|
Bedlington Ironworks
Bedlington Ironworks, in Blyth Dene, Northumberland, England, operated between 1736 and 1867. It is most remembered as the place where wrought iron rails were invented by John Birkinshaw in 1820, which triggered the railway age, with their first major use being in the Stockton and Darlington Railway opened in 1825, about to the south. Blyth Dene, near Bedlington, was an idyllic location next to the River Blyth which had all the right ingredients for an ironworks at the time: there were nodules of ironstone in the coal-laden banks of the river, there was plenty of wood for the traditional approach of charcoal making, water for driving the hammers, and the port of Blyth was only two miles downriver for shipping of the products. At the time, a Shropshire man, Abraham Darby had started a revolution in ironmaking by using coke instead of charcoal. The Bedlington ironworks originally consisted of two elements – a mill in Bebside and a furnace at Bedlington Mill Bebside A leas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey. It is bordered by land on three sides; by the Scottish Borders region to the north, County Durham and Tyne and Wear to the south, and Cumbria to the west. The fourth side is the North Sea, with a stretch of coastline to the east. A predominantly rural county with a landscape of moorland and farmland, a large area is part of Northumberland National Park. The area has been the site of a number of historic battles with Scotland. Name The name of Northumberland is recorded as ''norð hẏmbra land'' in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, meaning "the land north of the Humber". The name of the kingdom of ''Northumbria'' derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the people south of the Humber Estuary. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling Mill
In metalworking, rolling is a metal forming process in which metal stock is passed through one or more pairs of rolls to reduce the thickness, to make the thickness uniform, and/or to impart a desired mechanical property. The concept is similar to the rolling of dough. Rolling is classified according to the temperature of the metal rolled. If the temperature of the metal is above its recrystallization temperature, then the process is known as hot rolling. If the temperature of the metal is below its recrystallization temperature, the process is known as cold rolling. In terms of usage, hot rolling processes more tonnage than any other manufacturing process, and cold rolling processes the most tonnage out of all cold working processes... Roll stands holding pairs of rolls are grouped together into rolling mills that can quickly process metal, typically steel, into products such as structural steel (I-beams, angle stock, channel stock), bar stock, and rails. Most steel mills ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland. The city's Holyrood Palace, Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Stevenson (civil Engineer)
Robert Stevenson, FRSE, FGS, FRAS, FSA Scot, MWS (8 June 1772 – 12 July 1850) was a Scottish civil engineer, and designer and builder of lighthouses. His works include the Bell Rock Lighthouse. Early life Robert Stevenson was born in Glasgow. His father was Alan Stevenson, a partner in a West Indies sugar trading house in the city. Alan died of an epidemic fever on the island of St. Christopher in the West Indies on 26 May 1774, a few days before Robert's second birthday. Robert's uncle died of the same disease around the same time. Since this left Alan's widow, Jean Lillie Stevenson, in much-reduced financial circumstances, Robert was educated, as a young child, at a charity school. Robert's mother intended him to join the ministry, so when he was a bit older she enrolled him in the school of a locally famous Glasgow linguist, a Mr Macintyre. But when Robert was 15, she remarried and the family moved to 1 Blair Street, off the Royal Mile in Edinburgh. Robert's new stepfath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wagonway
Wagonways (also spelt Waggonways), also known as horse-drawn railways and horse-drawn railroad consisted of the horses, equipment and tracks used for hauling wagons, which preceded Steam locomotive, steam-powered rail transport, railways. The terms plateway, tramway (industrial), tramway, dramway, were used. The advantage of wagonways was that far bigger loads could be transported with the same power. Ancient systems The earliest evidence is of the 6 to 8.5 km long ''Diolkos'' paved trackway, which transported boats across the Isthmus of Corinth in Greece from around 600 BC. Wheeled vehicles pulled by men and animals ran in grooves in limestone, which provided the track element, preventing the wagons from leaving the intended route. The Diolkos was in use for over 650 years, until at least the 1st century AD. Paved trackways were later built in Roman Egypt. Wooden rails Such an operation was illustrated in Germany in 1556 by Georgius Agricola (image right) in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choppington
Choppington is a large village and civil parish in Northumberland, England. It is situated 5 miles to the south-east of Morpeth, and north of Bedlington. It was at one time part of the three big mid-Northumberland collieries (Ashington, Bomarsund and Choppington). The parish, which was until 1 July 2010 called North Bedlington, was created on 1 April 2009 also includes the settlements of Bomarsund, Guide Post Guide Post is a village in South East Northumberland, England, about 17 miles (27 km) north of Newcastle upon Tyne. It lies south of the River Wansbeck along with Stakeford Stakeford is a large village in south east Northumberland, E ..., Stakeford, Sheepwash, Scotland Gate and West Sleekburn. Governance An electoral ward exists. the population of this ward at the 2011 Census was 4,792. References External links Villages in Northumberland Civil parishes in Northumberland {{Northumberland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Longridge
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name "Michael" * Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and Islamic religions * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer Rulers =Byzantine emperors= *Michael I Rangabe (d. 844), married the daughter of Emperor Nikephoros I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawks Family
The Hawks family (c.1750 – 1889) was one of the most powerful British industrial dynasties of the British Industrial Revolution. The Hawks owned several companies in Northern England and in the City of London (including Hawks and Co., Hawks, Crawshay, and Stanley, and Hawks, Crawshay and Sons) all of which had the name Hawks in the company name, and which had iron manufacture and engineering, which they exported worldwide using their own ships, as their main enterprises. The Hawks family were involved in merchant banking, and in freemasonry, and in Whig free-trade politics. They developed areas of West London, including Pembroke Square, Kensington. The Hawks reached the apogee of their power during the Victorian period, when they employed over 2000 persons, when their reputation for engineering and bridge-building was worldwide. Their Gateshead factories were termed New Deptford and New Woolwich after the location of two of its warehouses on the River Thames, at Deptford and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
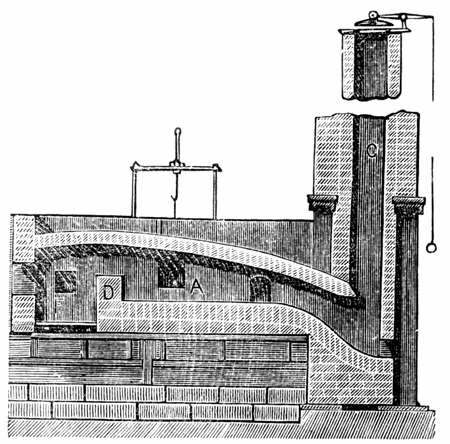
Puddling (metallurgy)
Puddling is the process of converting pig iron to bar (wrought) iron in a coal fired reverberatory furnace. It was developed in England during the 1780s. The molten pig iron was stirred in a reverberatory furnace, in an oxidizing environment, resulting in wrought iron. It was one of the most important processes of making the first appreciable volumes of valuable and useful bar iron (malleable wrought iron) without the use of charcoal. Eventually, the furnace would be used to make small quantities of specialty steels. Though it was not the first process to produce bar iron without charcoal, puddling was by far the most successful, and replaced the earlier potting and stamping processes, as well as the much older charcoal finery and bloomery processes. This enabled a great expansion of iron production to take place in Great Britain, and shortly afterwards, in North America. That expansion constitutes the beginnings of the Industrial Revolution so far as the iron industry is conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forge
A forge is a type of hearth used for heating metals, or the workplace (smithy) where such a hearth is located. The forge is used by the smith to heat a piece of metal to a temperature at which it becomes easier to shape by forging, or to the point at which work hardening no longer occurs. The metal (known as the "workpiece") is transported to and from the forge using tongs, which are also used to hold the workpiece on the smithy's anvil while the smith works it with a hammer. Sometimes, such as when hardening steel or cooling the work so that it may be handled with bare hands, the workpiece is transported to the slack tub, which rapidly cools the workpiece in a large body of water. However, depending on the metal type, it may require an oil quench or a salt brine instead; many metals require more than plain water hardening. The slack tub also provides water to control the fire in the forge. Types Coal/coke/charcoal forge A forge typically uses bituminous coal, indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundry
A foundry is a factory that produces metal castings. Metals are cast into shapes by melting them into a liquid, pouring the metal into a mold, and removing the mold material after the metal has solidified as it cools. The most common metals processed are aluminum and cast iron. However, other metals, such as bronze, brass, steel, magnesium, and zinc, are also used to produce castings in foundries. In this process, parts of desired shapes and sizes can be formed. Foundries are one of the largest contributors to the manufacturing recycling movement, melting and recasting millions of tons of scrap metal every year to create new durable goods. Moreover, many foundries use sand in their molding process. These foundries often use, recondition, and reuse sand, which is another form of recycling. Process In metalworking, casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |