|
Barrême
Barrême (; oc, Barrema) is a Communes of France, commune in the southeastern French Departments of France, department of Alpes-de-Haute-Provence. The inhabitants of this commune are known as ''Barrêmois'' or ''Barrêmoises''. Geography Barrême is located at an altitude of 722 m some 20 km south-east of Digne-les-Bains and 15 km north-west of Castellane. Access to the commune is by Route nationale N85 which comes from Chaudon-Norante in the north-east and ends in the village. The N202 goes east from the village to Moriez. The D4085 goes south from the village to Senez. Apart from the village there are two hamlets: Gévaudan on a height near the N202, and la Basse-Palud. The Nice to Digne railway passes through the commune running parallel with the N85 and N202. It has three halts and one station: Saut du Loup, Barrême Station, La Tuiliere, and Gévaudan. Two rivers flow through the commune and join at the village: the ''Asse de Moriez'' from the east and the ''Asse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asse (river)
The Asse (; oc, Assa) is a long river in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence ''département'', southeastern France. Its source is several small streams which converge at Tartonne, east of Digne-les-Bains. It flows generally southwest. It is a left tributary of the Durance into which it flows between Valensole and Oraison, northeast of Manosque. Its drainage basin is .Bassin versant : Asse (L') Observatoire Régional Eau et Milieux Aquatiques en PACA The Asse is called "Asse de Clumanc" between its source and its confluence with the "Asse de Blieux" and the "Asse de Moriez" at . The valleys of the Asse and its tributaries are protected as a |
Digne-les-Bains
Digne-les-Bains (; Occitan: ''Dinha dei Banhs''), or simply and historically Digne (''Dinha'' in the classical norm or ''Digno'' in the Mistralian norm), is the prefecture of the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of Southeastern France. As of 2018, the commune had a population of 16,333. Its inhabitants are called ''Dignois'' (masculine) and ''Dignoises'' (feminine). Geography Site and location Located on the edge of the and on both sides of the river Bléone, which flows southwest through the middle of the commune and crosses the town; it forms part of the commune's northeastern and southwestern borders. Digne-les-Bains is the capital of the Department of Alpes de Haute-Provence. Placed in the geographical centre of the Department, the commune is home to 17,400 inhabitants, making it one of the smaller prefectures of France by its population. The town centre is at altitude. Digne is a sprawling commune in the plain formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castellane
Castellane (; Provençal dialect, Provençal: ''Castelana'') is a Communes of France, commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence Departments of France, department in southeastern France. With about 1,600 inhabitants, Castellane has the distinction of being the least-populated sub-prefecture of France. Its inhabitants are referred to as ''Castellanais''. Geography Castellane is a very old city located upstream of the Verdon Gorge, Gorges du Verdon. The city is above sea level. The Roc, or the Roc of Notre-Dame, overlooks the city from above. It has been occupied since the High Middle Ages and is a registered historical site. It can be accessed from the centre of town behind the old Church of St. Andrew. The walk takes about 25 minutes. Two reservoirs are located in the territory of Castellane: * Lac de Castillon, Lake Castillon * Lake Chaudanne, created by the dam of the same name, the . The area has two water gaps: * the ''clue de Taulanne'' containing the Asse (river), Asse de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barremian
The Barremian is an age in the geologic timescale (or a chronostratigraphic stage) between 129.4 ± 1.5 Ma (million years ago) and 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma). It is a subdivision of the Early Cretaceous Epoch (or Lower Cretaceous Series). It is preceded by the Hauterivian and followed by the Aptian Stage.See Gradstein ''et al.'' (2004) or the online geowhen database (link below) Stratigraphic definitions The original type locality for the Barremian Stage is in the vicinity of the village of Barrême, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence, France. Henri Coquand defined the stage and named it in 1873. The base of the Barremian is determined by the first appearance of the ammonites ''Spitidiscus hugii'' and ''Spitidiscus vandeckii''. The end of the Barremian is determined by the geomagnetic reversal at the start of the M0r chronozone, which is biologically near the first appearance of the ammonite '' Paradeshayesites oglanlensis''. Regional equivalents The Barremian falls in the Gallic epoch, a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route Nationale
A ''route nationale'', or simply ''nationale'', is a class of trunk road in France. They are important roads of national significance which cross broad portions of the French territory, in contrast to departmental or communal roads which serve more limited local areas. Their use is free, except when crossing certain structures subject to a toll. They are open to all vehicles, except on certain sections having motorway ('' autoroute'') or express road (''voie express'') status, both of these categories being reserved for motorized vehicles only. France at one time had some 30,500 km of ''routes nationales'' and publicly owned motorways, but this figure has decreased with the transfer of the responsibility for many routes to the ''départements'' so that by 2010 the total length of motorways and other national roads was around 21,100 km. By way of comparison, ''routes départementales'' in the same year covered a total distance of 378,000 km. The layout of the main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Cretaceous
Lower may refer to: *Lower (surname) *Lower Township, New Jersey *Lower Receiver (firearms) *Lower Wick Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated about five miles south west of Dursley, eighteen miles southwest of Gloucester and fifteen miles northeast of Bristol. Lower Wick is within the civil ... Gloucestershire, England See also * Nizhny {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Clément-sur-Durance
Saint-Clément-sur-Durance (, literally ''Saint-Clément on Durance''; Vivaro-Alpine: ''Sant Clamenç sus Durença'') is a commune in the Hautes-Alpes department in southeastern France. Population See also *Communes of the Hautes-Alpes department The following is a list of the 162 communes of the Hautes-Alpes department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Hautes-Alpes {{HautesAlpes-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
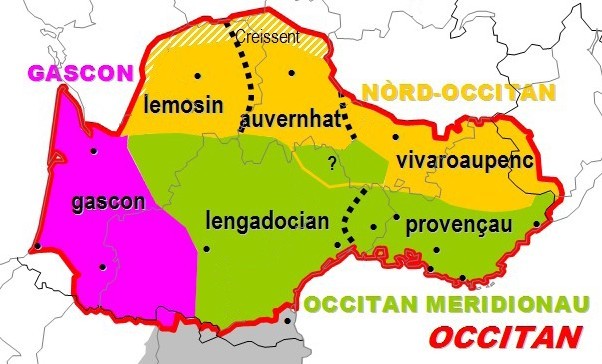
Vivaro-Alpine Dialect
Vivaro-Alpine ( oc, vivaroalpenc, vivaroaupenc) is a variety of Occitan spoken in southeastern France (namely, around the Dauphiné area) and northwestern Italy (the Occitan Valleys of Piedmont and Liguria). There is also a small Vivaro-Alpine enclave in the Guardia Piemontese, Calabria, where the language is known as ''gardiòl''. It belongs to the Northern Occitan dialect bloc, along with Auvergnat and Limousin. The name “vivaro-alpine” was coined by Pierre Bec in the 1970s. The Vivaro-Alpine dialects are traditionally called "gavot" from the Maritime Alps to the Hautes-Alpes. Naming and classification ''Vivaro-Alpine'' had been considered as a sub-dialect of Provençal, and named ''provençal alpin'' (Alpine Provençal) or Northern Provençal. Its use in the Dauphiné area has also led to the use of ''dauphinois'' or ''dauphinois alpin'' to name it. Jules Ronjat, ''Grammaire istorique des parlers provençaux modernes, vol. IV Les dialectes'', Montpellier, 1941 Along wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provençal Dialect
Provençal (, , ; french: provençal , ; oc, provençau or ) is a Romance language, either considered as a variety of Occitan or a separate language, spoken by people in Provence and parts of Drôme. Historically, the term Provençal has been used to refer to the whole of the Occitan language, but today it is considered more technically appropriate to refer only to the variety of Occitan spoken in Provence. However it can still be found being used to refer to Occitan as a whole, ''e.g.'' Merriam-Webster states that it can be used to refer to general Occitan, though this is going out of use. Provençal is also the customary name given to the older version of the Occitan language used by the troubadours of medieval literature, when Old French or the ' was limited to the northern areas of France. Thus the ISO 639-3 code for Old Occitan is ro In 2007, all the ISO 639-3 codes for Occitan dialects, including rvfor Provençal, were retired and merged into ciOccitan. The old cod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mistralian Norm
The Mistralian norm is a linguistic norm for the Occitan language. It was first used in a published work by Joseph Roumanille in 1853, and then by Frédéric Mistral in 1854. Its aim is to make Provençal Occitan orthography more logical, relying on a mix of traditional spelling and French spelling conventions. The ''Tresor dòu Felibrige'', published by the ''Félibrige The ''Félibrige'' (; in classical Occitan, in Mistralian spelling, ) is a literary and cultural association founded in 1854 by Frédéric Mistral and other Provençal writers to defend and promote the Occitan language (also called the ) and ...'' in 1878, was written entirely in the Mistralian norm. Comparison Some features include: * Using the letter ''o'' to represent a final or , where Classical Occitan uses ''a''. For example, becomes ''jouvenço'' in the text above. * Using ''ou'' to represent , where Classical Occitan uses ''o''. For example, ''Provença'' becomes ''Prouvènço'' in the tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |