|
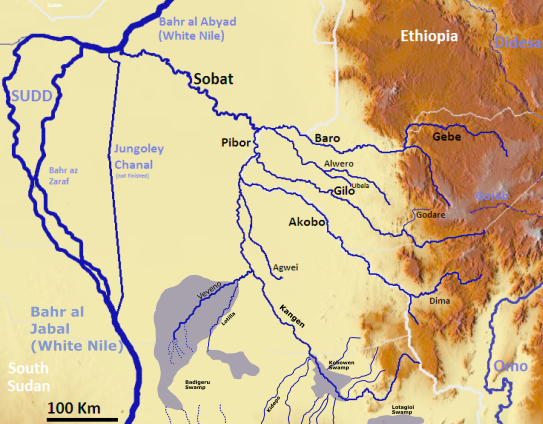
Baro River
The Baro River ( am, ባሮ ወንዝ) or Baro/Openo Wenz, known to the Anuak as Openo River, is a river in southwestern Ethiopia, which defines part of Ethiopian border with South Sudan. From its source in the Ethiopian Highlands it flows west for to join the Pibor River. The Baro-Pibor confluence marks the beginning of the Sobat River, a tributary of the White Nile. The Baro and its tributaries drain a watershed in size. The river's mean annual discharge at its mouth is 241 m³/s (8,510 ft³/s). Course The Baro/Openo river is created by the confluence of the Birbir and Gebba Rivers, east of Metu in the Illubabor Zone of the Oromia Region. It then flows west through the Gambela Region to join with the Pibor River, both of them creating the Sobat. Other notable tributaries of the Baro/Openo include the Alwero and Jikawo Rivers. The Baro meets the Pibor river to the west of Jikawo. During the rainy season the river floods to form the huge inundated area to the east and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alwero River
Alwero River (also spelt Aloru, Aluoro and Alwero) is a river in Abobo woreda of Gambela Region, Ethiopia. It flows through the Gambela National Park and through wetlands into the Openo/Baro River. The potential land for irrigation development in the Gambella region, where the present study was conducted, is estimated to be 500,000 ha 0 The region has a number of perennial rivers including, Baro, Alwero, Gillo, and Akobo, which can be used as a potential source of irrigation water. In fact, this study was initiated and carried out to assess the physical land suitability for irrigation in the lower Alwero river area of Abobo, Anywaa Zone of Gambella Region. See also * List of rivers of Ethiopia This is a list of streams and rivers in Ethiopia, arranged geographically by drainage basin. There is an alphabetic list at the end of this article. Flowing into the Mediterranean *''Nile (Egypt, Sudan)'' Atbarah River *Mareb River (or G ... Rivers of Ethiopia Gambela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambela, Ethiopia
Gambela ( am, ጋምቤላ), also spelled Gambella, is a city and separate woreda in Ethiopia and the capital of the Gambela Region. It was known as Paanywaa( Anyuak Country) Located in Anyuak Zone, at the confluence of the Openo River and its tributary the Jajjabe, the city has a latitude and longitude of and an elevation of 526 meters. It is surrounded by Gambela Zuria. Gambela is important because bridges over both the Baro and the Jajjaba are located in that city. The Anyuak are the inhabitants of Gambela and they have their own language. The town also boasts an airport (ICAO code HAGM, IATA GMB) and is near the Gambela National Park. History Gambela was founded because of its location on the Baro, a tributary of the Nile, which was seen by both the British and Ethiopia as an excellent highway for exporting coffee and other goods from the fertile Ethiopian Highlands to Sudan and Egypt. British concession (1902–1956) Emperor Menelik II granted Britain use of a por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambela Region
The Gambela Region (also spelled Gambella; am, ጋምቤላ), officially the Gambela Peoples' Region, is a regional state in western Ethiopia, bordering South Sudan. Previously known as Region 12, its capital is Gambela. The Region is situated between the Baro and Akobo Rivers, with its western part including the Baro River. Demographics Based on the 2007 Census conducted by the Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia (CSA), the Gambela region has total population of 307,096, consisting of 159,787 men and 147,309 women; urban inhabitants number 77,925 or 25.37% of the population. With an estimated area of 29,782.82 square kilometers, this region has an estimated density of 10 people per square kilometer. For the entire region, 66,467 households were counted, which results in an average for the region of 4.6 persons to a household, with urban ''households'' having on average 3.8 and rural households 4.9 people. The Gambela region is mainly inhabited by various Nilotic ethnic m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Africa Institute
Nordic Africa Institute ( sv, Nordiska Afrikainstitutet) serves as a research, documentation and information centre on modern Africa for the Nordic countries. The Institute also encourages research and studies on Africa. The institute was founded in 1962. The institute is financed jointly by the Nordic countries. Administratively, it functions as a Swedish government agency that answers to the Ministry for Foreign Affairs. It is located in Uppsala. The Nordic Africa Institute is part of AEGIS, a network of African Studies Centres in Europe, and organized its 4th international conference (ECAS) in 2011. The institute is headed by a Director, and a Programme and Research Council has the task of monitoring and advising the Director. On 18 July 2019, the Swedish government appointed Therése Sjömander Magnusson as new Director of NAI, a position which she took up on 1 October 2019. Previous Directors of NAI The list is partly based on a report to the Nordic Africa Institute's 50th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
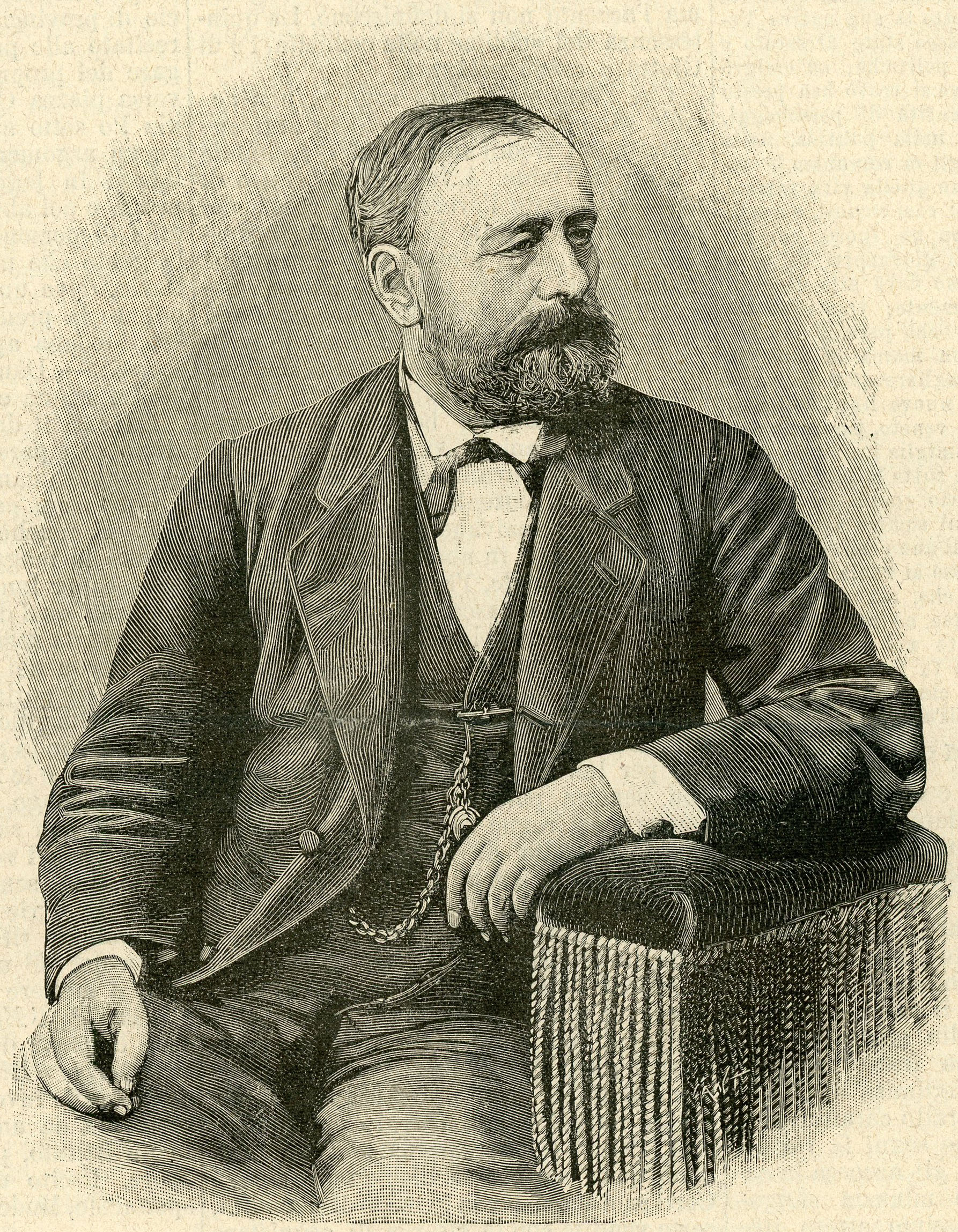
Simone Antonio Saint-Bon
Simone Antonio Pacoret de Saint-Bon (March 20, 1828 – November 26, 1892) was an admiral of the Italian ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy). Saint-Bon was born at Chambéry, now in France, then part of the Kingdom of Sardinia. Leaving the Naval Academy in 1847, he attained the rank of commander in 1860, and that of vice-admiral in 1867. He took part in the Crimean war, distinguished himself in 1860 at the siege of Ancona, and was decorated for valor at the Siege of Gaeta. At the battle of Battle of Lissa (1866), his vessel, the , forced the entrance of the port of San Giorgio and silenced the Austrian batteries, for which exploit he received a gold medal. In 1873 he was elected deputy, and appointed by Marco Minghetti to be minister of marine, in which position he revolutionized the Italian navy. Insisting upon the need for large battleships with high powers of attack and defense, and capable of fighting as single units, he introduced the colossal types of which and were the earlies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
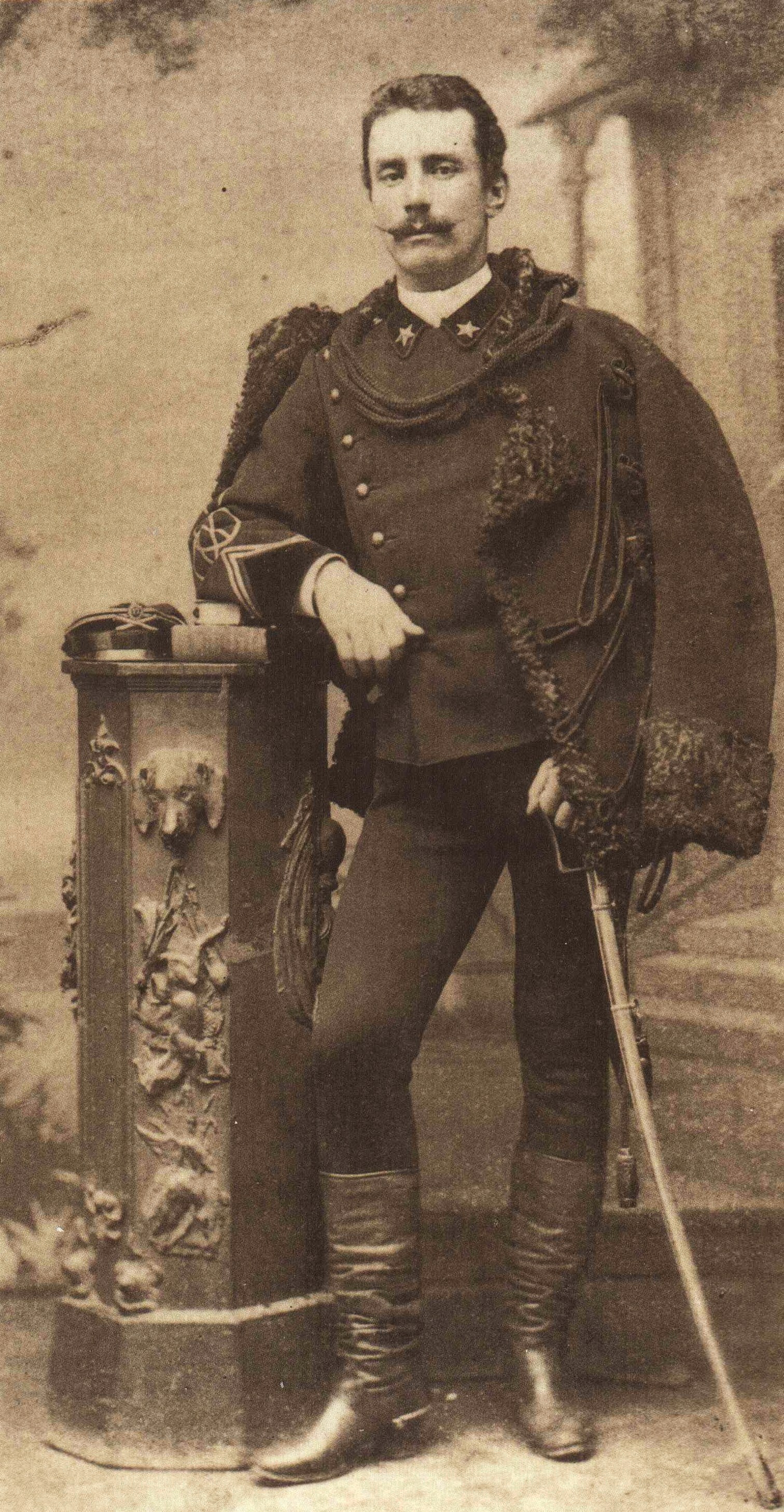
Vittorio Bottego
Vittorio Bottego (; Parma, 29 July 1860 – Dhaga Roba, 17 March 1897) was an Italian army officer and one of the first Western explorers of Jubaland in the Horn of Africa (now part of Gidami, West Wellega Ethiopia), where he led two expeditions. He was an artillery captain in the Italian Army. Expeditions In his first expedition Bottego concentrated on tracing the channels of the tributaries of the Ganale Doria, that he named after the Italian biologist Giacomo Doria. With Captain Matteo Grixoni, Bottego left Bardera on 30 September 1892, with one hundred and twenty-four men. They reached the Shebeli River at Imi on 7 November. After eight days they crossed the river, entering the country of the Arsi Oromo, who proved hostile to Bottego. He passed through Arkebla and reached the Ganale Guracha ("Black Ganale") on 11 December, along whose banks he led his men upstream for 20 days. Concluding that this was not the main stream of the river, Bottego left the river in a west-sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudanese Civil War (other) (1881–1899)
{{disambig ...
The term Sudanese Civil War refers to at least three separate conflicts: *First Sudanese Civil War (1955–1972) *Second Sudanese Civil War (1983–2005) *South Sudanese Civil War (2013–2020) It could also refer to other internal conflicts in Sudan and South Sudan: *Lord's Resistance Army insurgency (1987–present) *War in Darfur (2003–present) * Sudanese nomadic conflicts *Ethnic violence in South Sudan *Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile (2011–present) As well as conflicts between Sudan and South Sudan after the breakup: *Heglig Crisis (2012) See also * Mahdist War The Mahdist War ( ar, الثورة المهدية, ath-Thawra al-Mahdiyya; 1881–1899) was a war between the Mahdist Sudanese of the religious leader Muhammad Ahmad bin Abd Allah, who had proclaimed himself the "Mahdi" of Islam (the "Guided On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akobo River
The Akobo River is a river on the border between South Sudan and Ethiopia. From its source in the Ethiopian Highlands near Mizan Teferi it flows west for to join the Pibor River. The Pibor flows into the Sobat River, which in turn empties into the White Nile. The tributaries of the Akobo river include the Cechi, the Chiarini, and the Owag, on the right or Ethiopian side; and the Neubari, Ajuba and Kaia on the left or South Sudanese side. History The boundary between Sudan and Ethiopia was defined for the region near the Akobo River in 1899, by Major H.H. Austin and Major Charles W. Gwynn of the British Royal Engineers. They had no knowledge of the land, its inhabitants, or their languages, and were short on supplies. Rather than defining a line based on ethnic groups and traditional territories, essentially along the escarpment that separates the highlands and the plains, Majors Austin and Gwynn simply proposed drawing the line down the middle of the Akobo River and parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the ''Sappers'', is a corps of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is headed by the Chief Royal Engineer. The Regimental Headquarters and the Royal School of Military Engineering are in Chatham in Kent, England. The corps is divided into several regiments, barracked at various places in the United Kingdom and around the world. History The Royal Engineers trace their origins back to the military engineers brought to England by William the Conqueror, specifically Bishop Gundulf of Rochester Cathedral, and claim over 900 years of unbroken service to the crown. Engineers have always served in the armies of the Crown; however, the origins of the modern corps, along with those of the Royal Artillery, lie in the Board of Ordnance established in the 15th century. In Woolwich in 1716, the Board formed the Royal Regime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Egypt to the north, Eritrea to the northeast, Ethiopia to the southeast, Libya to the northwest, South Sudan to the south and the Red Sea. It has a population of 45.70 million people as of 2022 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres (728,215 square miles), making it Africa's List of African countries by area, third-largest country by area, and the third-largest by area in the Arab League. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the 2011 South Sudanese independence referendum, secession of South Sudan in 2011, since which both titles have been held by Algeria. Its Capital city, capital is Khartoum and its most populated city is Omdurman (part of the metropolitan area of Khar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |