|
Bathornis
''Bathornis'' ("tall bird") is an extinct lineage of birds related to modern day seriemas, that lived in North America about 37–20 million years ago. Like the closely related and also extinct phorusrhacids, it was a flightless predator, occupying predatory niches in environments classically considered to be dominated by mammals. It was a highly diverse and successful genus, spanning a large number of species that occurred from the Priabonian Eocene to the Burdigalian Miocene epochs. Description Though most material is highly incomplete, ''Bathornis'' is nonetheless known from a variety of skeletal elements: hindlimbs (most commonly tarso-metatarsals), forelimb elements (especially humeri), pelvises and skulls.Federico L. Agnolin (2009)"Sistemática y Filogenia de las Aves Fororracoideas (Gruiformes, Cariamae)"(PDF). Fundación de Historia Natural Felix de Azara: 1–79. ''Bathornis grallator'' is known from a mostly complete skeleton, including the skull, bearing a proportiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathornis
''Bathornis'' ("tall bird") is an extinct lineage of birds related to modern day seriemas, that lived in North America about 37–20 million years ago. Like the closely related and also extinct phorusrhacids, it was a flightless predator, occupying predatory niches in environments classically considered to be dominated by mammals. It was a highly diverse and successful genus, spanning a large number of species that occurred from the Priabonian Eocene to the Burdigalian Miocene epochs. Description Though most material is highly incomplete, ''Bathornis'' is nonetheless known from a variety of skeletal elements: hindlimbs (most commonly tarso-metatarsals), forelimb elements (especially humeri), pelvises and skulls.Federico L. Agnolin (2009)"Sistemática y Filogenia de las Aves Fororracoideas (Gruiformes, Cariamae)"(PDF). Fundación de Historia Natural Felix de Azara: 1–79. ''Bathornis grallator'' is known from a mostly complete skeleton, including the skull, bearing a proportiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathornithidae
Bathornithidae is an extinct family of birds from the Eocene to Miocene of North America. Part of Cariamiformes, they are related to the still extant seriemas and the also extinct Phorusrhacidae. They were likely similar in habits, being terrestrial, long-legged predators, some of which attained massive sizes. It has been suggested that most, if not all, North American Paleogene cariamiforme fossils are part of this group. Storrs Olson also referred the European '' Elaphrocnemus'' to this clade, though it has since been rejected. Conversely, some analysis have instead recovered them as a polyphyletic group, with ''Bathornis'' and kin being sister taxa to phorusrhacids while '' Paracrax'' is rendered closer to modern seriemas, though this assessment is heavily debated.Mayr, G., & Noriega, J. I. A well-preserved partial skeleton of the poorly known early Miocene seriema ''Noriegavis santacrucensis'' (Aves, Cariamidae). ''Acta palaeontologica Polonica'', 60(3):589-598. The most r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracrax
''Paracrax'' ("near curassow") is a genus of extinct North American flightless birds, possibly related to modern seriemas and the extinct terror birds. Part of Bathornithidae (though some analysis recover it as closer to the living seriemas instead, or possibly entirely out of Cariamiformes), it is a specialised member of this group, being cursorial carnivores much like their South American cousins, some species attaining massive sizes. Discovery ''Paracrax antiqua'' is the genus type species. The type specimen, YPM 537, was collected in Weld County, Colorado, in 1871 by Othniel Charles Marsh, which identified it as a sort of turkey. It was posteriorly referred to Cracidae by Pierce Brodkorb, before its identity as a bathornithid came to light. Material previously identified as a cormorant, "Phalacrocorax/Oligocrocorax" ''mediterraneus'', was posteriorly identified as ''P. antiqua'' remains. Since then, two more species have been identified: ''P. wetmorei'' and ''P. gigant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phorusrhacids
Phorusrhacids, colloquially known as terror birds, are an extinct clade of large carnivorous flightless birds that were one of the largest species of apex predators in South America during the Cenozoic era; their conventionally accepted temporal range covers from 62 to 0.1 million years ( Ma) ago. They ranged in height from . Their closest modern-day relatives are believed to be the seriemas. '' Titanis walleri'', one of the larger species, is known from Texas and Florida in North America. This makes the phorusrhacids the only known large South American predator to migrate north in the Great American Interchange that followed the formation of the Isthmus of Panama land bridge (the main pulse of the interchange began about 2.6 Ma ago; ''Titanis'' at 5 Ma was an early northward migrant). It was once believed that ''T. walleri'' became extinct in North America around the time of the arrival of humans, but subsequent datings of ''Titanis'' fossils provided no evidence for their sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugal
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species. Anatomy The jugal bone is located on either side of the skull in the circumorbital region. It is the origin of several masticatory muscles in the skull. The jugal and lacrimal bones are the only two remaining from the ancestral circumorbital series: the prefrontal, postfrontal, postorbital, jugal, and lacrimal bones. During development, the jugal bone originates from dermal bone. In dinosaurs This bone is considered key in the determination of general traits in cases in which the entire skull has not been found intact (for instance, as with dinosaurs in paleontology). In some dinosaur genera the jugal also forms part of the lower margin of either the antorbital fenestra or the infratemporal fenestra, or both. Most commonly, this bone artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of convergent evolution. The arrangement of the members of a polyphyletic group is called a polyphyly .. ource for pronunciation./ref> It is contrasted with monophyly and paraphyly. For example, the biological characteristic of warm-bloodedness evolved separately in the ancestors of mammals and the ancestors of birds; "warm-blooded animals" is therefore a polyphyletic grouping. Other examples of polyphyletic groups are algae, C4 photosynthetic plants, and edentates. Many taxonomists aim to avoid homoplasies in grouping taxa together, with a goal to identify and eliminate groups that are found to be polyphyletic. This is often the stimulus for major revisions of the classification schemes. Researchers concerned more with ecology than with systema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gruiformes
The Gruiformes are an order containing a considerable number of living and extinct bird families, with a widespread geographical diversity. Gruiform means "crane-like". Traditionally, a number of wading and terrestrial bird families that did not seem to belong to any other order were classified together as Gruiformes. These include 14 species of large cranes, about 145 species of smaller crakes and rails, as well as a variety of families comprising one to three species, such as the Heliornithidae, the limpkin, or the Psophiidae. Other birds have been placed in this order more out of necessity to place them ''somewhere''; this has caused the expanded Gruiformes to lack distinctive apomorphies. Recent studies indicate that these "odd Gruiformes" are if at all only loosely related to the cranes, rails, and relatives ("core Gruiformes"). Systematics There are only two suprafamilial clades (natural groups) among the birds traditionally classified as Gruiformes. Rails (Rallidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parrots
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoidea ("true" parrots), the Cacatuoidea (cockatoos), and the Strigopoidea (New Zealand parrots). One-third of all parrot species are threatened by extinction, with higher aggregate extinction risk ( IUCN Red List Index) than any other comparable bird group. Parrots have a generally pantropical distribution with several species inhabiting temperate regions in the Southern Hemisphere, as well. The greatest diversity of parrots is in South America and Australasia. Characteristic features of parrots include a strong, curved bill, an upright stance, strong legs, and clawed zygodactyl feet. Many parrots are vividly coloured, and some are multi-coloured. Most parrots exhibit little or no sexual dimorphism in the visual spectrum. They form the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passerines
A passerine () is any bird of the order Passeriformes (; from Latin 'sparrow' and '-shaped'), which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds, passerines are distinguished from other orders of birds by the arrangement of their toes (three pointing forward and one back), which facilitates perching. With more than 140 families and some 6,500 identified species, Passeriformes is the largest clade of birds and among the most diverse clades of terrestrial vertebrates, representing 60% of birds.Ericson, P.G.P. et al. (2003Evolution, biogeography, and patterns of diversification in passerine birds ''J. Avian Biol'', 34:3–15.Selvatti, A.P. et al. (2015"A Paleogene origin for crown passerines and the diversification of the Oscines in the New World" ''Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution'', 88:1–15. Passerines are divided into three clades: Acanthisitti (New Zealand wrens), Tyranni (suboscines), and Passeri (oscines or songbirds). The passerine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
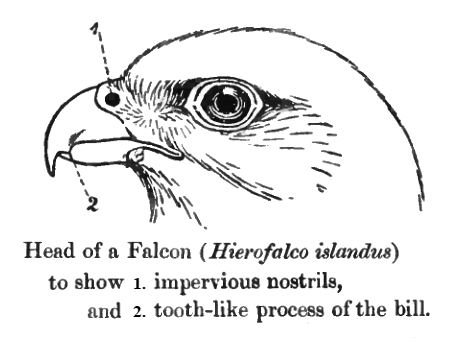
Falcons
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene. Adult falcons have thin, tapered wings, which enable them to fly at high speed and change direction rapidly. Fledgling falcons, in their first year of flying, have longer flight feathers, which make their configuration more like that of a general-purpose bird such as a broad wing. This makes flying easier while learning the exceptional skills required to be effective hunters as adults. The falcons are the largest genus in the Falconinae subfamily of Falconidae, which itself also includes another subfamily comprising caracaras and a few other species. All these birds kill with their beaks, using a tomial "tooth" on the side of their beaks—unlike the hawks, eagles, and other birds of prey in the Accipitridae, which use their feet. The largest falcon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australaves
Australaves is a recently defined clade of birds, consisting of the Eufalconimorphae (passerines, parrots and falcons) as well as the Cariamiformes (including seriemas and the extinct "terror birds").Prum, R.O. ''et al''. (2015A comprehensive phylogeny of birds (Aves) using targeted next-generation DNA sequencing Nature 526, 569–573. They appear to be the sister group of Afroaves. As in the case of Afroaves, the most basal clades have predatory extant members, suggesting this was the ancestral lifestyle; however, some researchers like Darren Naish are skeptical of this assessment, since some extinct representatives such as the herbivorous '' Strigogyps'' led other lifestyles. Basal parrots and falcons are at any rate vaguely crow-like and probably omnivorous.L. D. Martin. 2010. Paleogene avifauna of the holarctic. Vertebrata PalAsiatica 48:367-374 Cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



_white_background.jpg)