|
Solar Hot Water In New Zealand
Solar hot water in New Zealand is increasingly used on both new and existing buildings. Solar thermal technologies had a sizable initial uptake in the pioneering days of the 1970s. By 2001 more than 40GWhr was produced from solar hot water technologies, equating to 0.1% of the total electricity consumption in New Zealand. In 2006 the government announced an investment of $15.5 million over the first three and a half years of a five-year Solar Water Heating program to increase the number of solar hot water heating installations. As of 2006 there were about 35,000 solar hot water installations on domestic and commercial buildings. There are now eleven manufacturers and importers in the industry with most of the collector system being locally made. Barriers to adoption The main barrier for the installation of solar hot water systems is the initial capital investment. Other barriers are the conservatism of the building industry, lack of influence on increasing the sale price of hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Hot Water
Solar water heating (SWH) is heating water by sunlight, using a solar thermal collector A solar thermal collector collects heat by absorbing sunlight. The term "solar collector" commonly refers to a device for solar hot water heating, but may refer to large power generating installations such as solar parabolic troughs and sola .... A variety of configurations are available at varying cost to provide solutions in different climates and latitudes. SWHs are widely used for residential and some industrial applications (For example: in Israel). A sun-facing collector heats a working fluid that passes into a storage system for later use. SWH are active (pumped) and passive (Natural convection, convection-driven). They use water only, or both water and a working fluid. They are heated directly or via light-concentrating mirrors. They operate independently or as hybrids with electric or gas heaters. In large-scale installations, mirrors may concentrate sunlight into a smaller c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
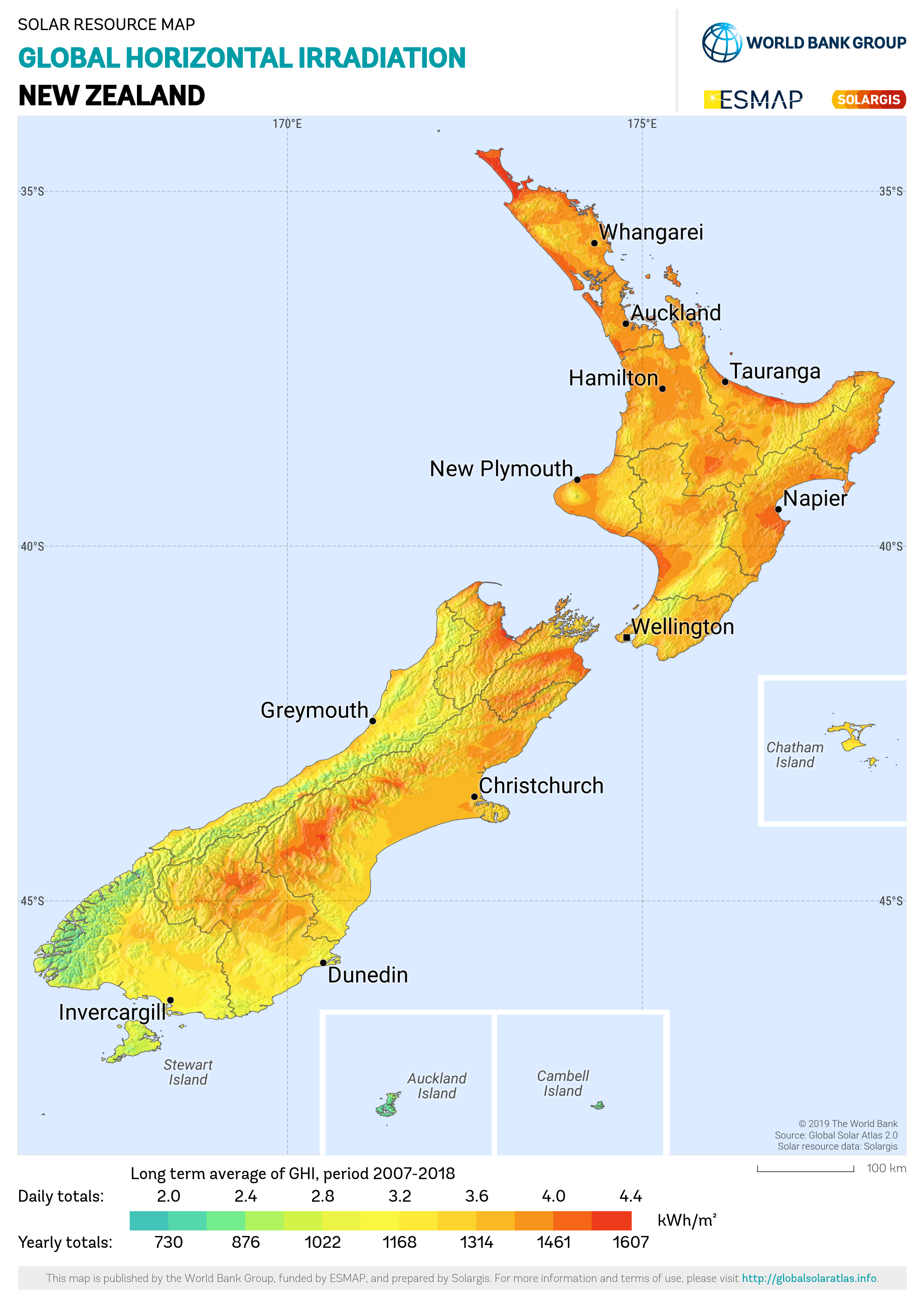
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renewable Energy In New Zealand
Approximately 40% of primary energy (Heat and power) is from renewable energy sources in New Zealand. Approximately 80% of electricity comes from renewable energy, primarily hydropower and geothermal power. Renewable energy by type Renewable electricity Renewable electricity in New Zealand is primarily from hydropower. In 2017, 82% of the electricity generated in New Zealand came from renewable sources. In September 2007, former Prime Minister Helen Clark announced a national target of 90 percent renewable electricity by 2025, with wind energy to make up much of that increase. Solar power Solar technologies in New Zealand only became affordable alternatives in the mid-2010s, compared to previous renewable offerings. The uptake in the residential and commercial market, though slow, has increased steadily. As with all renewable options, price of generation is key to the sustainability. It is only these recent changes in pricing that may see solar generation plants in the future. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Power In New Zealand
Solar power in New Zealand is increasing in capacity, despite no government subsidies or interventions being available. As at the end of December 2022, New Zealand has 255 MW of grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) solar power installed, of which 65 MW (25%) was installed that year. In the 12 months to September 2022, 249 gigawatt-hours of electricity was estimated to have been generated by grid-connected solar, 0.57% of all electricity generated in the country. Although there are no subsidies, the declining costs of photovoltaics has caused a large increase in demand over the last few years. In 2009, the average turnkey price for a standard PV system of three kilowatts (kW) was about NZ$40,000; by 2019 this had dropped to approx. NZ$8,500. Distributed systems As of the end of December 2022, 45,761 solar power systems had been installed in New Zealand. For new installations added in December 2022, the average residential system size was 5.7 kW and the average commerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Thermal Energy
Solar thermal energy (STE) is a form of energy and a technology for harnessing solar energy to generate thermal energy for use in industry, and in the residential and commercial sectors. Solar thermal collectors are classified by the United States Energy Information Administration as low-, medium-, or high-temperature collectors. Low-temperature collectors are generally unglazed and used to heat swimming pools or to heat ventilation air. Medium-temperature collectors are also usually flat plates but are used for heating water or air for residential and commercial use. High-temperature collectors concentrate sunlight using mirrors or lenses and are generally used for fulfilling heat requirements up to 300 deg C / 20 bar pressure in industries, and for electric power production. Two categories include Concentrated Solar Thermal (CST) for fulfilling heat requirements in industries, and Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) when the heat collected is used for electric power generation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |