|
Big Horn Expedition
:''This event should not be confused with the Powder River Expedition (1865).'' The Big Horn Expedition, or Bighorn Expedition, was a military operation of the United States Army against the Sioux, and Cheyenne Indians in Wyoming Territory and Montana Territory. Although soldiers destroyed one Cheyenne and Oglala Sioux village, the expedition solidified Lakota Sioux and northern Cheyenne resistance against the United States attempt to force them to sell the Black Hills and live on a reservation, beginning the Great Sioux War of 1876. Background The Treaty of Fort Laramie (1868) granted the Lakota Sioux and their northern Cheyenne allies a reservation, including the Black Hills, in Dakota Territory and a large area of "unceded territory" in what became Montana and Wyoming. Both areas were for the exclusive use of the Indians, and whites except for government officials, were forbidden to trespass. In August, 1874, soldiers of the Black Hills Expedition under Lieutenant Colonel Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Sioux War Of 1876
The Great Sioux War of 1876, also known as the Black Hills War, was a series of battles and negotiations that occurred in 1876 and 1877 in an alliance of Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne against the United States. The cause of the war was the desire of the US government to obtain ownership of the Black Hills. Gold had been discovered in the Black Hills, settlers began to encroach onto Native American lands, and the Sioux and the Cheyenne refused to cede ownership. Traditionally, American military and historians place the Lakota at the center of the story, especially because of their numbers, but some Native Americans believe the Cheyenne were the primary target of the American campaign. Among the many battles and skirmishes of the war was the Battle of the Little Bighorn; often known as Custer's Last Stand, it is the most storied of the many encounters between the US Army and mounted Plains Indians. Despite the Indian victory, the Americans leveraged national resources to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbia, and Saskatchewan to the north. It is the fourth-largest state by area, the eighth-least populous state, and the third-least densely populated state. Its state capital is Helena. The western half of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges, while the eastern half is characterized by western prairie terrain and badlands, with smaller mountain ranges found throughout the state. Montana has no official nickname but several unofficial ones, most notably "Big Sky Country", "The Treasure State", "Land of the Shining Mountains", and " The Last Best Place". The economy is primarily based on agriculture, including ranching and cereal grain farming. Other significant economic resources include oil, gas, coal, mining, and lumber. The health ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
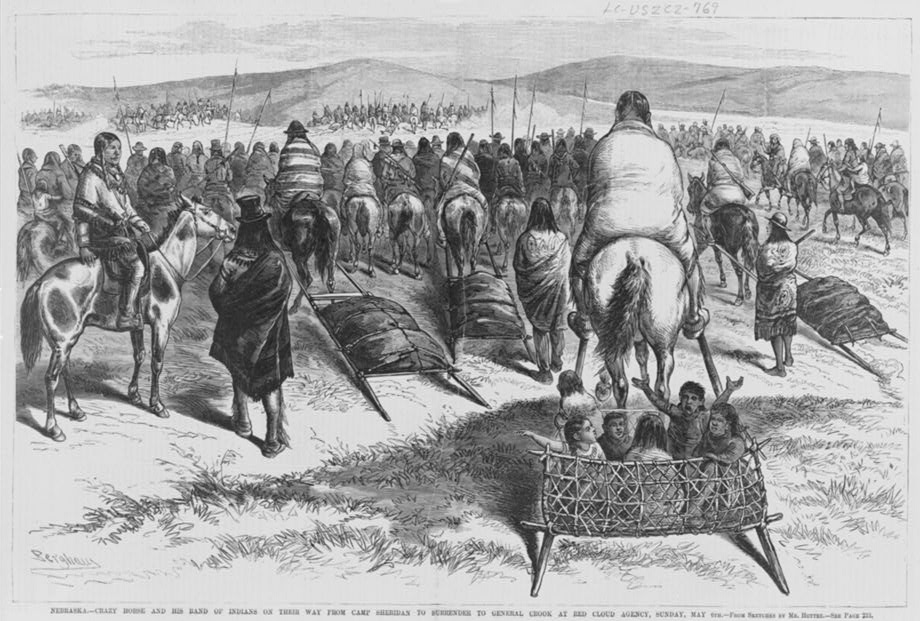
Crazy Horse
Crazy Horse ( lkt, Tȟašúŋke Witkó, italic=no, , ; 1840 – September 5, 1877) was a Lakota war leader of the Oglala band in the 19th century. He took up arms against the United States federal government to fight against encroachment by white American settlers on Native American territory and to preserve the traditional way of life of the Lakota people. His participation in several famous battles of the Black Hills War on the northern Great Plains, among them the Fetterman Fight in 1866, in which he acted as a decoy, and the Battle of the Little Bighorn in 1876, in which he led a war party to victory, earned him great respect from both his enemies and his own people. In September 1877, four months after surrendering to U.S. troops under General George Crook, Crazy Horse was fatally wounded by a bayonet-wielding military guard while allegedly resisting imprisonment at Camp Robinson in present-day Nebraska. He was honored by the U.S. Postal Service in 1982 with a 13¢ Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas, Wyoming
Douglas is a city in Converse County, Wyoming, United States. The population was 6,120 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Converse County and the home of the Wyoming State Fair. History Douglas was platted in 1886 when the Wyoming Central Railway (later the Chicago and North Western Transportation Company) established a railway station; the settlement had been in existence since 1867 when Fort Fetterman was built and was first known as "Tent City"American Automobile Association (2002) ''Tourbook: Idaho, Montana & Wyoming'' AAA Publishing, Heathrow, Florida, p. 148 ISSN 0363-2695 before it was officially named "Douglas", after Senator Stephen A. Douglas. It served as a supply point, warehousing and retail, for surrounding cattle ranches, as well as servicing railway crews, cowboys and the troops of the U.S. Army stationed at Fort Fetterman. Douglas was the home of a World War II internment camp. Its former railroad passenger depot is listed on the National Registe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Fetterman
Fort Fetterman was constructed in 1867 by the United States Army on the Great Plains frontier in Dakota Territory, approximately 11 miles northwest of present-day Douglas, Wyoming. Located high on the bluffs south of the North Platte River, it served as a major base for the start of several United States military expeditions against warring Native American tribes. The fort is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. History Fort Fetterman was built as a major supply point for the United States army's operations in the area. Established on July 19, 1867, by Companies A, C, H, and I of the 4th U.S. Infantry under the command of Major William E. Dye, the fort was named in honor of Captain William J. Fetterman, who was killed in a battle with Indians near Fort Phil Kearny on December 21, 1866. "It contained quarters for three hundred enlisted men, and the necessary officers; the various magazines and store-houses required for the preservation of ammunition, rations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of The Platte
The Department of the Platte was a military administrative district established by the U.S. Army on March 5, 1866, with boundaries encompassing Iowa, Nebraska, Dakota Territory, Utah Territory and a small portion of Idaho. With headquarters in Omaha, the district commander oversaw the army's role initially along the Overland route (or Oregon Trail) to Salt Lake City, then later the construction route of the Union Pacific Railroad. The district also included the Montana road (or Bozeman Trail) through eastern Wyoming. The district was discontinued when the Army's command was reorganized in 1898. Headquarters The Headquarters of the Department of the Platte was located in downtown Omaha, Nebraska for many years. When the headquarters was transferred to Fort Omaha in 1878, the building it was located in was found unsuitable, and the headquarters were again transferred downtown.Mattes, M.J. (1998) ''Indians, Infants, and Infantry: Andrew and Elizabeth Burt on the Frontier.'' Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops (four battalions). Variants Brigadier general Brigadier general (Brig. Gen.) is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries, usually sitting between the ranks of colonel and major general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops (four battalions). In some countries, this rank is given the name of ''brigadier'', which is usually equivalent to ''brigadier general'' in the armies of nations that use the rank. The rank can be traced back to the militaries of Europe where a "brigadier general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Howe Terry
Alfred Howe Terry (November 10, 1827 – December 16, 1890) was a Union general in the American Civil War and the military commander of the Dakota Territory from 1866 to 1869, and again from 1872 to 1886. In 1865, Terry led Union troops to victory at the Second Battle of Fort Fisher in North Carolina. Early life and career Although born in Hartford, Connecticut, Alfred Terry's family quickly moved to New Haven, where he spent most of his childhood. Terry graduated from the Hopkins School in New Haven in 1838. After attending Yale Law School in 1848, Terry became a lawyer and was appointed clerk of the Superior Court of New Haven County. Civil War South Carolina When the Civil War started, Terry raised the 2nd Connecticut Infantry Regiment, and was appointed colonel. The regiment fought at First Bull Run, after which Terry and his regiment were transferred to South Carolina. On September 13, 1861, at New Haven, Connecticut, Col. Terry organized an elite and special regiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillip Sheridan
General of the Army Philip Henry Sheridan (March 6, 1831 – August 5, 1888) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War. His career was noted for his rapid rise to major general and his close association with General-in-chief Ulysses S. Grant, who transferred Sheridan from command of an infantry division in the Western Theater to lead the Cavalry Corps of the Army of the Potomac in the East. In 1864, he defeated Confederate forces under General Jubal Early in the Shenandoah Valley and his destruction of the economic infrastructure of the Valley, called "The Burning" by residents, was one of the first uses of scorched-earth tactics in the war. In 1865, his cavalry pursued Gen. Robert E. Lee and was instrumental in forcing his surrender at Appomattox Courthouse. Sheridan fought in later years in the Indian Wars of the Great Plains. Both as a soldier and private citizen, he was instrumental in the development and protection of Ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitting Bull
Sitting Bull ( lkt, Tȟatȟáŋka Íyotake ; December 15, 1890) was a Hunkpapa Lakota leader who led his people during years of resistance against United States government policies. He was killed by Indian agency police on the Standing Rock Indian Reservation during an attempt to arrest him, at a time when authorities feared that he would join the Ghost Dance movement. Before the Battle of the Little Bighorn, Sitting Bull had a vision in which he saw many soldiers, "as thick as grasshoppers", falling upside down into the Lakota camp, which his people took as a foreshadowing of a major victory in which many soldiers would be killed. About three weeks later, the confederated Lakota tribes with the Northern Cheyenne defeated the 7th Cavalry under Lt. Col. George Armstrong Custer on June 25, 1876, annihilating Custer's battalion and seeming to bear out Sitting Bull's prophetic vision. Sitting Bull's leadership inspired his people to a major victory. In response, the U.S. governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Q
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commissioner Of Indian Affairs
The Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA), also known as Indian Affairs (IA), is a United States federal government of the United States, federal agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior, Department of the Interior. It is responsible for implementing Federal law (United States), federal laws and policies related to Native Americans in the United States, American Indians and Alaska Natives, and administering and managing over of land Trust law, held in trust by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government for List of federally recognized tribes, Indian Tribes. It renders services to roughly 2 million indigenous Americans across 574 federally recognized tribes. The BIA is governed by a director and overseen by the assistant secretary for Indian affairs, who answers to the United States Secretary of the Interior, secretary of the interior. The BIA works with Tribal sovereignty in the United States, tribal governments to help administer law enforcement a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |