|
Boons Offered To Kaliyan
Kali (Kaliyan in Tamil) was the sixth fragment of the primordial manifestation of Kroni (evil) according to Akilathirattu, the source of Ayyavazhi mythology and the holy book of Ayyavazhi religion. Unlike other previous manifestations, Kali spread in this yugam (yukam in Tamizh) as maya (illusion). Details of Kali were restated in Ayyavazhi Religion and he is the same Kali mentioned in Kalki Purana. Kali Yugam As the time is close to the ascendancy of Kali Yuga, a sage named Guru Muni told Shiva, "Your greatness, the Kroni was created and fragmented into six parts. Five of those parts were made to take birth. However, because none of them obeyed you, all were destroyed by Vishnu(Mayon/Thirumal in Tamizh), and his spirit (the spirit Vishnu took only in the Avatars) was kept in Parvatha Ucchi Malai (In Sanskrit 'uccha' means high, in Tamil 'malai' means mountain). Nonetheless, by the ''sixth'' fragment, Kroni still has a birth in Kali Yugam." He also requested that in this y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kali (demon)
In Hinduism, Kali ( Devanāgari: , IAST: ', with both vowels short; from a root ', 'suffer, hurt, startle, confuse') is the being who reigns during the age of the Kali Yuga and acts as the nemesis of Kalki, the tenth and final avatar of the Hindu preserver deity, Vishnu. Mahabharata According to the Mahabharata, the gandharva Kali became jealous when he was late to Princess Damayanti's marriage ceremony and discovered she had overlooked the deities Indra, Agni, Varuna, and Yama (and ultimately himself) to choose Nala as her husband. In anger, Kali spoke to his companion Dvapara, the personification of Dvapara Yuga: Kali traveled to Nala's kingdom of Nishadhas and waited twelve long years for the right moment to strike. Because Nala had rendered himself impure by not washing his feet before his prayers, Kali was able to bewitch his soul. Kali then appeared before Pushkara and invited him to play a game of dice with his brother, guaranteeing Nala's downfall. Dwapara took the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
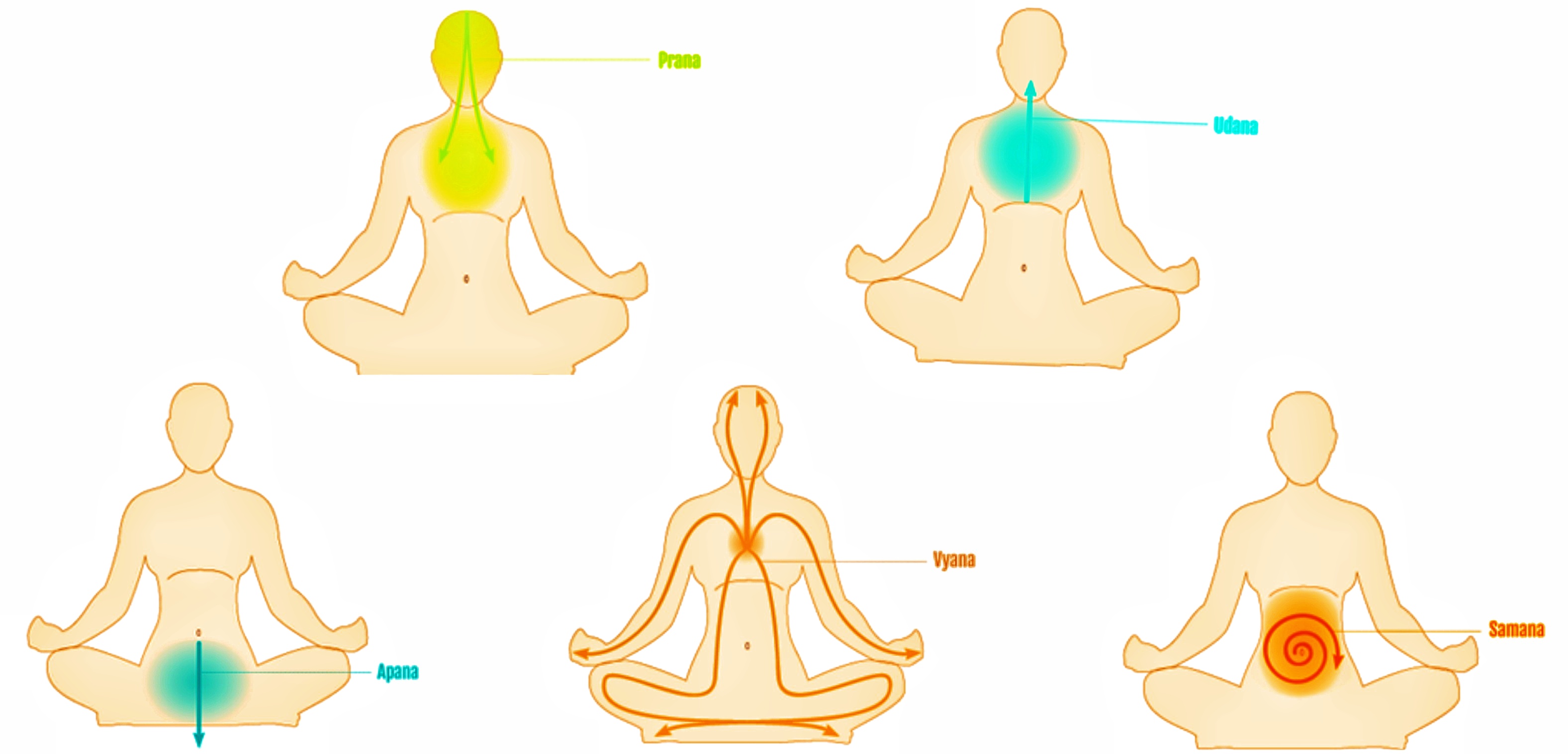
Prana
In yoga, Indian medicine and Indian martial arts, prana ( sa2, प्राण, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five ''vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand prana. Etymology V. S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products. At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames are produced. The ''flame'' is the visible portion of the fire. Flames consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce Plasma (physics), plasma. Depending on the substances alight, and any impurities outside, the color of the flame and the fire's Intensity (heat transfer), intensity will be different. Fire in its most common form can result in conflagration, which has the potential to cause physical damage through burning. Fire is an important process that affects ecological systems around the globe. The positive effects of fire include stimulating growth and maintaining various ecological systems. Its negative effects include hazard to life and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmam
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' ( sa, ब्रह्मन्) connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality in the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part XII In major schools of Hindu philosophy, it is the material, efficient, formal and final cause of all that exists.For dualism school of Hinduism, see: Francis X. Clooney (2010), ''Hindu God, Christian God: How Reason Helps Break Down the Boundaries between Religions'', Oxford University Press, , pages 51–58, 111–115;For monist school of Hinduism, see: B. Martinez-Bedard (2006), ''Types of Causes in Aristotle and Sankara'', Thesis – Department of Religious Studies (Advisors: Kathryn McClymond and Sandra Dwyer), Georgia State University, pages 18–35 It is the pervasive, infinite, eternal truth, consciousness and bliss which does not change, yet is the cause of all changes. ''Brahman'' as a metaphysical concept refers to the single bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Kailash
Mount Kailash (also Kailasa; ''Kangrinboqê'' or ''Gang Rinpoche''; Standard Tibetan, Tibetan: གངས་རིན་པོ་ཆེ; ; sa, कैलास, ), is a mountain in the Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It has an altitude of . It lies in the Gangdise Shan, Kailash Range (Gangdisê Mountains) of the Transhimalaya, in the western part of the Tibetan Plateau. Mount Kailash is less than 100 km towards the north from the western trijunction of the borders of China, India, and Nepal. Mount Kailash is located close to Lake Manasarovar and Lake Rakshastal. The sources of four major Asian rivers lie close to this mountain and the two lakes. These rivers are the Indus River, Indus, the Sutlej, the Brahmaputra River, Brahmaputra, and the Karnali River, Karnali (a tributary of the Ganges). Mount Kailash is considered sacred in four religions: Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Bon. Etymology The mountain is known as “'” (; var. ' ) in Sanskrit. The nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hinduism. Shiva is known as "The Destroyer" within the Trimurti, the Hindu trinity which also includes Brahma and Vishnu. In the Shaivite tradition, Shiva is the Supreme Lord who creates, protects and transforms the universe. In the goddess-oriented Shakta tradition, the Supreme Goddess ( Devi) is regarded as the energy and creative power (Shakti) and the equal complementary partner of Shiva. Shiva is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. Shiva has many aspects, benevolent as well as fearsome. In benevolent aspects, he is depicted as an omniscient Yogi who lives an ascetic life on Mount Kailash as well as a householder with his wife Parvati and his three children, Ganesha, Kartikeya and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru or acharya). The other three varnas are the Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra. The traditional occupation of Brahmins is that of priesthood at the Hindu temples or at socio-religious ceremonies, and rite of passage rituals such as solemnising a wedding with hymns and prayers.James Lochtefeld (2002), Brahmin, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , page 125 Traditionally, the Brahmins are accorded the highest ritual status of the four social classes. Their livelihood is prescribed to be one of strict austerity and voluntary poverty ("A Brahmin should acquire what just suffices for the time, what he earns he should spend all that the same day"). In practice, Indian texts suggest that some Brahmins historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wise Old Man
The wise old man (also called senex, sage or sophos) is an archetype as described by Carl Jung, as well as a classic literary figure, and may be seen as a stock character. The wise old man can be a profound philosopher distinguished for wisdom and sound judgment. Traits This type of character is typically represented as a kind and wise, older father-type figure who uses personal knowledge of people and the world to help tell stories and offer guidance that, in a mystical way, may impress upon his audience a sense of who they are and who they might become, thereby acting as a mentor. He may occasionally appear as an absent-minded professor, appearing absent-minded due to a predilection for contemplative pursuits. The wise old man is often seen to be from a different culture, nation, or occasionally time, from those he advises. In extreme cases, he may be a liminal being, such as Merlin, who was only half human. In medieval chivalric romance and modern fantasy literature, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuga
A ''yuga'', in Hinduism, is generally used to indicate an age of time. In the ''Rigveda'', a ''yuga'' refers to generations, a long period, a very brief period, or a yoke (joining of two things). In the ''Mahabharata'', the words ''yuga'' and ''kalpa'' (a day of Brahma) are used interchangeably to describe the cycle of creation and destruction. The names "''Yuga''" and "Age" commonly denote a (pronounced ''Chatur Yuga''), a cycle of four world ages, for example, in the '' Surya Siddhanta'' and ''Bhagavad Gita'' (part of the ''Mahabharata''), unless expressly limited by the name of one of its minor ages: '' Krita (Satya) Yuga'', ''Treta Yuga'', '' Dvapara Yuga'', or ''Kali Yuga''. Etymology ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग) means "a yoke" (joining of two things), "generations", or "a period of time" such as an age, where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yuge'', derived from ''yuj'' ( sa, युज्, , to join or yoke), believed derived from ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence (trait)
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information, and to retain it as knowledge to be applied towards adaptive behaviors within an environment or context. Intelligence is most often studied in humans but has also been observed in both non-human animals and in plant intelligence, plants despite controversy as to whether some of these forms of life exhibit intelligence. Intelligence in computers or other machines is called artificial intelligence. Etymology The word ''wikt:intelligence#English, intelligence'' derives from the Latin nouns ''wikt:intelligentia, intelligentia'' or ''wikt:intellectus, intellēctus'', which in turn stem from the verb ''wikt:intelligere, intelligere'', to comprehend or perceive. In the Middle Ages, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Bhumi_Puja%2C_yajna.jpg)

