|
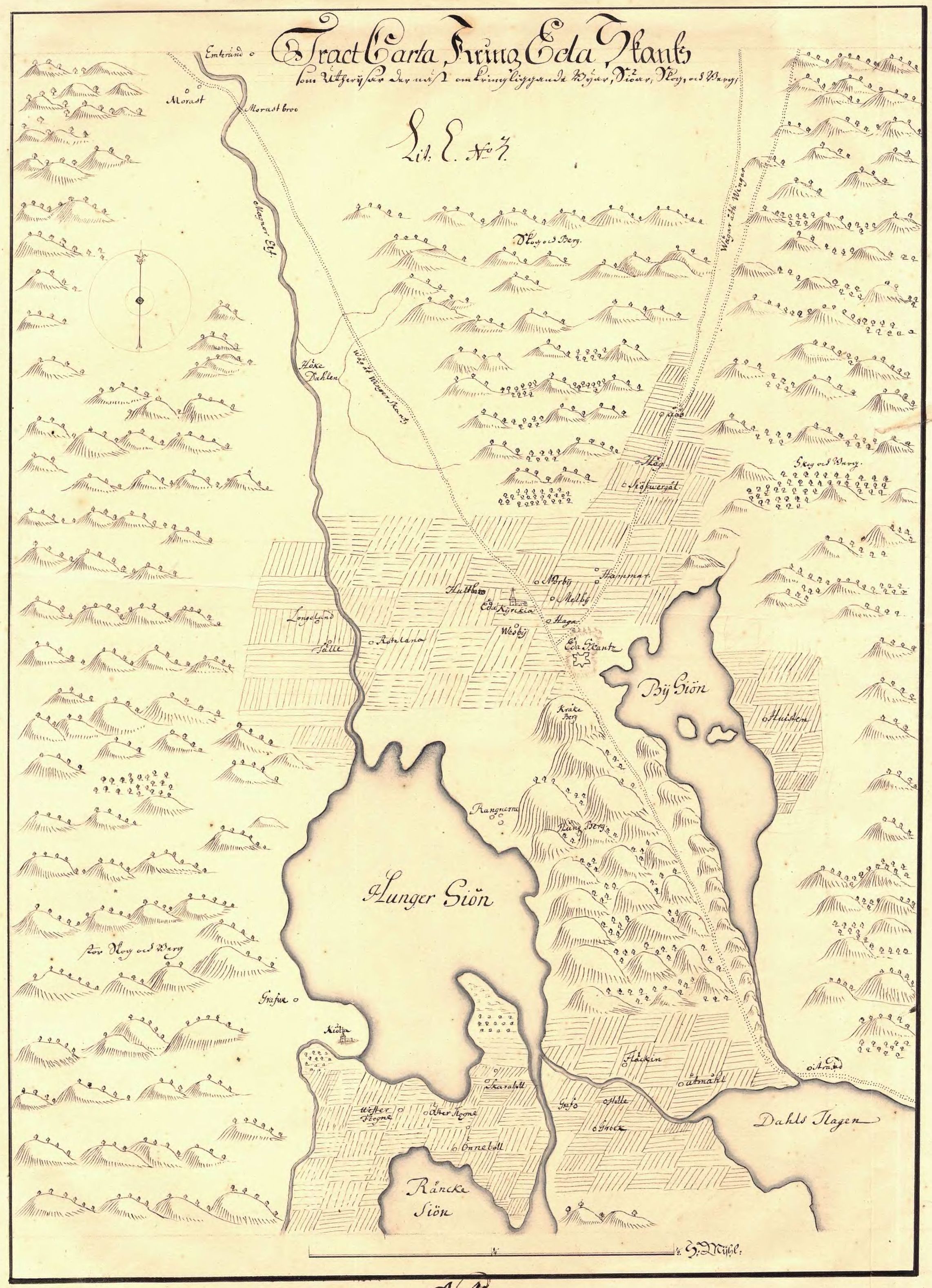
Battle Of Bysjön
The Battle of Bysjön was fought between Sweden, Swedish and, for the most part, Norway, Norwegian troops on 22 December 1644. The battle took place on the ice of the frozen Lake Bysjön in the parish of Eda (''Eda socken, Värmland'') in Värmland, Sweden. The battle was part of the Torstenson War (1643-1645), known locally as the Hannibal Feud (''Hannibalsfejden'') between Sweden and Denmark-Norway. The Danish-Norwegian victory meant the invading army could potentially continue into Värmland and Dalsland. Introduction In the autumn 1643 Field Marshal Lennart Torstensson (1603–1651), by order of the Swedish Riksråd, Council of the Realm, led the Swedish army which was then embroiled in the Thirty Years' War into Danish Jutland, initiating the Torstenson War. To ease the military pressure in Denmark, Hannibal Sehested (governor), Hannibal Sehested (1609–1666), Governor-general of Norway, began preparations for military operations against Sweden along the Norwegian bord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torstenson War
The Torstenson War was fought between Sweden and Denmark–Norway from 1643 to 1645. The name derives from Swedish general Lennart Torstenson. Denmark-Norway had withdrawn from the Thirty Years' War in the 1629 Treaty of Lübeck. After its victories in the war, Sweden felt it had to attack Denmark-Norway due to its advantageous geographical position in relation to Sweden. Sweden invaded in a short two-year war. In the Second Treaty of Brömsebro (1645), which concluded the war, Denmark-Norway had to make huge territorial concessions and exempt Sweden from the Sound Dues, ''de facto'' acknowledging the end of the Danish-Norwegian ''dominium maris baltici''. Danish-Norwegian efforts to reverse this result in the Second Northern, Scanian and Great Northern wars failed. Background Sweden had been highly successful in the Thirty Years' War, having defeated Imperial armies in Germany and seen substantial victories under Gustavus Adolphus and after his death, under the leadership o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothenburg
Gothenburg ( ; ) is the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, second-largest city in Sweden, after the capital Stockholm, and the fifth-largest in the Nordic countries. Situated by the Kattegat on the west coast of Sweden, it is the gubernatorial seat of Västra Götaland County, with a population of approximately 600,000 in the city proper and about 1.1 million inhabitants in Metropolitan Gothenburg, the metropolitan area. Gustavus Adolphus, King Gustavus Adolphus founded Gothenburg by royal charter in 1621 as a heavily fortified, primarily Dutch, trading colony. In addition to the generous privileges given to his Dutch allies during the ongoing Thirty Years' War, e.g. tax relaxation, he also attracted significant numbers of his German and Scottish allies to populate his only town on the western coast; this trading status was furthered by the founding of the Swedish East India Company. At a key strategic location at the mouth of the , where Scandinavia's largest dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Cavalry
This is a list of Swedish cavalry regiments, battalions, corps and companies that have existed in the Swedish Army. They are listed in three ways, first by the actual units that have existed, then by the various names these units have had, and last by the various designations these units have had. By unit * Adelsfanan (1571–1901) * Aschebergska regementet (1674–1720) * Blå (Putbusska) husarregemenetet (1762–1766) * Bohus dragonbataljon (1679–1720) * Bohus-Jämtlands kavalleribataljon (1661–1670) * Bohusläns dragonregemente (1727–1776) * Bohusläns kavalleri- och dragonregemente (1720–1727) * Bohusläns kavallerikompani (1670–1674) * Bohusläns lätta dragonregemente (1776–1791) * Cederströmska husarregementet (1816–1822) * Finska lätta dragonkåren (1770–1772) * Gula (Wrangelska) husarregementet (1762–1766) * Gröna dragonerna (1675–1679) * Hornska husarregementet (1797–1801) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Reichwein
Georg Reichwein, Jr. (1630–1710) was a military government official. He was the son of general major Georg Reichwein, Sr., who immigrated to Denmark-Norway from Hesse in 1628. In 1658 he became captain in charge of the ''Sør-Gudbrandsdalske'' company. In a letter written in 1664 we find he lived at Jørstad farm in Fåberg. His father was raised to a peerage in 1655, and he would have been foremost in rank at Fåberg in his time. He bought both Nordre Jørstad and Søndre Jørstad farms in 1672. Reichwein was promoted to Major in 1675, and as Lieutenant Colonel in 1682 he was commander of Kongsvinger Fortress. He remained at Kongsvinger and became a Colonel in 1689. He lived at Vingnes Vingnes is a village in Lillehammer Municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. The village is located on the west bank of lake Mjøsa, just across the Gudbrandsdalslågen river from the town of Lillehammer. The European route E6 highway runs thro ... in 1695, where he is recorded as marrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Närke-Värmland Regiment
The Närke-Värmland Regiment () was a Swedish Army infantry regiment that traced its origins back to the 16th century. It was split into two new regiments in 1812. The regiment's soldiers were recruited from the provinces of Närke and Värmland. History The regiment has its origins in fänikor (companies) raised in Närke and Värmland in the 16th century. In 1614, these units—along with fänikor from the nearby province of Södermanland—were organised by Gustav II Adolph into Södermanlands storregemente, of which eleven of the total 24 companies were recruited in Värmland and five in Närke. Södermanlands storregemente consisted of three field regiments, of which Närke Regiment and Värmland Regiment were two. Sometime around 1624, the grand regiment was permanently split into three smaller regiments, of which Närke Regiment and Värmland Regiment were two. In 1629, these two regiments were merged to form Närke-Värmland Regiment. The Närke-Värmland Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breastwork (fortification)
A breastwork is a temporary fortification, often an earthwork thrown up to breast or shoulder height to provide protection to defenders firing over it from a standing position. A more permanent structure, normally in stone, would be described as a parapet or the battlement of a castle wall. In warships, a breastwork is the armored superstructure in the ship that did not extend all the way out to the sides of the ship. It was generally only used in ironclad turret ships designed between 1865 and 1880. References See also *List of established military terms (Fortifications A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...) Fortifications by type {{Fort-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnor
Magnor is a village in Eidskog Municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. The village is located from the border with Sweden. The village lies along the Norwegian National Road 2 and the Kongsvingerbanen railway line. The municipal centre, Skotterud lies about to the northwest of Magnor and the Swedish village of Charlottenberg lies about to the southeast of Magnor. The village has a population (2021) of 918 and a population density of . The village is known as a production site for glass, made at Magnor Glassverk (lit. Magnor Glass Works) and also for the production of aluminium, made at Hydro Extrusion Norway. During the border wars in the middle of the 17th century, there were fortifications in the area. In 1914, the famous Peace Monument was built in Magnor. It was designed by the Swedish architect Lars Johan Lehming and funded by the Swedish Peace and Arbitration Society The Swedish Peace and Arbitration Society (SPAS) () is a non-governmental organization in Swed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlottenberg
Charlottenberg is a locality in Värmland County, Sweden, and the administrative centre of Eda Municipality. Situated some seven kilometres from the Norwegian border, the town has a population of around 3,000. Charlottenberg railway station is the last in Sweden before the Norwegian border, and serves as the frontier point between the Swedish and Norwegian railway systems. The town lies on Swedish national road (''riksväg'') 61, which becomes Norwegian national road (''riksvei'') 2 at the border. Nearby towns include Åmotfors (14 km) and Arvika (30 km) in Sweden, Magnor (9 km), Skotterud (14 km), and Kongsvinger Kongsvinger () is a municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Glåmdal. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Kongsvinger. Other settlements in the municipality include Aust ... (38 km) in Norway. As a border town, Charlottenberg benefits greatly from the '' border tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morast
''Morass'' (German:''Morast'') is a 1922 German silent film directed by Wolfgang Neff and starring Maria Zelenka. The film's sets were designed by the art director Mathieu Oostermann. Cast * Maria Zelenka as Lissy * Henri Peters-Arnolds * Karl Elzer * Bella Polini as Frau Tertiol * Colette Corder as Meta * Willy Kaiser-Heyl Willy Kaiser-Heyl (4 August 1876 – 2 December 1953) was a German film actor. He appeared in 92 films between 1919 and 1952. He was born in Frankfurt, Germany and died in Berlin. Selected filmography * ''The Tragedy of a Great'' (1920) * ... * Julius Frucht as Dr. Herrmann External links * 1922 films Films of the Weimar Republic Films directed by Wolfgang Neff German silent feature films German black-and-white films {{1920s-Germany-silent-film-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlstad
Karlstad (, ) is the 20th-largest city in Sweden, the seat of Karlstad Municipality, the capital of Värmland County, and the largest city in the province Värmland in Sweden. The city proper had 67,122 inhabitants in 2020 with 97,233 inhabitants in the wider municipality in 2023, and is the 21st largest municipality in Sweden. Karlstad has a university and a cathedral. During recent years, Karlstad has started seeing big growth with many new buildings, for example the new apartment complexes around Orrholmen and Tullholmen, hosting a brand new Coop store and a 17 story high rise apartment which was finished in late 2022. Karlstad is built on the river delta where Sweden's longest river, Klarälven, runs into Sweden's largest lake, Vänern. It has the second largest lake port in the country after Västerås. Karlstad is often associated with sunshine and the symbol for Karlstad is a smiling sun. Karlstad is reputed to be one of the sunniest towns in Sweden and a local wai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kongsvinger
Kongsvinger () is a municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Glåmdal. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Kongsvinger. Other settlements in the municipality include Austmarka, Brandval, Lundersæter, and Roverud. The municipality is the 111th largest by area out of the 356 municipalities in Norway. Kongsvinger is the 72nd most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 17,966. The municipality's population density is and its population has increased by 1.9% over the previous 10-year period. Kongsvinger's eastern municipal boundary is the Norway–Sweden border. General information In 1854, the King designated the market town of Kongsvinger as a kjøpstad, which gave it special rights. The designation included a small patch of land on both sides of the river Glomma with an area of approximately . Because of this designation, on 7 February 1855, the town was separated from the municipalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |