|
Bibio Pomonae
''Bibio pomonae'', common name red-thighed St Mark's fly or heather fly, is a species of fly (Diptera) belonging to the family Bibionidae. Description ''Bibio pomonae'' can reach a length of about , while the length of the wings reaches . The basic body color is shiny black, with a black long abdomen, deep crimson-red femurs and dark tibiae and tarsi. Front tibia show a pair of large spurs. Wings are milky-white with darkened veins on the costal area and a dark spot on the leading edge. The 10-segmented antennae are relatively short and thick. Males and females are very different, as the holoptic males show very large eyes and a flattened abdomen, while the females have small head and eyes and a sharp abdomen. The larvae are reddish brown. Biology Adults feed mostly on nectar and are important pollinators. Larvae develop during Fall and Winter feeding on dead leaves, compost, decaying organic matter and Poaceae Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Christian Fabricius
Johan Christian Fabricius (7 January 1745 – 3 March 1808) was a Danish zoologist, specialising in "Insecta", which at that time included all arthropods: insects, arachnids, crustaceans and others. He was a student of Carl Linnaeus, and is considered one of the most important entomologists of the 18th century, having named nearly 10,000 species of animals, and established the basis for the modern insect classification. Biography Johan Christian Fabricius was born on 7 January 1745 at Tønder in the Duchy of Schleswig, where his father was a doctor. He studied at the gymnasium at Altona and entered the University of Copenhagen in 1762. Later the same year he travelled together with his friend and relative Johan Zoëga to Uppsala, where he studied under Carl Linnaeus for two years. On his return, he started work on his , which was finally published in 1775. Throughout this time, he remained dependent on subsidies from his father, who worked as a consultant at Frederiks Hospital. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handbooks For The Identification Of British Insects
''Handbooks for the Identification of British Insects'' is a series of books produced by the Royal Entomological Society (RES). The aim of the Handbooks is to provide illustrated identification keys to the insects of Britain, together with concise morphological, biological and distributional information. The series also includes several Check Lists of British Insects. All books contain line drawings, with the most recent volumes including colour photographs. In recent years, new volumes in the series have been published by Field Studies Council, and benefit from association with the AIDGAP identification guides and Synopses of the British Fauna. Full list of titles Vol : 1 - Small Orders Vol : 2 - Hemiptera Vol : 4 - Coleoptera Vol : 5 - Coleoptera Vol : 6 - Hymenoptera Vol : 7 - Hymenoptera: Ichneumonoidea Vol : 8 - Hymenoptera: Cynipoidea, Chalcidoidea & Proctotrupoidea Vol : 9 - Diptera: Nematocera & Brachycera Vol : 10 - Diptera: Cyclorrhapha Vol : 11 & 12 - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Entomological Society Of London
The Royal Entomological Society is devoted to the study of insects. Its aims are to disseminate information about insects and improving communication between entomologists. The society was founded in 1833 as the Entomological Society of London. It had many antecedents beginning as the Society of Entomologists of London. History The foundation of the society began with a meeting of "gentlemen and friends of entomological science", held on 3 May 1833 in the British Museum convened by Nicholas Aylward Vigors with the presidency of John George Children. Those present were the Reverend Frederick William Hope, Cardale Babington, William Yarrell, John Edward Gray, James Francis Stephens, Thomas Horsfield, George Thomas Rudd and George Robert Gray. Letters of Adrian Hardy Haworth, George Bennett and John Curtis were read where they expressed their regrets to be unable to attend the meeting. They decided that a society should be created for the promotion of the science of entomology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
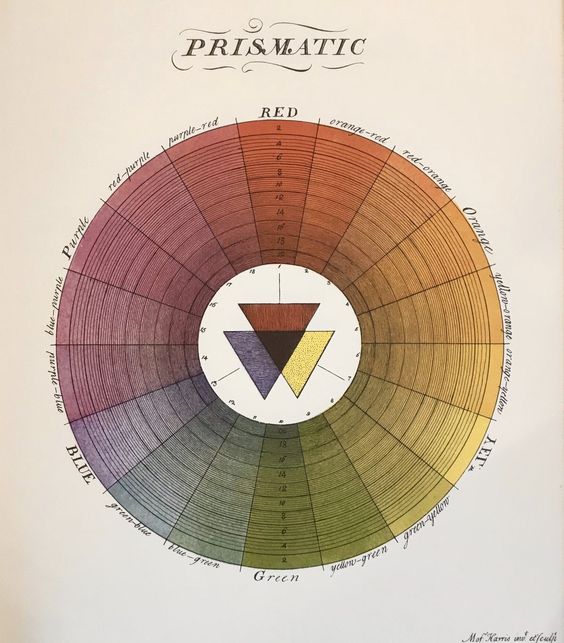
Moses Harris
Moses Harris (15 April 1730 – 1787) was an English entomologist and engraver. Life and work Harris was encouraged in entomology from a young age by his uncle, a member of the Society of the Aurelians. In 1762 he became secretary of a second Society of Aurelians. He was a skilled artist, displaying some of his insect drawings at the Royal Academy in 1785. He drew and engraved illustrations for books including Dru Drury's ''Illustrations of Natural History'' (3 volumes, 1770–1782) and John Coakley Lettsom's ''The Naturalist's and Traveller's Companion'' (1772). Colour theory In "The Natural System of Colours" published in 1766, Harris discussed the multitude of colours that can be created using three "grand or principle" colours: red, yellow and blue. As a naturalist and an engraver, Harris focussed on the relationships between colours and how they are coded and created. He explained how three colours can be íntermixed, tinted and shaded to create 660 colours "materially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles De Geer
Baron Charles de Geer (the family is usually known as De Geer with a capitalized "De" and is pronounced "de yer"); Finspång in Risinge 30 January 1720 – Stockholm 7 March 1778) was a Swedish industrialist and entomologist. Life De Geer, who came from a family with strong Dutch connections, grew up in Utrecht from the age of three. He returned to Sweden at the age of 19. He had inherited the entailed manor and important iron-works of Leufsta (Lövsta) in Uppland from his childless uncle and namesake and would substantially increased the wealth of the estate. Ever since he had received a present of some silk worms at the age of eight, he had an interest in entomology and became a respected amateur entomologist at an early age. His major work was the ''Mémoires pour servir à l'histoire des insectes'' (eight volumes, 1752-1778). He was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences already in 1739, at the age of nineteen, and a corresponding member of the Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diptera
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced mechanosensory organs known as halteres, which act as high-speed sensors of rotational movement and allow dipterans to perform advanced aerobatics. Diptera is a large order containing an estimated 1,000,000 species including horse-flies, crane flies, hoverflies and others, although only about 125,000 species have been described. Flies have a mobile head, with a pair of large compound eyes, and mouthparts designed for piercing and sucking (mosquitoes, black flies and robber flies), or for lapping and sucking in the other groups. Their wing arrangement gives them great maneuverability in flight, and claws and pads on their feet enable them to cling to smooth surfaces. Flies undergo complete metamorphosis; the eggs are often laid on the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibionidae
Bibionidae (March flies) is a family of flies (Diptera) containing approximately 650–700 species worldwide. Adults are nectar feeders and emerge in numbers in spring. Because of the likelihood of adults flies being found ''in copula'', they have earned colloquial names such as "love bugs" or "honeymoon flies". Description Bibionidae are medium-sized flies with a body length from 4.0 to 10.0 mm. The body is black, brown, or rusty, and thickset, with thick legs. The antennae are moniliform. The front tibiae bear large strong spurs or a circlet of spines. The tarsi are five-segmented and bear tarsal claws, pulvilli, and a well developed empodium. The wings have two basal cells (posterior basal wing cell and basal wing cell), but are without a discoidal wing cell. R4+5 is simple or branched; at most, only three branches of R developed. The leading edge wing veins are stronger than the weak veins of the trailing edge. Biology Bibionid larvae grow up in grassy areas and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holoptic
Holoptic refers to one of the ways in which the arthropod eye develops, particularly the eyes of various species of insects. Unlike dichoptic and cycloptic eyes, holoptic eyes meet along the median dorsal line of the head, in many species nearly covering the exterior of the head. Holoptic eyes are typical of several Dipteran males, in particular some Syrphidae, Tabanidae, Pipunculidae, and Acroceridae. Some other insect orders that include species with holoptic males and some in which the females are holoptic as well, include the Coleoptera, Anisoptera, and Archaeognatha The Archaeognatha are an order of apterygotes, known by various common names such as jumping bristletails. Among extant insect taxa they are some of the most evolutionarily primitive; they appeared in the Middle Devonian period at about the sa .... References * {{Insect-anatomy-stub Insect anatomy Eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poaceae
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palearctic Realm
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa. The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Siberian region; the Mediterranean Basin; the Sahara and Arabian Deserts; and Western, Central and East Asia. The Palaearctic realm also has numerous rivers and lakes, forming several freshwater ecoregions. The term 'Palearctic' was first used in the 19th century, and is still in use as the basis for zoogeographic classification. History In an 1858 paper for the ''Proceedings of the Linnean Society'', British zoologist Philip Sclater first identified six terrestrial zoogeographic realms of the world: Palaearctic, Aethiopian/Afrotropic, Indian/Indomalayan, Australasian, Nearctic, and Neotropical. The six indicated general groupings of fauna, based on shared biogeography and large-scale geographic barriers to migration. Alfred Wallace ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents of Earth#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insects Described In 1775
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from eggs. Inse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(10144905255).jpg)
