|
Biofuel In New Zealand
There are a number of biofuels used in New Zealand. Biofuels Biodiesel Ecodiesel, a company owned by a group of New Zealand farmers, plans to build a biodiesel plant by the end of 2008. The plant will be built in stages and cheaper than Argent's, and could produce 20 million litres of tallow-based biodiesel per year by April 2009. In the effort to develop an aviation biofuel, Air New Zealand and Boeing are researching the jatropha plant to see if it can provide a renewable alternative to conventional fuel. Bioethanol Gull Force 10, a bioethanol blend, was introduced commercially in New Zealand for the first time by the company Gull on 1 August 2007. It contained 10% ethanol made from dairy by product by Anchor Ethanol, a subsidiary of Fonterra Ltd. On 8 August 2008, Gull introduced a 91-octane bioethanol blend in Albany. The blend, 'regular plus', contained 10% ethanol and included bioethanol made from whey. Gull planned to release the fuel to 33 stations, and marketed it a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (EIA), biofuels are mostly used for transportation, but can also be used for heating and electricity. Biofuel can be produced from plants or from agricultural, domestic or industrial biowaste. The greenhouse gas mitigation potential of biofuel varies considerably, from emission levels comparable to fossil fuels in some scenarios to negative emissions in others. See the biomass article for more on this particular subject. The two most common types of biofuel are bioethanol and biodiesel. The U.S. is the largest producer of bioethanol, while the EU is the largest producer of biodiesel. The energy content in the global production of bioethanol and biodiesel is 2.2 and 1.8 EJ per year, respectively. * Bioethanol is an alcohol made by fermen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area and the seventh most populous. Its capital is Brasília, and its most populous city is São Paulo. The federation is composed of the union of the 26 States of Brazil, states and the Federal District (Brazil), Federal District. It is the largest country to have Portuguese language, Portuguese as an List of territorial entities where Portuguese is an official language, official language and the only one in the Americas; one of the most Multiculturalism, multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, due to over a century of mass Immigration to Brazil, immigration from around the world; and the most populous Catholic Church by country, Roman Catholic-majority country. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
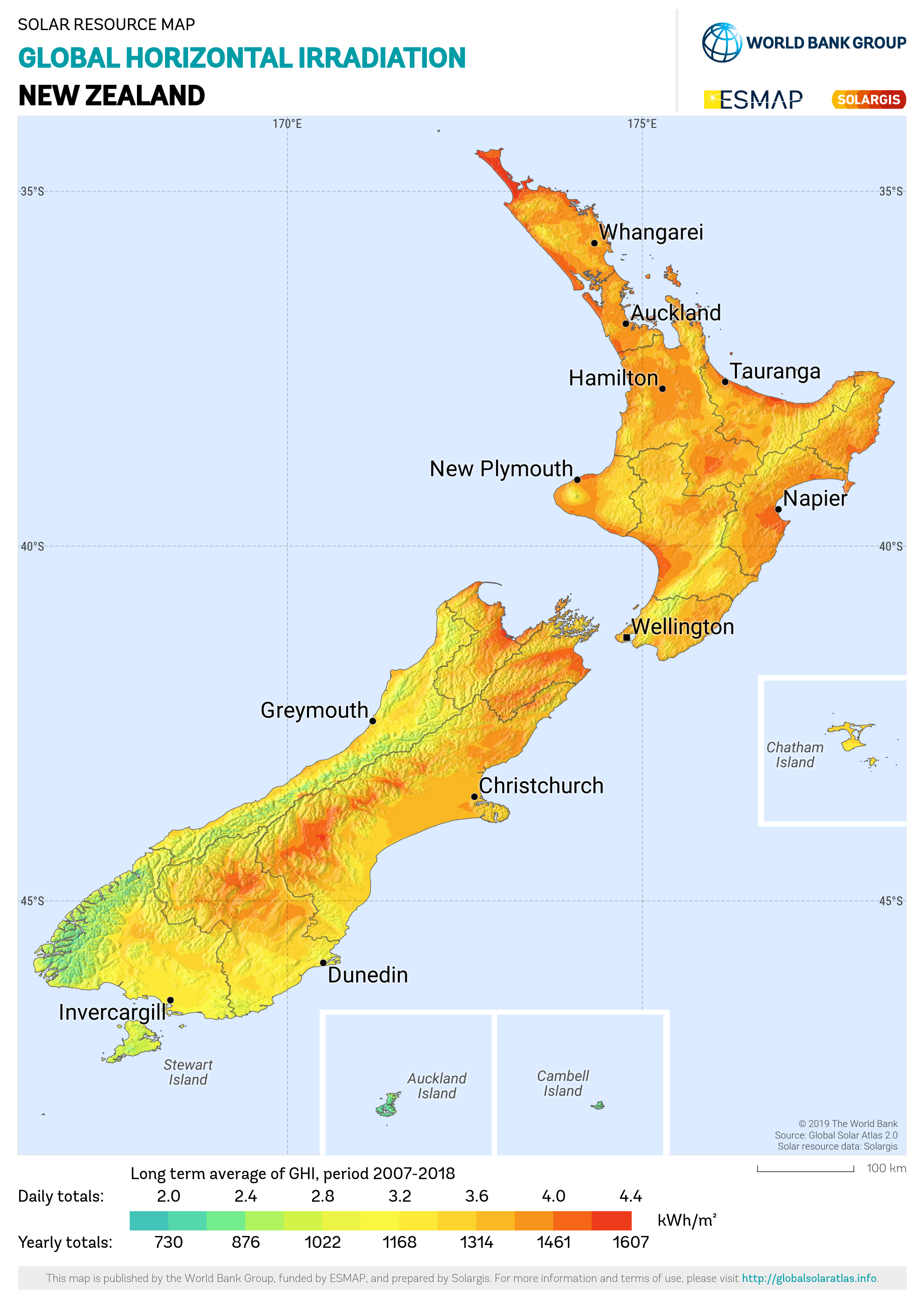
Renewable Energy In New Zealand
Approximately 40% of primary energy (Heat and power) is from renewable energy sources in New Zealand. Approximately 80% of electricity comes from renewable energy, primarily hydropower and geothermal power. Renewable energy by type Renewable electricity Renewable electricity in New Zealand is primarily from hydropower. In 2017, 82% of the electricity generated in New Zealand came from renewable sources. In September 2007, former Prime Minister Helen Clark announced a national target of 90 percent renewable electricity by 2025, with wind energy to make up much of that increase. Solar power Solar technologies in New Zealand only became affordable alternatives in the mid-2010s, compared to previous renewable offerings. The uptake in the residential and commercial market, though slow, has increased steadily. As with all renewable options, price of generation is key to the sustainability. It is only these recent changes in pricing that may see solar generation plants in the future. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Hot Water In New Zealand
Solar hot water in New Zealand is increasingly used on both new and existing buildings. Solar thermal technologies had a sizable initial uptake in the pioneering days of the 1970s. By 2001 more than 40GWhr was produced from solar hot water technologies, equating to 0.1% of the total electricity consumption in New Zealand. In 2006 the government announced an investment of $15.5 million over the first three and a half years of a five-year Solar Water Heating program to increase the number of solar hot water heating installations. As of 2006 there were about 35,000 solar hot water installations on domestic and commercial buildings. There are now eleven manufacturers and importers in the industry with most of the collector system being locally made. Barriers to adoption The main barrier for the installation of solar hot water systems is the initial capital investment. Other barriers are the conservatism of the building industry, lack of influence on increasing the sale price of hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric Power In New Zealand
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Power In New Zealand
Geothermal power in New Zealand is a small but significant part of the energy generation capacity of the country, providing approximately 17% of the country's electricityElectricity in New Zealand 2018 (from the New Zealand Electricity Authority. Accessed 2019-17-06.) with installed capacity of over 900 MW.Geothermal Energy and Electricity Generation (from the New Zealand Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority website. Accessed 2019-17-06.) New Zealand, like only a small number of other countries w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Power In New Zealand
New Zealand has large ocean energy resources but does not yet generate any power from them. TVNZ reported in 2007 that over 20 wave and tidal power projects are currently under development. However, not a lot of public information is available about these projects. The Aotearoa Wave and Tidal Energy Association was established in 2006 to "promote the uptake of marine energy in New Zealand". According to their 10 February 2008 newsletter, they have 59 members. However, the association doesn't list its members. From 2008 to 2011, the government Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority is allocating $2 million each year from a Marine Energy Deployment Fund, set up to encourage the utilisation of this resource. The greater Cook Strait and Kaipara Harbour seem to offer the most promising sites for using underwater turbines. Two resource consents have been granted for pilot projects in Cook Strait itself and in the Tory Channel, and consent is being sought for a project sites at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Power In New Zealand
Wind power constitutes a small but growing proportion of New Zealand's electricity. As of December 2020, wind power accounts for 690 MW of installed capacity and over 5 percent of electricity generated in the country. New Zealand has abundant wind resources. The country is in the path of the Roaring Forties, strong and constant westerly winds, and the funneling effect of Cook Strait and the Manawatu Gorge increase the resource's potential. Over three-quarters (512 MW) of the country's wind generation is installed within a radius of Palmerston North, with some turbines in the area having a capacity factor of over 50 percent. Generation capacity and expansion As of December 2020, New Zealand had an installed wind generation capacity of 690 MW. In the 2020 calendar year, wind power produced 2,282 GWh of electricity, 5.5 percent of the country's electricity generation that year. A further 2,500 MW of wind farms have received resource consent. The New Zeal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Power In New Zealand
Solar power in New Zealand is increasing in capacity, despite no government subsidies or interventions being available. As at the end of December 2022, New Zealand has 255 MW of grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) solar power installed, of which 65 MW (25%) was installed that year. In the 12 months to September 2022, 249 gigawatt-hours of electricity was estimated to have been generated by grid-connected solar, 0.57% of all electricity generated in the country. Although there are no subsidies, the declining costs of photovoltaics has caused a large increase in demand over the last few years. In 2009, the average turnkey price for a standard PV system of three kilowatts (kW) was about NZ$40,000; by 2019 this had dropped to approx. NZ$8,500. Distributed systems As of the end of December 2022, 45,761 solar power systems had been installed in New Zealand. For new installations added in December 2022, the average residential system size was 5.7 kW and the average commerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofuels By Region
The use of biofuels varies by region. The world leaders in biofuel development and use are Brazil, United States, France, Sweden and Germany. Americas Brazil The government of Brazil hopes to build on the success of the Proálcool ethanol program by expanding the production of biodiesel which must contain 2% biodiesel by 2008, and 5% by 2013. Canada The government of Canada aims for 45% of the country's gasoline consumption to contain 10% ethanol by 2010. Colombia and Venezuela Colombia mandates the use of 10% ethanol in all gasoline sold in cities with populations exceeding 500,000. In Venezuela, the state oil company is supporting the construction of 15 sugar cane distilleries over the next five years, as the government introduces an E10 (10% ethanol) blending mandate. United States The Energy Policy Act of 2005 was passed by the United States Congress on July 29, 2005, and signed into law by President George W. Bush on August 8, 2005, at Sandia National Laboratorie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Generation Biofuels
Second-generation biofuels, also known as advanced biofuels, are fuels that can be manufactured from various types of non-food biomass. Biomass in this context means plant materials and animal waste used especially as a source of fuel. First-generation biofuels are made from sugar-starch feedstocks (e.g., sugarcane and corn) and edible oil feedstocks (e.g., rapeseed and soybean oil), which are generally converted into bioethanol and biodiesel, respectively. Second-generation biofuels are made from different feedstocks and therefore may require different technology to extract useful energy from them. Second generation feedstocks include lignocellulosic biomass or woody crops, agricultural residues or waste, as well as dedicated non-food energy crops grown on marginal land unsuitable for food production. The term second-generation biofuels is used loosely to describe both the 'advanced' technology used to process feedstocks into biofuel, but also the use of non-food crops, biomass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliamentary Commissioner For The Environment
__NOTOC__ The Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment (''Te Kaitiaki Taiao a Te Whare Pāremata'' in Māori) is an independent Officer of the New Zealand Parliament appointed by the Governor-General on the recommendation of the House of Representatives for a five-year term under the Environment Act 1986. The Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment replaced the Commission for the Environment, a Government agency which was formed in 1972. Role The Commissioner is one of three officers of Parliament (the Ombudsmen and the controller and auditor general) who are independent of the executive and who may review activities of the executive government and report directly to Parliament. The Commissioner's role is to review and provide advice on environmental issues and the system of agencies and processes established by the Government to manage the environment. The primary objective of the office is to contribute to maintaining and improving the quality of the environment i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |