|
Beejoliya Kalan
Bijoliya is a census town in Bhilwara district in the state of Rajasthan, India and is surrounded by nature and waterfalls and is famous for Tapodaya Teerth Kshetra and Mandakini Temple. Geography Bijoliya Kalan is located at . It has an average elevation of The town is in the southeast of Bhilwara. It is close to the borders of the District Bundi. It is walled with two gates (north and south) and situated on a plateau called the Uparmal. Distance from various cities: 50 km from Bundi on the Bundi-Chittauragarh road, 70 km from Kota on NH 27, 85 km from Bhilwara on Bhilwara-Kota national highway via NH 758 and NH 27. Demographics India census, Beejoliya Kalan had a population of 12,384. Males constitute 52% of the population and females 48%. Beejoliya Kalan has an average literacy rate of 64%, higher than the national average of 59.5%; with 59% of the males and 41% of females literate. 15% of the population is under 6 years of age. Tourism The Hindu god Shiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Indian Cities
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
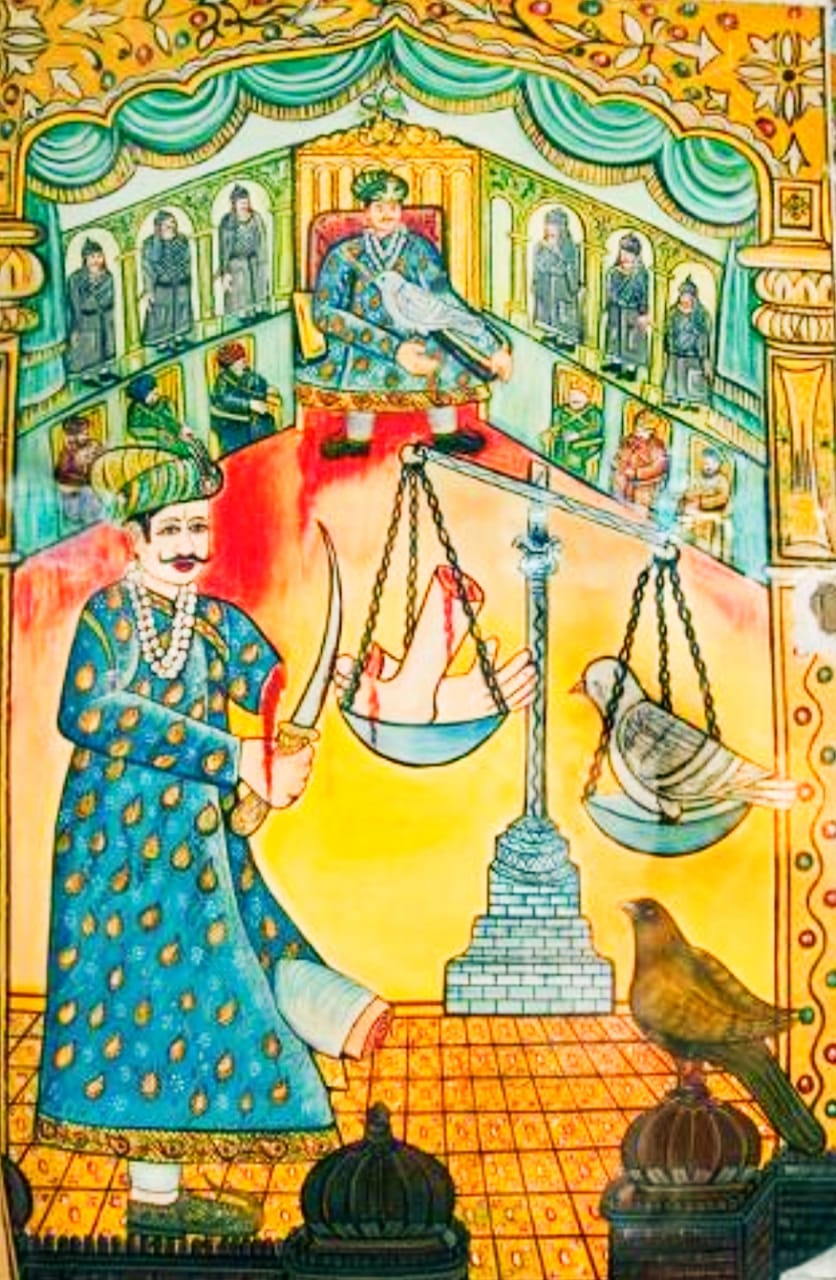
Someshvara (Chahamana Dynasty)
Someshvara (IAST: Someśvara, r. c. 1169–1178 CE ) was an Indian king belonging to the Chahamana dynasty and ruled parts of present-day Rajasthan in north-western India. He was brought up at the Chaulukya court in Gujarat by his maternal relatives. After death of Prithviraja II, the Chahamana ministers brought him to the capital Ajmer and appointed him as the new king. He is said to have commissioned several Shiva temples in Ajmer, and is best known as the father of Prithviraja III (Prithviraj Chauhan). Early life Someshvara was a son of the Chahamana king Arnoraja. His mother Kanchana-devi was a daughter of Jayasimha Siddharaja, the Chaulukya king of Gujarat. According to the legendary chronicle ''Prithviraja Vijaya'', some astrologers told Jayasimha that Someshvara's son would be an incarnation of Rama. Because of this, Jayasimha took Someshvara to Gujarat, where he was brought up. Jayasimha's successor Kumarapala was also very affectionate towards Someshvara, although h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hindu
''The Hindu'' is an Indian English-language daily newspaper owned by The Hindu Group, headquartered in Chennai, Tamil Nadu. It began as a weekly in 1878 and became a daily in 1889. It is one of the Indian newspapers of record and the second most circulated English-language newspaper in India, after '' The Times of India''. , ''The Hindu'' is published from 21 locations across 11 states of India. ''The Hindu'' has been a family-owned newspaper since 1905, when it was purchased by S. Kasturi Ranga Iyengar from the original founders. It is now jointly owned by Iyengar's descendants, referred to as the "Kasturi family", who serve as the directors of the holding company. The current chairperson of the group is Malini Parthasarathy, a great-granddaughter of Iyengar. Except for a period of about two years, when S. Varadarajan held the editorship of the newspaper, the editorial positions of the paper were always held by members of the family or held under their direction. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
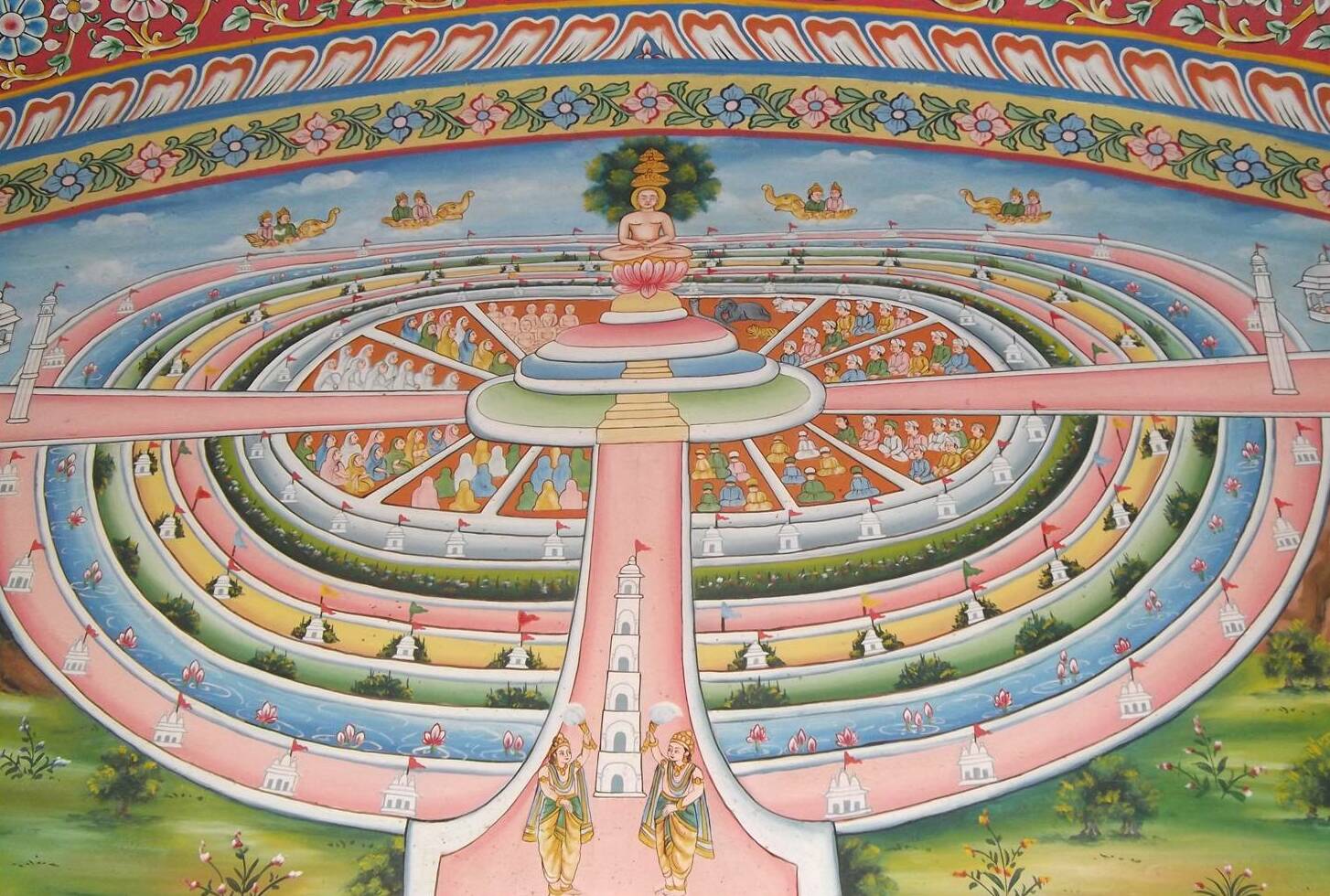
Samavasarana
In Jainism, Samavasarana or Samosharana ("Refuge to All") is the divine preaching hall of the Tirthankara, stated to have more than 20,000 stairs in it. The word ''samavasarana'' is derived from two words, ''sama'', meaning general and ''avasara'', meaning opportunity. It is an important feature in Jain art. The Samavasarana seems to have replaced the original Jain stupa as an object of worship. Samavasarana Hall In samavasarana hall, the ''tirthankara'' sits on a throne without touching it (about two inches above it). Around the tirthankara sit the ''ganadharas'' (chief disciples). Living beings sit in the following order: *In the first hall, ascetics *In the second hall, one class of deva ladies *In the third hall, ''aryikas'' (nuns) and laywomen *In the next three halls, three other classes of deva ladies *In the next four halls, the four classes of devas (heavenly beings) *Men, in the eleventh hall *Animals, in the last hall According to Jain texts, there would be four w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahavira
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6th century BCE into a royal Kshatriya Jain family in ancient India. His mother's name was Trishala and his father's name was Siddhartha. They were lay devotees of Parshvanatha. Mahavira abandoned all worldly possessions at the age of about 30 and left home in pursuit of spiritual awakening, becoming an ascetic. Mahavira practiced intense meditation and severe austerities for twelve and a half years, after which he attained '' Kevala Jnana'' (omniscience). He preached for 30 years and attained Moksha (liberation) in the 6th century BCE, although the year varies by sect. Historically, Mahavira, who revived and preached Jainism in ancient India, was an older contemporary of Gautama Buddha. Jains celebrate ''Mahavir Janma Kalyanak'' every ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parshvanatha
''Parshvanatha'' (), also known as ''Parshva'' () and ''Parasnath'', was the 23rd of 24 ''Tirthankaras'' (supreme preacher of dharma) of Jainism. He is the only Tirthankara who gained the title of ''Kalīkālkalpataru (Kalpavriksha in this "Kali Yuga").'' Parshvanatha is one of the earliest ''Tirthankaras'' who are acknowledged as historical figures. He was the earliest exponent of Karma philosophy in recorded history. The Jain sources place him between the 9th and 8th centuries BCE whereas historians consider that he lived in the 8th or 7th century BCE. Parshvanatha was born 273 years before Mahavira. He was the spiritual successor of 22nd tirthankara Neminatha. He is popularly seen as a propagator and reviver of Jainism. Parshvanatha attained moksha on Mount Sammeda ( Madhuban, Jharkhand) popular as Parasnath hill in the Ganges basin, an important Jain pilgrimage site. His iconography is notable for the serpent hood over his head, and his worship often includes Dharanendr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shantinatha
Shantinatha was the sixteenth Jain tirthankar of the present age (Avasarpini). Shantinatha was born to King Vishvasena and Queen Aiira at Hastinapur in the Ikshvaku dynasty. His birth date is the thirteenth day of the Jyest Krishna month of the Indian calendar. He was also a Chakravartin and a Kamadeva. He ascended to the throne when he was 25 years old. After over 25,000 years at the throne, he became a Jain monk and started his penance. According to Jain beliefs, he became a siddha, a liberated soul which has destroyed all of its karma. Biography in Jain tradition Shantinatha was the sixteenth Jain '' Tīrthankara'' of the 24 tirthankars of the present age ('' avasarpini''). Life before renunciation He was born to King Vishvasena and Queen Achira at Hastinapur on 13th day of Jestha Krishna in the Ikshvaku clan. Before the birth of Shantinatha, Queen Achira dreamt the sixteen most auspicious dreams. Shantinatha spent 25,000 years as a youth (''kumāra kāla'') and marrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
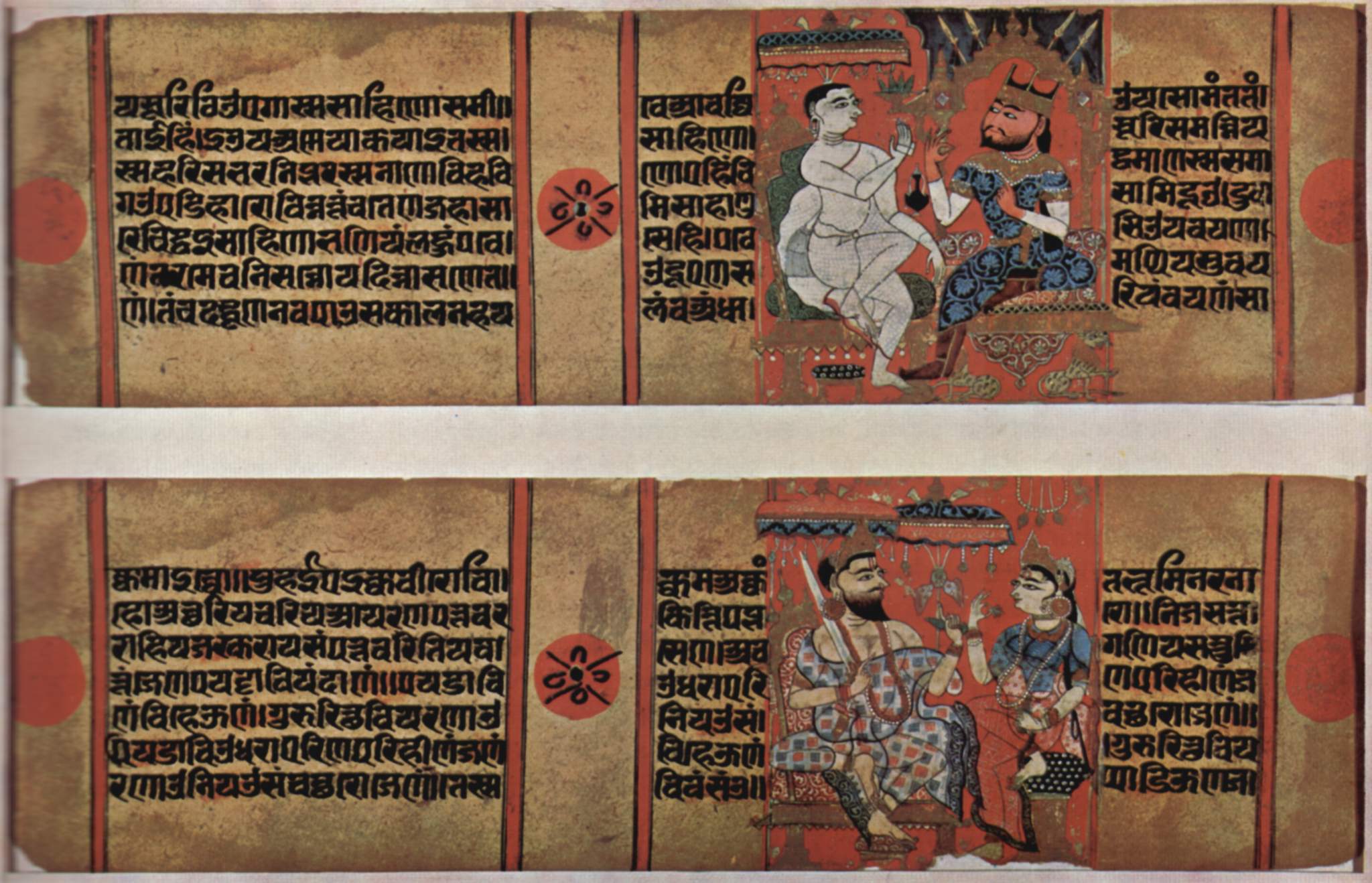
Chahamanas Of Shakambhari
The Chahamanas of Shakambhari (IAST: Cāhamāna), colloquially known as the Chauhans of Sambhar or Chauhans of Ajmer, were an Indian dynasty that ruled parts of the present-day Rajasthan and neighbouring areas in India, between the 6th and 12th centuries. The territory ruled by them was known as Sapadalaksha. They were the most prominent ruling family of the Chahamana (Chauhan) Rajput clan. The Chahamanas originally had their capital at Shakambhari (present-day Sambhar Lake Town). Until the 10th century, they ruled as Pratihara vassals. When the Pratihara power declined after the Tripartite Struggle, the Chahamana ruler Simharaja assumed the title Maharajadhiraja. In the early 12th century, Ajayaraja II moved the kingdom's capital to Ajayameru (modern Ajmer). For this reason, the Chahamana rulers are also known as the "Chauhans of Ajmer". The Chahamanas fought several wars with their neighbours, including the Chaulukyas of Gujarat, the Tomaras of Delhi, the Paramaras of Malwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikrama Samvat
Vikram Samvat (IAST: ''Vikrama Samvat''; abbreviated VS) or Bikram Sambat B.S. and also known as the Vikrami calendar, is a Hindu calendar historically used in the Indian subcontinent. Vikram Samvat is generally 57 years ahead of Gregorian Calendar, except during January to April, when it is ahead by 56 years. Alongside Nepal Sambat, it is one of the two official calendars used in Nepal. In India, it is used in several states. The traditional Vikram Samvat calendar, as used in India, uses lunar months and solar sidereal years. The Nepali Bikram Sambat introduced in 1901 CE, also uses a solar sidereal year. History A number of ancient and medieval inscriptions used the Vikram Samvat. Although it was reportedly named after the legendary king Vikramaditya, the term "Vikrama Samvat" does not appear in the historical record before the 9th century; the same calendar system is found with other names, such as Krita and Malava. In colonial scholarship, the era was believed to be bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)



