|
Biotextile
Biotextiles are structures composed of textile fibers designed for use in specific biological environments where their performance depends on biocompatibility and biostability with cells and biological fluids. Biotextiles include implantable devices such as surgical sutures, hernia repair fabrics, arterial grafts, artificial skin and parts of artificial hearts. They were first created 30 years ago by Dr. Martin W. King, a professor in North Carolina State University’s College of Textiles. Medical textiles are a broader group which also includes bandages, wound dressings, hospital linen, preventive clothing etc. Antiseptic biotextiles are textiles used in fighting against cutaneous bacterial proliferation. Zeolite and triclosan are at the present time the most used molecules. This original property allows to fightinhibits the development of odours or bacterial proliferation in the diabetic foot. New developments In the new paradigm of tissue engineering, professionals are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Textiles
Medical textiles are various fiber-based materials intended for medical purposes. Medical textile is a sector of technical textiles that focuses on fiber-based products used in health care applications such as prevention, care, and hygiene. The spectrum of applications of medical textiles ranges from simple cotton bandages to advanced tissue engineering. Common examples of products made from medical textiles include dressings, implants, surgical sutures, certain medical devices, healthcare textiles, diapers, menstrual pads, wipes, and barrier fabrics. Medical textiles include many fiber types, yarns, fabrics, non-woven materials, woven, braided, as well as knitted fabrics. Physical and chemical alterations of fiber architectures, the use of functional finishes, and the production of stimuli-sensitive materials are major approaches for developing innovative medical textiles. Advances in textile manufacturing and medical technologies have made medical healthcare an important in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Textiles
A technical textile is a textile product manufactured for non-aesthetic purposes, where function is the primary criterion. Technical textiles include textiles for automotive applications, medical textiles (e.g., implants), geotextiles (reinforcement of embankments), agrotextiles (textiles for crop protection), and protective clothing (e.g., heat and radiation protection for fire fighter clothing, molten metal protection for welders, stab protection and bulletproof vests, and spacesuits).Techtextil: Application areas Techtextil, Frankfurt: Trade fair for Technical Textiles and Nonwovens] consulted 28 March 2015 The sector is large, growing, and supports a vast array of other industries. The global growth rate of technical textiles is about 4% per year. Currently, te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes onsumer textilesand technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. Geotextiles, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and many other areas are examples of technical textiles, whereas clothing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The university forms one of the corners of the Research Triangle together with Duke University in Durham and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. It is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". The North Carolina General Assembly established the North Carolina College of Agriculture and Mechanic Arts, now NC State, on March 7, 1887, originally as a land-grant college. The college underwent several name changes and officially became North Carolina State University at Raleigh in 1965. However, by longstanding convention, the "at Raleigh" portion is usually omitted. Today, NC State has an enrollment of more than 35,000 students, making it among the largest in the country. NC State has historical strengths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
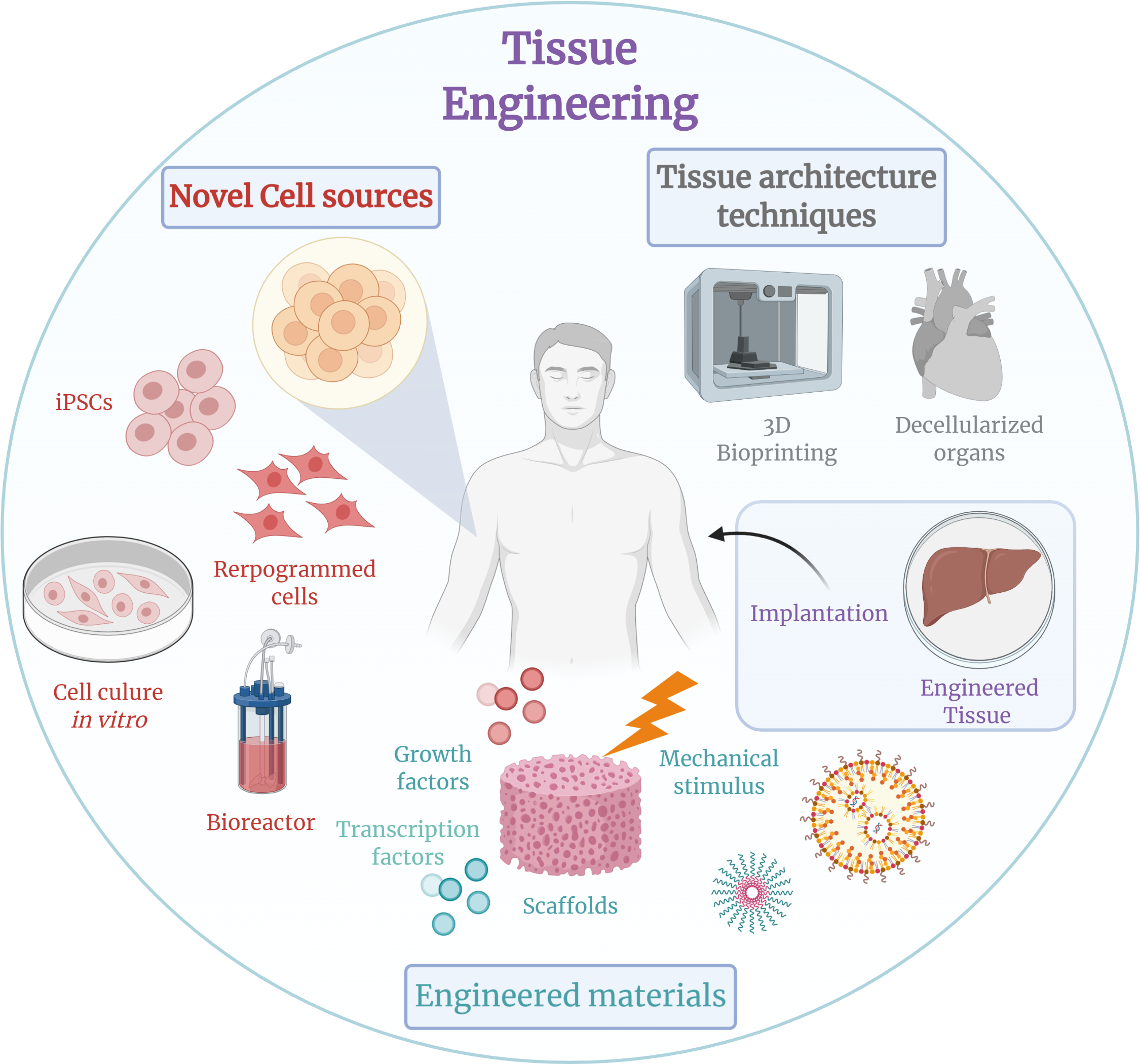
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of Cell (biology), cells, engineering, Materials science, materials methods, and suitable biochemistry, biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biology, biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field of its own. While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e. bone, Autologous chondrocyte implantation, cartilage, blood vessels, Urinary bladder, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triclosan
Triclosan (sometimes abbreviated as TCS) is an antibiotic, antibacterial and fungus, antifungal agent present in some consumer products, including toothpaste, soaps, detergents, toys, and surgical cleaning treatments. It is similar in its uses and mechanism of action to triclocarban. Its efficacy as an antimicrobial agent, the risk of antimicrobial resistance, and its possible role in endocrine disruptor, disrupted hormonal development remains controversial. Additional research seeks to understand its potential effects on organisms and environmental health. Triclosan was developed in 1966. A 2006 study recommended showering with 2% triclosan as a regimen in surgical units Decolonization (medicine), to rid patients' skin of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). While finding benefit for consumers and no proven risk to human health, but assumed risk of antibiotic resistance, in December 2017, the FDA announced that "co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeolite
Zeolites are microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate materials commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula ・y where is either a metal ion or H+. These positive ions can be exchanged for others in a contacting electrolyte solution. exchanged zeolites are particularly useful as solid acid catalysts. The term ''zeolite'' was originally coined in 1756 by Swedish mineralogist Axel Fredrik Cronstedt, who observed that rapidly heating a material, believed to have been stilbite, produced large amounts of steam from water that had been adsorbed by the material. Based on this, he called the material ''zeolite'', from the Greek , meaning "to boil" and , meaning "stone". Zeolites occur naturally but are also produced industrially on a large scale. , 253 unique zeolite frameworks have been identified, and over 40 naturally occurring zeolite frameworks are known. Every new zeolite structure that is ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutaneous
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, dolphins, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiseptic
An antiseptic (from Greek ἀντί ''anti'', "against" and σηπτικός ''sēptikos'', "putrefactive") is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from ''disinfectants'', which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects. Antibacterials include antiseptics that have the proven ability to act against bacteria. Microbicides which destroy virus particles are called viricides or antivirals. Antifungals, also known as antimycotics, are pharmaceutical fungicides used to treat and prevent mycosis (fungal infection). Surgery The widespread introduction of antiseptic surgical methods was initiated by the publishing of the paper ''Antiseptic Principle of the Practice of Surgery'' in 1867 by Joseph Lister, which was inspired by Louis Pasteur's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Heart
An artificial heart is a device that replaces the heart. Artificial hearts are typically used to bridge the time to heart transplantation, or to permanently replace the heart in the case that a heart transplant (from a deceased human or, experimentally, from a deceased genetically engineered pig) is impossible. Although other similar inventions preceded it from the late 1940s, the first artificial heart to be successfully implanted in a human was the Jarvik-7 in 1982, designed by a team including Willem Johan Kolff, William DeVries and Robert Jarvik. An artificial heart is distinct from a ventricular assist device (VAD; for either one or both of the ventricles, the heart's lower chambers), which can be a permanent solution also, or the intra-aortic balloon pump – both devices are designed to support a failing heart. It is also distinct from a cardiopulmonary bypass machine, which is an external device used to provide the functions of both the heart and lungs, used only for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibers
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate fibers, for example carbon fiber and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. Synthetic fibers can often be produced very cheaply and in large amounts compared to natural fibers, but for clothing natural fibers can give some benefits, such as comfort, over their synthetic counterparts. Natural fibers Natural fibers develop or occur in the fiber shape, and include those produced by plants, animals, and geological processes. They can be classified according to their origin: *Vegetable fibers are generally based on arrangements of cellulose, often with lignin: examples include cotton, hemp, jute, flax, abaca, piña, ramie, sisal, bagasse, and banana. Plant fibers are employed in the manufacture of paper and textile (cloth), and diet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |