|
British Military Regime In New France
The British military regime in New France was the British army's occupation of New France from 1759 to 1763 as part of its Conquest of New France. Between 1760, following the surrender of Montreal, and 1763, when the colonial province of Quebec (1763-1791) was created, a temporary military regime administered the colony of Canada. The military regime officially ended following the enactment of the Treaty of Paris (1763), which ended the Seven Years' War and created the province of Quebec a new colony in British North America. However, it was not until August 10, 1764, that this military regime was replaced by a civilian regime, because of the 18-month delay allowed by the ratification of the Treaty of Paris. Beginning On September 8, 1760, the city of Montreal was surrounded by the British army. In order to avoid a destructive siege like the one the city of Québec experienced in 1759, the city capitulated. This led the whole of New France to be under the domination of the Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitulation Montreal
{{disambig ...
Capitulation may have the following special meanings. *Capitulation (surrender) ** Stock market capitulation *Capitulation (treaty) **Capitulations of the Ottoman Empire * Capitulation (algebra) * Conclave capitulation *Electoral capitulation An electoral capitulation (german: Wahlkapitulation) was initially a written agreement in parts of Europe, principally the Holy Roman Empire, whereby from the 13th century onward, a candidate to a prince-bishopric had to agree to a set of precondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre De Rigaud, Marquis De Vaudreuil-Cavagnial
Pierre de Rigaud de Vaudreuil de Cavagnial, marquis de Vaudreuil (22 November 1698 – 4 August 1778) was a Canadian-born colonial governor of French Canada in North America. He was governor of French Louisiana (1743–1753) and in 1755 became the last Governor-General of New France. In 1759 and 1760 the British conquered the colony in the Seven Years' War (known in the United States as the French and Indian War). Life and work He was born to the Governor-General of New France, Philippe de Rigaud Vaudreuil and his wife, Louise-Élisabeth, the daughter of Pierre de Joybert de Soulanges et de Marson, in Quebec. He was the uncle of Louis-Philippe de Vaudreuil. Vaudreuil rose quickly through the New France military and civil service, in part owing to his father's patronage but also due to his own innate ability. Commissioned an officer of the French army An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1759 In Canada
Events from the year 1759 in Canada. Incumbents *French Monarch: Louis XV * British and Irish Monarch: George II Governors *Governor General of New France: Pierre François de Rigaud, Marquis de Vaudreuil-Cavagnal * Colonial Governor of Louisiana: Louis Billouart *Governor of Nova Scotia: Charles Lawrence * Commodore-Governor of Newfoundland: Richard Edwards Events * Tuesday May 22 - A British fleet approaches Quebec. * Thursday June 28 - French fire ships, intended to burn the British fleet, at Quebec, are taken ashore by British sailors. * Thursday July 26 - Carillon (Fort Ticonderoga) is abandoned by the French. * Saturday July 28 - Another French fireship attack fails against the British. * Tuesday July 31 - British forces attempt to take French fortifications at Montmorency and fail bitterly. * August 8 to August 9 - British guns, on Pointe Lévis, fire the lower town of Quebec. * Thursday September 13 - James Wolfe lands a force at Fuller's Cove, between 1 and 2 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominion Of Canada
While a variety of theories have been postulated for the name of Canada, its origin is now accepted as coming from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word , meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. In 1535, indigenous inhabitants of the present-day Quebec City region used the word to direct French explorer Jacques Cartier to the village of Stadacona. Cartier later used the word ''Canada'' to refer not only to that particular village but to the entire area subject to Donnacona (the chief at Stadacona); by 1545, European books and maps had begun referring to this small region along the Saint Lawrence River as ''Canada''. From the 16th to the early 18th century, ''Canada'' referred to the part of New France that lay along the Saint Lawrence River. In 1791, the area became two British colonies called Upper Canada and Lower Canada. These two colonies were collectively named the Canadas until their union as the British Province of Canada in 1841. Upon Confederation in 1867, ''Canada'' was adop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area and the second-largest by Population of Canada by province and territory, population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois people, Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York (state), New York in the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Proclamation Of 1763
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The Proclamation forbade all settlements west of a line drawn along the Appalachian Mountains, which was delineated as an Indian Reserve. Exclusion from the vast region of Trans-Appalachia created discontent between Britain and colonial land speculators and potential settlers. The proclamation and access to western lands was one of the first significant areas of dispute between Britain and the colonies and would become a contributing factor leading to the American Revolution. The 1763 proclamation line is situated similar to the Eastern Continental Divide, extending from Georgia to the divide's northern terminus near the middle of the northern border of Pennsylvania, where it intersects the northeasterly St. Lawrence Divide, and extends further thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
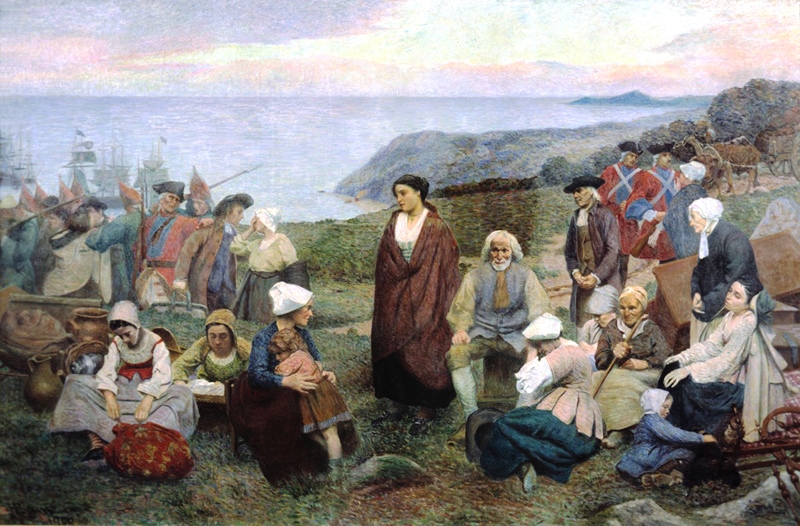
Deportation Of The Acadians
The Expulsion of the Acadians, also known as the Great Upheaval, the Great Expulsion, the Great Deportation, and the Deportation of the Acadians (french: Le Grand Dérangement or ), was the forced removal, by the British, of the Acadian people from parts of a Canadian-American region historically known as '' Acadia'', between 1755–1764. The area included the present-day Canadian Maritime provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island, and the present-day U.S. state of Maine. The Expulsion, which caused the deaths of thousands of people, occurred during the French and Indian War (the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War) and was part of the British military campaign against New France. The British first deported Acadians to the Thirteen Colonies, and after 1758, transported additional Acadians to Britain and France. In all, of the 14,100 Acadians in the region, approximately 11,500 were deported, at least 5,000 Acadians died of dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acadians
The Acadians (french: Acadiens , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Most Acadians live in the region of Acadia, as it is the region where the descendants of a few Acadians who escaped the Expulsion of the Acadians (aka The Great Upheaval / ''Le Grand Dérangement'') re-settled. Most Acadians in Canada continue to live in majority French-speaking communities, notably those in New Brunswick where Acadians and Francophones are granted autonomy in areas such as education and health. Acadia was one of the 5 regions of New France. Acadia was located in what is now Eastern Canada's Maritime provinces, as well as parts of Quebec and present-day Maine to the Kennebec River. It was ethnically, geographically and administratively different from the other French colonies and the French colony of Canada (modern-day Quebec). As a result, the Acadians developed a distinct history and cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Trading
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued. Historically the trade stimulated the exploration and colonization of Siberia, northern North America, and the South Shetland and South Sandwich Islands. Today the importance of the fur trade has diminished; it is based on pelts produced at fur farms and regulated fur-bearer trapping, but has become controversial. Animal rights organizations oppose the fur trade, citing that animals are brutally killed and sometimes skinned alive. Fur has been replaced in some clothing by synthetic imitations, for example, as in ruffs on hoods of parkas. Continental fur trade Russian fur trade Before the European colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major supplier of fur pelts to Western Europe and parts of Asia. Its trade develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffery Amherst
Field Marshal Jeffery Amherst, 1st Baron Amherst, (29 January 1717 – 3 August 1797) was a British Army officer and Commander-in-Chief of the Forces in the British Army. Amherst is credited as the architect of Britain's successful campaign to conquer the territory of New France during the Seven Years' War. Under his command, British forces captured the cities of Louisbourg, Quebec City and Montreal, as well as several major fortresses. He was also the first British Governor General in the territories that eventually became Canada. Numerous places and streets are named for him, in both Canada and the United States. Amherst's legacy is controversial due to his expressed desire to exterminate the race of indigenous people during Pontiac's War, and his alleged gifting of blankets infected with smallpox as a weapon, notably at the Siege of Fort Pitt. This has led to a reconsideration of his legacy. In 2019, the city of Montreal removed his name from a street, renaming it Rue A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)