|
Bellikon
Bellikon is a municipality in the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. History The area was settled during Roman times. The Roman road between Vindonissa (Windisch) and Turicum ( Zurich) ran through here. In 1934, bricks were found which on examination proved to belong to a villa, which was excavated and documented in 1941, and afterwards covered up again with the help of interned Polish soldiers. Articles found on the site indicate a construction date at the end of the 1st century. In the middle of the 6th century, the Alamanni settled here and cleared the forest, destroying the Roman settlement. Bellikon was first documented on October 11, 1064, in the foundation charter of Muri Abbey, though it was first individually mentioned in the 12th Century as ''Pellikon''. Bellikon and Hausen at first paid tithes to Murbach Abbey in Alsace, but was later part of the Habsburg territories. In 1415, the Aargau was conquered and thereafter Bellikon belonged to the vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden (district, Aargau)
Baden District is a district in the canton of Aargau, Switzerland. The district capital is the town of Baden and the largest municipality is Wettingen, located in the Limmat Valley (German: ''Limmattal''). The district has a total of 26 municipalities, an area of , and a population () of about 138,000. Geography Baden District has an area, , of . Of this area, 37.1% is used for agricultural purposes, while 38.5% is forested. The rest of the land, (22.4%) is settled. History The district is descended from the historic County of Baden, which was dissolved in 1798 upon the creation of the short-lived Canton of Baden (1798–1803). The first district of Baden existed during the existence of that canton, covering part of the former county, and upon its merging into the canton of Aargau, the contemporary district was formed. Upon the merging of the canton of Baden into Aargau in 1803, the district gained the municipalities of Würenlingen, Bellikon, Künten, Remetschwil, Stetten, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
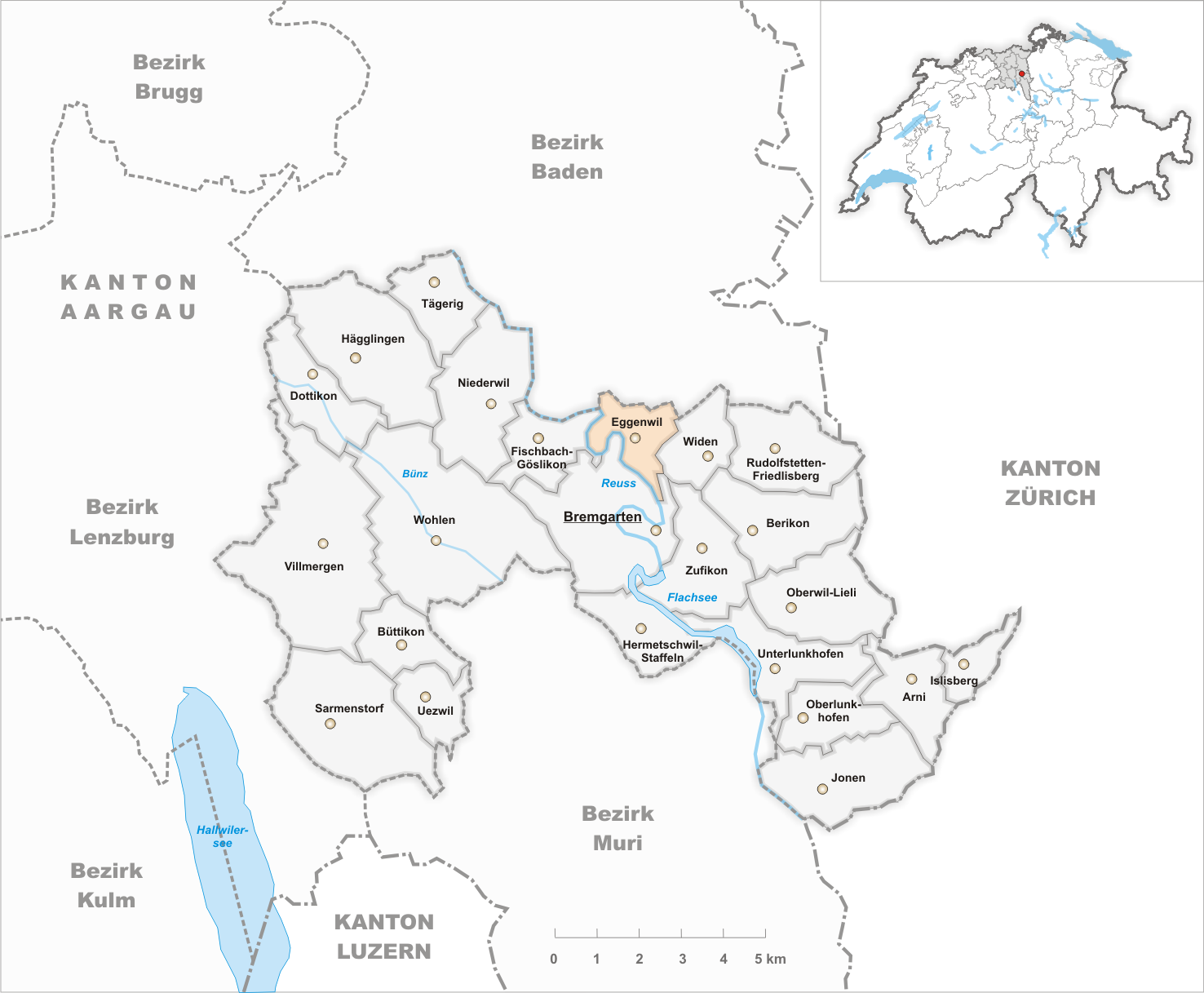
Widen
Widen is a municipality in the district of Bremgarten in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. History At the end of the 12th century a manor called "Wyda" is mentioned the first time, there's no exact year. "Widen", in the way like it's written today, appears the first time during the 14th century. In medieval times, the manor belonged to Habsburg. 1415 the Eidgenossen conquered the Aargau and Widen then belonged to the Grafschaft Baden. In March 1798 the French conquered Switzerland and proclamated the Helvetic Republic, in which Widen and Eggenwil formed one single municipality in the short-dated canton of Baden. After the foundation of the canton of Aargau 1803, Widen and Eggenwil were separated. Up to that time, there's not much known about Widen, because there are almost no documents left. During the 19th century Widen stayed a small village. Many poor inhabitants had to leave their homes and emigrated. The given up farms were freshly occupied by people from the canto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Baden
The County of Baden (German: ''Grafschaft Baden'') was a condominium of the Old Swiss Confederacy and is now part of the Swiss Canton of Aargau. The county was established in 1415 after the Swiss conquest of the Aargau and was ruled as a shared condominium until 1798 when it became part of the short lived Canton of Baden. History The land that became the County of Baden was originally ruled by the Counts of Lenzburg. Once that family's main line died out, it came under the Kyburgs and then in 1264 the Habsburgs. The exact territories in the county changed often, but originally included the western part of the Zürichgau and parts of the territory between the Rhine, Aare and Reuss rivers. In the 14th Century the territory of Baden became a triangle between the Limmat and Reuss rivers, though it was later divided further. As part of the Habsburg bailiwick of Aargau, it was managed by a bailiff, who had his seat in the town of Baden. On 16 November 1414, Emperor Sigismu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eggenwil
Eggenwil is a municipality in the district of Bremgarten in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. History Eggenwil is first mentioned about 1160 as ''Egenwilare'' in a donation document, the ''Acta Murensia''. The village and church were given by Albert II, Count of Habsburg (died 1140) to Muri Abbey. However, the Habsburg rights of Low justice were given to the Hermetschwil abbey. In 1415 the canton of Aargau was taken from the Habsburgs by the Swiss Confederates. While Bern kept the southwest portion (Zofingen, Aarburg, Aarau, Lenzburg, and Brugg). Some districts, named the ''Freie Ämter'' or ''free bailiwicks'', with the County of Baden, were governed as "subject lands" by all or some of the Confederates. Part of Eggenwil was transferred to the ''Amt Hermetschwil'' of the ''Freie Ämter'', and the portions of the village north of the main road became part of the County of Baden. During the Helvetic Republic (1798–1803) Eggenwil and Widen formed a single muni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Künten
Künten is a municipality in the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It lies on the Reuss River and includes the previously independent community of Sulz, which merged with Künten in 1973. History Künten is first mentioned around 1101-50 as ''Chünten'' though this comes from a 14th Century copy of the original document. Geography Künten has an area, , of . Of this area, 56.3% is used for agricultural purposes, while 26.9% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 12.7% is settled (buildings or roads) and the remainder (4.1%) is non-productive (rivers or lakes). The municipality is located in the Baden district. It consists of the village of Künten on the Bremgarten-Fislisbach road and the village of Sulz along the Reuss river valley. Coat of arms The blazon of the municipal coat of arms is ''Per pale Argent a Latin Cross pattee couped and Gules a Bend Wavy Argent.'' Demographics Künten has a population (as of ) of . , 13.7% of the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remetschwil
Remetschwil is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Baden (district, Aargau), Baden in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Aargau in Switzerland. History Remetschwil is first mentioned in 1184 as ''Reimiswilare''. In 1854 the independent municipality was created when Rohrdorf split into Niederrohrdorf, Oberrohrdorf and Remetschwil.Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office accessed 14 January 2010 Geography Remetschwil has an area, , of . Of this area, 59.2% is used for agricultural purposes, while 24.2% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 16.4% is settled (buildings or roads) and the remainder (0.3%) is non-productive (rivers or lakes). T ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spreitenbach
Spreitenbach (High Alemannic: ''Spräitebach'') is a municipality in the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland, located in the Limmat Valley (German: ''Limmattal''). It lies southeast of the district center, directly on the border with the canton of Zurich. It is one of the smallest cities in Switzerland. In Switzerland, a city needs a population of 10,000 or more to be considered as a city. Geography The town lies between Baden and Zurich on the south side of the Limmat, located in the Limmat Valley (German: ''Limmattal''). The settled area stretches along a plain between the Heitersberg and the waterfront. The old town center, through which the Spreitenbach stream flows, lies to the south and has preserved its original character well. North of that is the modern city, with wide apartment buildings, industrial areas, and shopping centers. To the far north, across the highway and railway, in a bend in the Limmat, is the expanded industrial zone Neuhard. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergdietikon
Bergdietikon is a municipality in the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It is located in the Limmat Valley (German: ''Limmattal''). History Bergdietikon was originally part of the municipality of Dietikon in the Swiss County of Baden and was part of the short lived Canton of Baden. Following the Act of Mediation in 1803, the Canton of Baden was dismantled and the municipality of Dietikon was split. The mountain settlements in the west became the ''Berggemeinde Dietikon'' (Mountain municipality of Dietikon) until 1840 when it was renamed Bergdietikon. While Dietikon went to the Canton of Zurich, Bergdietikon went to Aargau. The creation of a municipality without any historic roots together and with a scattered geography meant that it took quite a while for any municipal center to appear. Geography Bergdietikon has an area, , of . Of this area, 54.6% is used for agricultural purposes, while 27.3% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 16.8% is se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash or cheques or more recently via online giving, whereas historically tithes were required and paid in kind, such as agricultural produce. After the separation of church and state, church tax linked to the tax system are instead used in many countries to support their national church. Donations to the church beyond what is owed in the tithe, or by those attending a congregation who are not members or adherents, are known as offerings, and often are designated for specific purposes such as a building program, debt retirement, or mission work. Many Christian denominations hold Jesus taught that tithing must be done in conjunction with a deep concern for "justice, mercy and faithfulness" (cf. Matthew 23:23). Tithing was taught at early Christian church councils, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murbach Abbey
Murbach Abbey (french: Abbaye de Murbach) was a famous Benedictine monastery in Murbach, southern Alsace, in a valley at the foot of the Grand Ballon in the Vosges. The monastery was founded in 727 by Eberhard, Count of Alsace, and established as a Benedictine house by Saint Pirmin. Its territory once comprised three towns and thirty villages. The buildings, including the abbey church, one of the earliest vaulted Romanesque structures, were laid waste in 1789 during the Revolution by the peasantry and the abbey was dissolved shortly afterwards. Of the 12th-century Romanesque abbey church, dedicated to Saint Leodegar (''St. Léger''), only the transept remains with its two steeples, and the east end with the quire. The site of the nave now serves as a burial ground. The building is located on the ''Route Romane d'Alsace''. History Early history The founder of the abbey, Count Eberhard, brother of Luitfrid of the Etichonids, brought Bishop Pirmin from Reichenau Abbey on Lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had a population of 1,898,533. Alsatian culture is characterized by a blend of Germanic and French influences. Until 1871, Alsace included the area now known as the Territoire de Belfort, which formed its southernmost part. From 1982 to 2016, Alsace was the smallest administrative ''région'' in metropolitan France, consisting of the Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin departments. Territorial reform passed by the French Parliament in 2014 resulted in the merger of the Alsace administrative region with Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine to form Grand Est. On 1 January 2021, the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the new European Collectivity of Alsace but remained part of the region Grand Est. Alsatian is an Alemannic dialect closely related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helvetic Republic
The Helvetic Republic (, , ) was a sister republic of France that existed between 1798 and 1803, during the French Revolutionary Wars. It was created following the French invasion and the consequent dissolution of the Old Swiss Confederacy, marking the end of the ''ancien régime'' in Switzerland. Throughout its existence, the republic incorporated most of the territory of modern Switzerland, excluding the cantons of Geneva and Neuchâtel and the old Prince-Bishopric of Basel. The Swiss Confederacy, which until then had consisted of self-governing cantons united by a loose military alliance (and ruling over subject territories such as Vaud), was invaded by the French Revolutionary Army and turned into an ally known as the "Helvetic Republic". The interference with localism and traditional liberties was deeply resented, although some modernizing reforms took place. Resistance was strongest in the more traditional Catholic cantons, with armed uprisings breaking out in spring 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_restoracio_Fahr_152.jpg)





