|
Bayesian Game
In game theory, a Bayesian game is a strategic decision-making model which assumes players have incomplete information. Players may hold private information relevant to the game, meaning that the payoffs are not common knowledge. Bayesian games model the outcome of player interactions using aspects of Bayesian probability. They are notable because they allowed the specification of the solutions to games with incomplete information for the first time in game theory. Hungarian economist John C. Harsanyi introduced the concept of Bayesian games in three papers from 1967 and 1968: He was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for these and other contributions to game theory in 1994. Roughly speaking, Harsanyi defined Bayesian games in the following way: players are assigned a set of characteristics by nature at the start of the game. By mapping probability distributions to these characteristics and by calculating the outcome of the game using Bayesian probability, the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which a participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by the losses and gains of the other participant. In the 1950s, it was extended to the study of non zero-sum games, and was eventually applied to a wide range of Human behavior, behavioral relations. It is now an umbrella term for the science of rational Decision-making, decision making in humans, animals, and computers. Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. His paper was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Strategy (game Theory)
In game theory, a move, action, or play is any one of the options which a player can choose in a setting where the optimal outcome depends ''not only'' on their own actions ''but'' on the actions of others. The discipline mainly concerns the action of a player in a game affecting the behavior or actions of other players. Some examples of "games" include chess, bridge, poker, monopoly, diplomacy or battleship. The term strategy is typically used to mean a complete algorithm for playing a game, telling a player what to do for every possible situation. A player's strategy determines the action the player will take at any stage of the game. However, the idea of a strategy is often confused or conflated with that of a move or action, because of the correspondence between moves and pure strategies in normal-form game, most games: for any move ''X'', "always play move ''X''" is an example of a valid strategy, and as a result every move can also be considered to be a strategy. Other autho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Economically Efficient
In microeconomics, economic efficiency, depending on the context, is usually one of the following two related concepts: * Allocative or Pareto efficiency: any changes made to assist one person would harm another. * Productive efficiency: no additional output of one good can be obtained without decreasing the output of another good, and production proceeds at the lowest possible average total cost. These definitions are not equivalent: a market or other economic system may be allocatively but not productively efficient, or productively but not allocatively efficient. There are also other definitions and measures. All characterizations of economic efficiency are encompassed by the more general engineering concept that a system is efficient or optimal when it maximizes desired outputs (such as utility) given available inputs. Standards of thought There are two main standards of thought on economic efficiency, which respectively emphasize the distortions created by ''governments'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adverse Selection
In economics, insurance, and risk management, adverse selection is a market situation where Information asymmetry, asymmetric information results in a party taking advantage of undisclosed information to benefit more from a contract or trade. In an ideal world, buyers should pay a price which reflects their willingness to pay and the value to them of the product or service, and sellers should sell at a price which reflects the quality of their goods and services. However, when one party holds information that the other party does not have, they have the opportunity to damage the other party by maximizing self-utility, concealing relevant information, and perhaps even lying. This opportunity has secondary effects: the party without the information may take steps to avoid entering into an unfair contract, perhaps by withdrawing from the interaction; a party may ask for higher or lower prices, diminishing the volume of trade in the market; or parties may be deterred from participatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Strategic Dominance
In game theory, a strategy ''A'' dominates another strategy ''B'' if ''A'' will always produce a better result than ''B'', regardless of how any other player plays. Some very simple games (called straightforward games) can be solved using dominance. Terminology A player can compare two strategies, A and B, to determine which one is better. The result of the comparison is one of: * B strictly dominates (>) A: choosing B always gives a better outcome than choosing A, no matter what the other players do. * B weakly dominates (≥) A: choosing B always gives at least as good an outcome as choosing A, no matter what the other players do, and there is at least one set of opponents' actions for which B gives a better outcome than A. (Notice that if B strictly dominates A, then B weakly dominates A. Therefore, we can say "B dominates A" to mean "B weakly dominates A".) * B is weakly dominated by A: there is at least one set of opponents' actions for which B gives a worse outcome than A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Common Knowledge (logic)
Common knowledge is a special kind of knowledge for a group of agents. There is ''common knowledge'' of ''p'' in a group of agents ''G'' when all the agents in ''G'' know ''p'', they all know that they know ''p'', they all know that they all know that they know ''p'', and so on ''ad infinitum''.Osborne, Martin J., and Ariel Rubinstein. ''A Course in Game Theory''. Cambridge, MA: MIT, 1994. Print. It can be denoted as C_G p. The concept was first introduced in the philosophical literature by David Kellogg Lewis in his study ''Convention'' (1969). The sociologist Morris Friedell defined common knowledge in a 1969 paper. It was first given a mathematical formulation in a set-theoretical framework by Robert Aumann (1976). Computer scientists grew an interest in the subject of epistemic logic in general – and of common knowledge in particular – starting in the 1980s. There are numerous puzzles based upon the concept which have been extensively investigated by mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perfect Information
Perfect information is a concept in game theory and economics that describes a situation where all players in a game or all participants in a market have knowledge of all relevant information in the system. This is different than complete information, which implies Common knowledge (logic), common knowledge of each agent's utility functions, payoffs, strategies and "types". A system with perfect information may or may not have complete information. In economics this is sometimes described as "no hidden information" and is a feature of perfect competition. In a market with perfect information all consumers and producers would have complete and instantaneous knowledge of all market prices, their own utility and cost functions. In game theory, a sequential game has perfect information if each player, when making any decision, is perfectly informed of all the events that have previously occurred, including the "initialization event" of the game (e.g. the starting hands of each player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Agency (sociology)
In social science, agency is the capacity of individuals to have the power and resources to fulfill their potential. Social structure consists of those factors of influence (such as social class, religion, gender, ethnicity, ability, customs, etc.) that determine or limit agents and their decisions. The influences from structure and agency are debated—it is unclear to what extent a person's actions are constrained by social systems. One's agency is one's independent capability or ability to act on one's will. This ability is affected by the cognitive belief structure which one has formed through one's experiences, and the perceptions held by the society and the individual, of the structures and circumstances of the environment one is in and the position one is born into. Disagreement on the extent of one's agency often causes conflict between parties, e.g. parents and children. History The overall concept of agency has existed since the Enlightenment where there was debat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
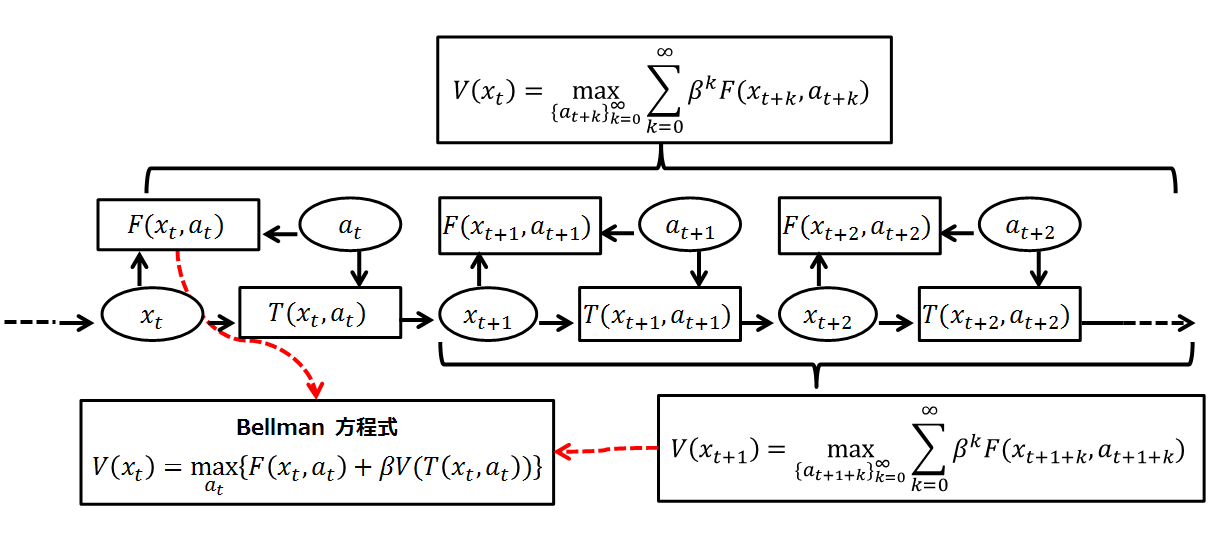
Bellman Equation
A Bellman equation, named after Richard E. Bellman, is a necessary condition for optimality associated with the mathematical Optimization (mathematics), optimization method known as dynamic programming. It writes the "value" of a decision problem at a certain point in time in terms of the payoff from some initial choices and the "value" of the remaining decision problem that results from those initial choices. This breaks a dynamic optimization problem into a sequence of simpler subproblems, as Bellman's “principle of optimality" prescribes. The equation applies to algebraic structures with a total ordering; for algebraic structures with a partial ordering, the generic Bellman's equation can be used. The Bellman equation was first applied to engineering control theory and to other topics in applied mathematics, and subsequently became an important tool in economic theory; though the basic concepts of dynamic programming are prefigured in John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stochastic Game
In game theory, a stochastic game (or Markov game) is a repeated game with probabilistic transitions played by one or more players. The game is played in a sequence of stages. At the beginning of each stage the game is in some state. The players select actions and each player receives a payoff that depends on the current state and the chosen actions. The game then moves to a new random state whose distribution depends on the previous state and the actions chosen by the players. The procedure is repeated at the new state and play continues for a finite or infinite number of stages. The total payoff to a player is often taken to be the discounted sum of the stage payoffs or the limit inferior of the averages of the stage payoffs. Stochastic games were introduced by Lloyd Shapley in the early 1950s. They generalize Markov decision processes to multiple interacting decision makers, as well as strategic-form games to dynamic situations in which the environment changes in response to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Artificial Intelligence (journal)
''Artificial Intelligence'' is a scientific journal on artificial intelligence research. It was established in 1970 and is published by Elsevier. The journal is abstracted and indexed in Scopus and Science Citation Index. The 2021 Impact Factor for this journal is 14.05 and the 5-Year Impact Factor is 11.616.Journal Citation Reports 2022, Published by Thomson Reuters References External links Official website Artificial intelligence journals Elsevier academic journals Academic journals established in 1970 {{compu-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
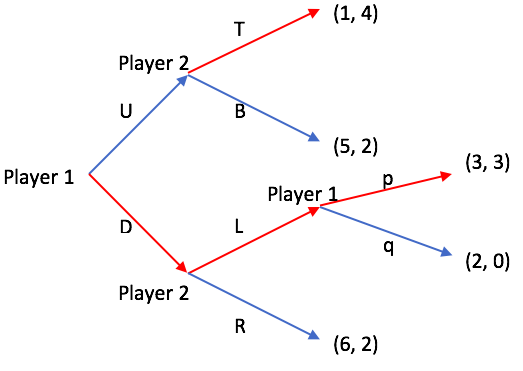
Subgame Perfect Equilibrium
In game theory, a subgame perfect equilibrium (SPE), or subgame perfect Nash equilibrium (SPNE), is a refinement of the Nash equilibrium concept, specifically designed for dynamic games where players make sequential decisions. A strategy profile is an SPE if it represents a Nash equilibrium in every possible subgame of the original game. Informally, this means that at any point in the game, the players' behavior from that point onward should represent a Nash equilibrium of the continuation game (i.e. of the subgame), no matter what happened before. This ensures that strategies are credible and rational throughout the entire game, eliminating non-credible threats. Every finite extensive game with complete information (all players know the complete state of the game) and perfect recall (each player remembers all their previous actions and knowledge throughout the game) has a subgame perfect equilibrium. A common method for finding SPE in finite games is backward induction, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |