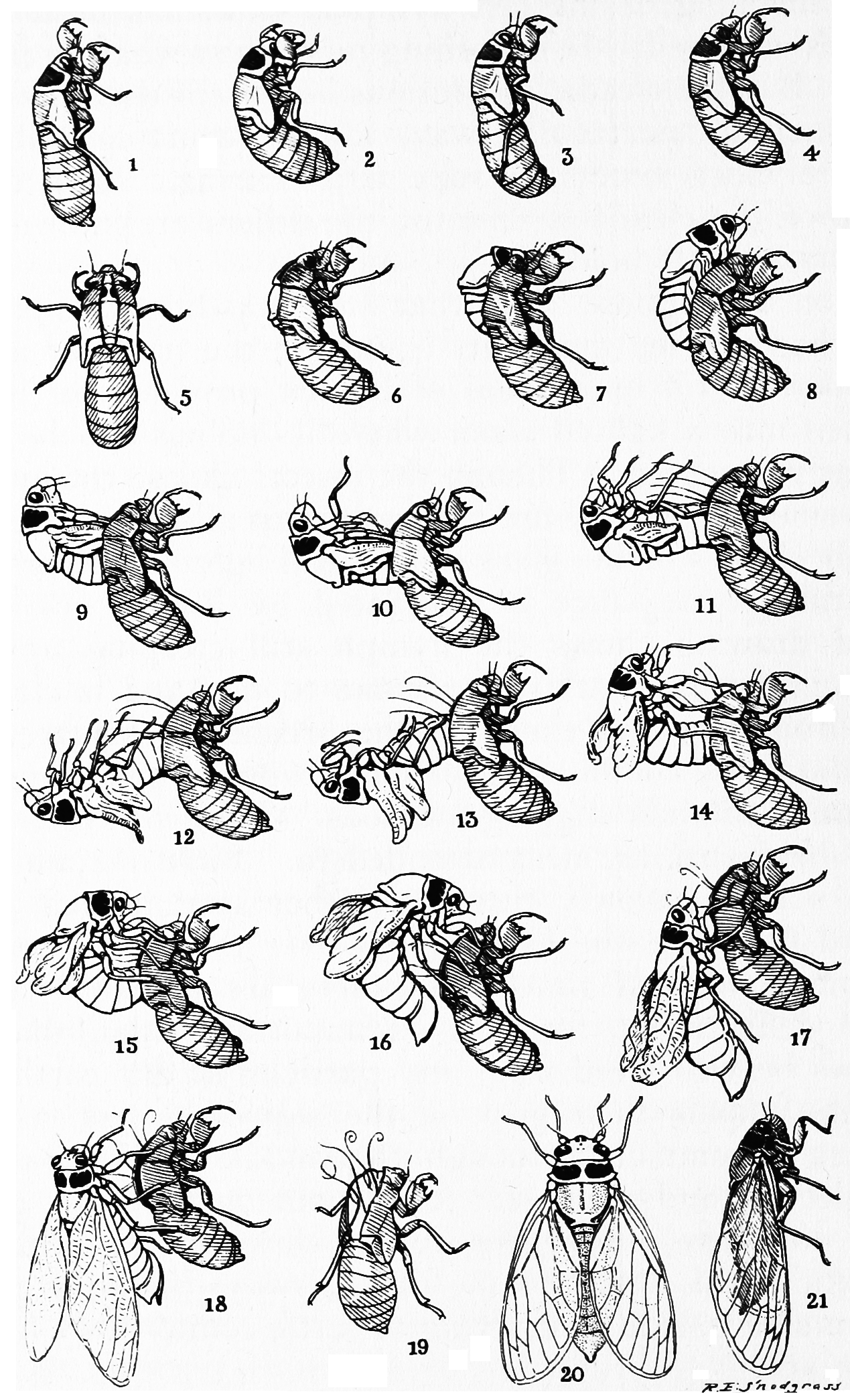
Periodical Cicadas
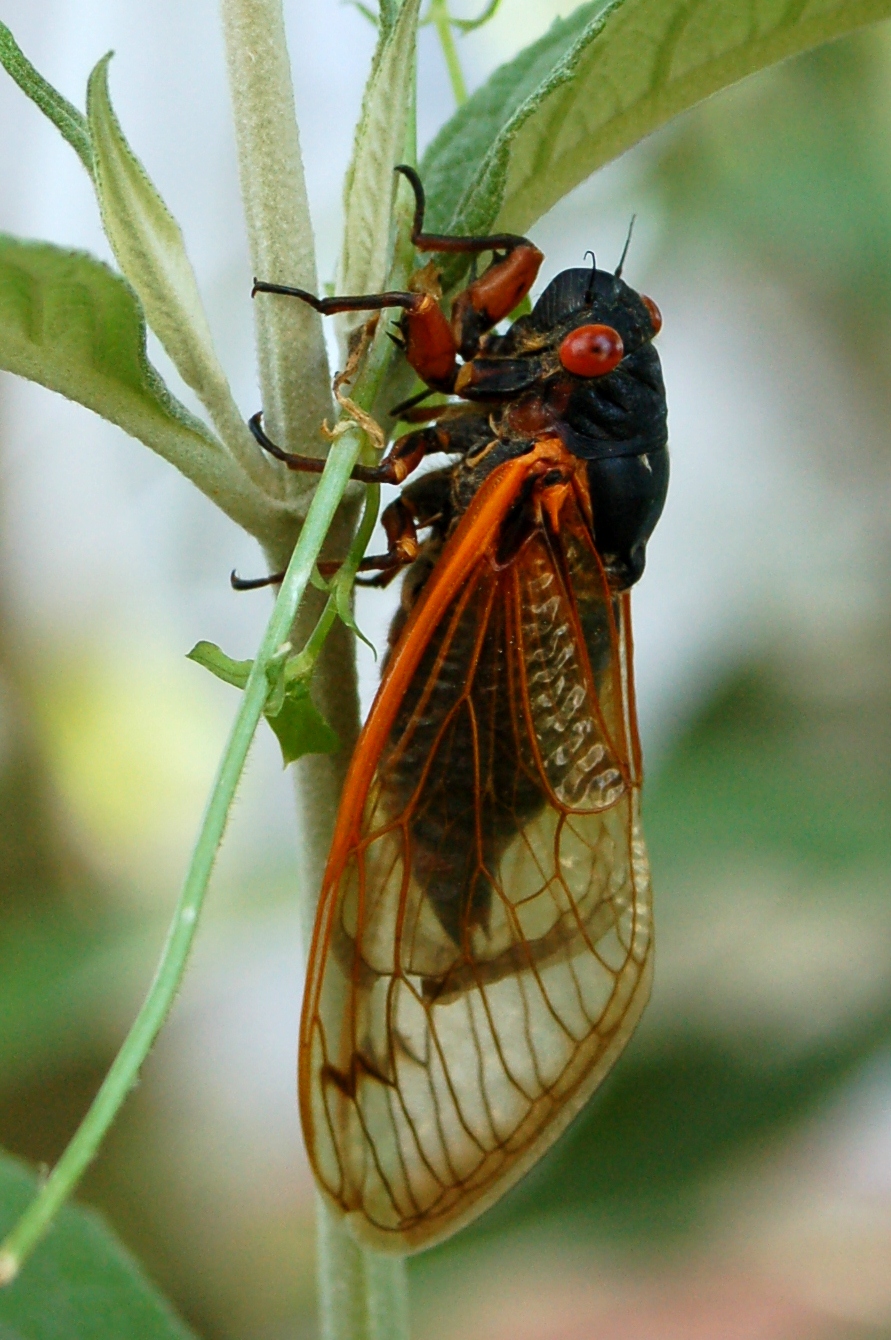
The term periodical cicada is commonly used to refer to any of the seven species of the genus ''Magicicada'' of eastern North America, the 13- and 17-year cicadas. They are called periodical because nearly all individuals in a local population are developmentally synchronized and emerge in the same year. Although they are sometimes called "locusts", this is a misnomer, as cicadas belong to the taxonomic order Hemiptera (true bugs), suborder Auchenorrhyncha, while locusts are grasshoppers belonging to the order Orthoptera. ''Magicicada'' belongs to the cicada tribe Lamotialnini, a group of genera with representatives in Australia, Africa, and Asia, as well as the Americas. ''Magicicada'' species spend around 99.5% of their long lives underground in an immature state called a nymph. While underground the nymphs feed on xylem fluids from the roots of deciduous forest trees in the eastern United States. In the spring of their 13th or 17th year mature cicada nymphs emerge between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Baton Rouge ( ; ) is a city in and the capital of the U.S. state of Louisiana. Located the eastern bank of the Mississippi River, it is the parish seat of East Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana's most populous parish—the equivalent of counties in other U.S. states. Since 2020, it has been the 99th-most-populous city in the United States and the second-largest city in Louisiana, after New Orleans; Baton Rouge is the 18th-most-populous state capital. According to the 2020 United States census, the city-proper had a population of 227,470; its consolidated population was 456,781 in 2020. The city is the center of the Greater Baton Rouge area—Louisiana's second-largest metropolitan area—with a population of 870,569 as of 2020, up from 802,484 in 2010. The Baton Rouge area owes its historical importance to its strategic site upon the Istrouma Bluff, the first natural bluff upriver from the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. This allowed development of a business qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bordered by the state of Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, Mississippi to the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. A large part of its eastern boundary is demarcated by the Mississippi River. Louisiana is the only U.S. state with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are equivalent to counties, making it one of only two U.S. states not subdivided into counties (the other being Alaska and its boroughs). The state's capital is Baton Rouge, and its largest city is New Orleans, with a population of roughly 383,000 people. Some Louisiana urban environments have a multicultural, multilingual heritage, being so strongly influenced by a mixture of 18th century Louisiana French, Dominican Creole, Spanish, French Canadian, Acadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Mississippi's western boundary is largely defined by the Mississippi River. Mississippi is the 32nd largest and 35th-most populous of the 50 U.S. states and has the lowest per-capita income in the United States. Jackson is both the state's capital and largest city. Greater Jackson is the state's most populous metropolitan area, with a population of 591,978 in 2020. On December 10, 1817, Mississippi became the 20th state admitted to the Union. By 1860, Mississippi was the nation's top cotton-producing state and slaves accounted for 55% of the state population. Mississippi declared its secession from the Union on January 9, 1861, and was one of the seven original Confederate States, which constituted the largest slaveholding states in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lester Marlatt
Charles Lester Marlatt (1863–1954) was an American entomologist. Born in 1863 at Atchison, Kansas, he was educated at Kansas State Agricultural College (B.S., 1884; M.S., 1886), where he was assistant professor for two years. He is the person who introduced the ladybug insect '' Chilocorus similis'' into the United States to control the San Jose scale insect, which was first discovered in San Jose, California in 1880 by John Henry Comstock and named by him. Marlatt worked for the Bureau of Entomology, United States Department of Agriculture. In 1912 he was appointed chairman of the Federal Horticultural Board. He was president of the Entomological Society of Washington in 1897–98 and of the American Association of Economic Entomologists in 1899. His 1907 description of periodic cicadas remains a classic in the field. In this article, Marlatt proposed a grouping of periodic cicadas into 30 different broods, each given a Roman numeral Roman numerals are a nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood XIX
Brood XIX (also known as The Great Southern Brood) is the largest (most widely distributed) brood of 13-year periodical cicadas, last seen in 2011 across a wide stretch of the southeastern United States. Periodical cicadas (''Magicicada spp.'') are often referred to as "17-year locusts" because most of the known distinct broods have a 17-year life cycle. Brood XIX is one of only three surviving broods with a 13-year cycle. It is also notable because it includes four different 13-year species, one of which was discovered in Brood XIX in 1998 by scientists listening to cicada songs. Position among other broods of cicadas Every 13 years, Brood XIX tunnels ''en masse'' to the surface of the ground, mates, lays eggs, and then dies off in several weeks. In 1907, entomologist C. L. Marlatt postulated the existence of 30 different broods of periodical cicadas: 17 distinct broods with a 17-year life cycle, to which he assigned Roman numerals I through XVII (with emerging years 1893 th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood XXIII
Brood XXIII (also known as the Mississippi Valley Brood) is a brood of 13-year periodical cicadas that last emerged in 2015 around the Mississippi River in the states of Louisiana, Mississippi, Arkansas, Tennessee, Missouri, Kentucky, and Illinois. The brood was also seen in Southwestern Indiana and Western Kentucky around the Ohio River, and as far north as Weldon Springs State Park in DeWitt County, Illinois. Brood XXIII is one of three extant periodical cicada broods with a 13-year life cycle, and thus is expected to be seen again in 2028. Lifecycle and history Every 13 years Brood XXIII cicadas tunnel ''en masse'' to the surface of the ground in late-April to early-June of emergence years to molt, mate, lay eggs, and subsequently die off over the course of a few weeks. After the eggs hatch, the nymphs burrow back underground to further develop and grow for the next 13 years before emerging again, completing the cycle. The extreme number of emerging cicadas is often give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood XXI
The term periodical cicada is commonly used to refer to any of the seven species of the genus ''Magicicada'' of eastern North America, the 13- and 17-year cicadas. They are called periodical because nearly all individuals in a local population are developmentally synchronized and emerge in the same year. Although they are sometimes called " locusts", this is a misnomer, as cicadas belong to the taxonomic order Hemiptera (true bugs), suborder Auchenorrhyncha, while locusts are grasshoppers belonging to the order Orthoptera. ''Magicicada'' belongs to the cicada tribe Lamotialnini, a group of genera with representatives in Australia, Africa, and Asia, as well as the Americas. ''Magicicada'' species spend around 99.5% of their long lives underground in an immature state called a nymph. While underground the nymphs feed on xylem fluids from the roots of deciduous forest trees in the eastern United States. In the spring of their 13th or 17th year mature cicada nymphs emerge between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida Panhandle
The Florida Panhandle (also West Florida and Northwest Florida) is the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Florida; it is a Salient (geography), salient roughly long and wide, lying between Alabama on the north and the west, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia on the north, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. Its eastern boundary is arbitrarily defined. In terms of population, major communities include Tallahassee, Florida, Tallahassee, Pensacola, Florida, Pensacola, and Panama City, Florida, Panama City. As is the case with the other eight U.S. states that have Salient (geography)#Panhandles in the United States, panhandles, the geographic meaning of the term is inexact and elastic. References to the Florida Panhandle always include the ten List of counties in Florida, counties west of the Apalachicola River, a natural geographic boundary, which was the historic dividing line between the British colonies of West Florida and East Florida. These western counties also lie in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magicicada Tredecim
''Magicicada tredecim'' is a 13-year species of periodical cicada, closely related to the newly discovered 13-year species '' Magicicada neotredecim'', from which it differs in male song pitch, female song pitch preferences, abdomen color, and mitochondrial DNA. Both ''M. tredecim'' and ''M. neotredecim'' are closely related to the 17-year species '' M. septendecim'', which was identified by Linnaeus in 1758; these three species are often grouped together under the name decim periodical cicadas. Description Like other species included in its genus, ''M. tredicim'' has reddish eyes and wing veins. Its dorsal thorax is black. The underside of the abdomen of ''M. tredecim'' is light orange or caramel colored, lacking the dark bands seen in ''M. neotredicim'' and ''M. septendecim''. Life cycle Their median life cycle from egg to natural adult death is around thirteen years. However, their life cycle can range from nine years to seventeen years. Habitat, distribution, and cicada "br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magicicada Tredecassini
''Magicicada tredecassini'' is a species of periodical cicada endemic to the United States. It has a 13-year lifecycle but is otherwise indistinguishable from the 17-year periodical cicada ''Magicicada cassini''. The two species are usually discussed together as "cassini periodical cicadas The Cassini periodical cicadas are a pair of closely related species of periodical cicadas: ''Magicicada cassini'' (Fisher, 1852), having a 17-year life cycle, and '' Magicicada tredecassini'' (Alexander and Moore, 1962), a nearly identical speci ..." or "cassini-type periodical cicadas." Unlike other periodical cicadas, cassini-type males may synchronize their courting behavior so that tens of thousands of males sing and fly in unison. Life cycle Their median life cycle from egg to natural adult death is around thirteen years. However, their life cycle can range from nine years to seventeen years. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q16754783 Insects of the United States Insects described in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magicicada Tredecula
''Magicicada tredecula'' is a species of periodical cicada in the family Cicadidae. It is endemic to the United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie .... As its specific epithet implies, they emerge as adults once every thirteen years. Life Cycle Their median life cycle from egg to natural adult death is around thirteen years. However, their life cycle can range from nine years to seventeen years. References * Insects of the United States Insects described in 1962 Lamotialnini {{Cicadidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |