|
Bolzano–Weierstrass Theorem
In mathematics, specifically in real analysis, the Bolzano–Weierstrass theorem, named after Bernard Bolzano and Karl Weierstrass, is a fundamental result about convergence in a finite-dimensional Euclidean space \R^n. The theorem states that each infinite bounded sequence in \R^n has a limit of a sequence, convergent subsequence. An equivalent formulation is that a subset of \R^n is Sequentially compact space, sequentially compact if and only if it is closed set, closed and bounded set, bounded. The theorem is sometimes called the sequential compactness theorem. History and significance The Bolzano–Weierstrass theorem is named after mathematicians Bernard Bolzano and Karl Weierstrass. It was actually first proved by Bolzano in 1817 as a Lemma (mathematics), lemma in the proof of the intermediate value theorem. Some fifty years later the result was identified as significant in its own right, and proved again by Weierstrass. It has since become an essential theorem of Real ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
There Exists
In predicate logic, an existential quantification is a type of quantifier, a logical constant which is interpreted as "there exists", "there is at least one", or "for some". It is usually denoted by the logical operator symbol ∃, which, when used together with a predicate variable, is called an existential quantifier ("" or "" or "). Existential quantification is distinct from universal quantification ("for all"), which asserts that the property or relation holds for ''all'' members of the domain. Some sources use the term existentialization to refer to existential quantification. Basics Consider a formula that states that some natural number multiplied by itself is 25. : 0·0 = 25, or 1·1 = 25, or 2·2 = 25, or 3·3 = 25, ... This would seem to be a logical disjunction because of the repeated use of "or". However, the ellipses make this impossible to integrate and to interpret it as a disjunction in formal logic. Instead, the statement could be rephrased more formally a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preference Relation
The term preference relation is used to refer to orderings that describe human preferences for one thing over an other. * In mathematics, preferences may be modeled as a weak ordering or a semiorder, two different types of binary relation. One specific variation of weak ordering, a total preorder (= a connected, reflexive and transitive relation), is also sometimes called a preference relation. * In computer science, machine learning algorithms are used to infer preferences, and the binary representation of the output of a preference learning algorithm is called a preference relation, regardless of whether it fits the weak ordering or semiorder mathematical models. * Preference relations are also widely used in economics; see preference (economics). {{sia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (plural matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two by three matrix", a "-matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Without further specifications, matrices represent linear maps, and allow explicit computations in linear algebra. Therefore, the study of matrices is a large part of linear algebra, and most properties and operations of abstract linear algebra can be expressed in terms of matrices. For example, matrix multiplication represents composition of linear maps. Not all matrices are related to linear algebra. This is, in particular, the case in graph theory, of incidence matrices, and adjacency matrices. ''This article focuses on matrices related to linear algebra, and, unle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareto Efficiency
Pareto efficiency or Pareto optimality is a situation where no action or allocation is available that makes one individual better off without making another worse off. The concept is named after Vilfredo Pareto (1848–1923), Italian civil engineer and economist, who used the concept in his studies of economic efficiency and income distribution. The following three concepts are closely related: * Given an initial situation, a Pareto improvement is a new situation where some agents will gain, and no agents will lose. * A situation is called Pareto-dominated if there exists a possible Pareto improvement. * A situation is called Pareto-optimal or Pareto-efficient if no change could lead to improved satisfaction for some agent without some other agent losing or, equivalently, if there is no scope for further Pareto improvement. The Pareto front (also called Pareto frontier or Pareto set) is the set of all Pareto-efficient situations. Pareto originally used the word "optimal" for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
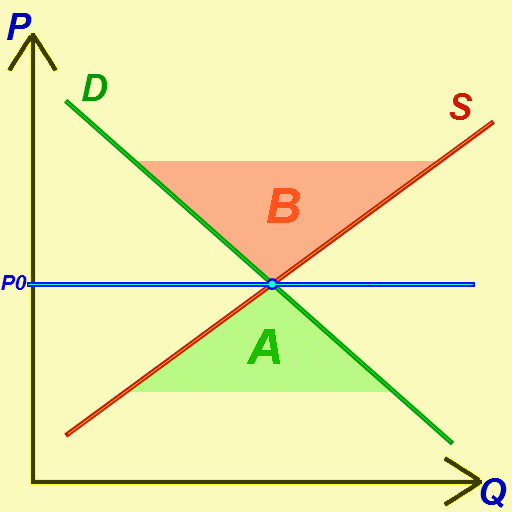
Economic Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the ( equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. But the concept of ''equilibrium'' in economics also applies to imperfectly competitive markets, where it takes the form of a Nash equilibrium. Understanding economic equilibriu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrizable Space
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a metrizable space is a topological space that is homeomorphic to a metric space. That is, a topological space (X, \mathcal) is said to be metrizable if there is a metric Metric or metrical may refer to: * Metric system, an internationally adopted decimal system of measurement * An adjective indicating relation to measurement in general, or a noun describing a specific type of measurement Mathematics In mathem ... d : X \times X \to [0, \infty) such that the topology induced by d is \mathcal. Metrization theorems are theorems that give sufficient conditions for a topological space to be metrizable. Properties Metrizable spaces inherit all topological properties from metric spaces. For example, they are Hausdorff space, Hausdorff paracompact spaces (and hence Normal space, normal and Tychonoff space, Tychonoff) and First-countable space, first-countable. However, some properties of the metric, such as completeness, cannot be said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Space
In mathematics, specifically general topology, compactness is a property that seeks to generalize the notion of a closed and bounded subset of Euclidean space by making precise the idea of a space having no "punctures" or "missing endpoints", i.e. that the space not exclude any ''limiting values'' of points. For example, the open interval (0,1) would not be compact because it excludes the limiting values of 0 and 1, whereas the closed interval ,1would be compact. Similarly, the space of rational numbers \mathbb is not compact, because it has infinitely many "punctures" corresponding to the irrational numbers, and the space of real numbers \mathbb is not compact either, because it excludes the two limiting values +\infty and -\infty. However, the ''extended'' real number line ''would'' be compact, since it contains both infinities. There are many ways to make this heuristic notion precise. These ways usually agree in a metric space, but may not be equivalent in other topologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspace Topology
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a subspace of a topological space ''X'' is a subset ''S'' of ''X'' which is equipped with a topology induced from that of ''X'' called the subspace topology (or the relative topology, or the induced topology, or the trace topology). Definition Given a topological space (X, \tau) and a subset S of X, the subspace topology on S is defined by :\tau_S = \lbrace S \cap U \mid U \in \tau \rbrace. That is, a subset of S is open in the subspace topology if and only if it is the intersection of S with an open set in (X, \tau). If S is equipped with the subspace topology then it is a topological space in its own right, and is called a subspace of (X, \tau). Subsets of topological spaces are usually assumed to be equipped with the subspace topology unless otherwise stated. Alternatively we can define the subspace topology for a subset S of X as the coarsest topology for which the inclusion map :\iota: S \hookrightarrow X is continuous. More ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequentially Compact
In mathematics, a topological space ''X'' is sequentially compact if every sequence of points in ''X'' has a convergent subsequence converging to a point in X. Every metric space is naturally a topological space, and for metric spaces, the notions of compactness and sequential compactness are equivalent (if one assumes countable choice). However, there exist sequentially compact topological spaces that are not compact, and compact topological spaces that are not sequentially compact. Examples and properties The space of all real numbers with the standard topology is not sequentially compact; the sequence (s_n) given by s_n = n for all natural numbers ''n'' is a sequence that has no convergent subsequence. If a space is a metric space, then it is sequentially compact if and only if it is compact. The first uncountable ordinal with the order topology is an example of a sequentially compact topological space that is not compact. The product of 2^=\mathfrak c copies of the clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accumulation Point
In mathematics, a limit point, accumulation point, or cluster point of a set S in a topological space X is a point x that can be "approximated" by points of S in the sense that every neighbourhood of x with respect to the topology on X also contains a point of S other than x itself. A limit point of a set S does not itself have to be an element of S. There is also a closely related concept for sequences. A cluster point or accumulation point of a sequence (x_n)_ in a topological space X is a point x such that, for every neighbourhood V of x, there are infinitely many natural numbers n such that x_n \in V. This definition of a cluster or accumulation point of a sequence generalizes to nets and filters. The similarly named notion of a (respectively, a limit point of a filter, a limit point of a net) by definition refers to a point that the sequence converges to (respectively, the filter converges to, the net converges to). Importantly, although "limit point of a set" is synon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |